consciousness
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): When protons (here brain protons) are placed in a magnetic field, they become capable of receiving and then transmitting electromagnetic energy. The strength of the transmitted energy is proportional to the number of protons in the tissue. Signal strength is modifi ...
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): When protons (here brain protons) are placed in a magnetic field, they become capable of receiving and then transmitting electromagnetic energy. The strength of the transmitted energy is proportional to the number of protons in the tissue. Signal strength is modifi ...
Module 3:Neural conduction and transmission Lecture 13
... the membrane of soma is not excitable. The magnitude of these impulses do not depend upon the magnitude of the sensation, rather they follow all-or-none principle. This principle states that the nerve fibers either respond to the limit of their capability or do not get excited at all. A weak stimula ...
... the membrane of soma is not excitable. The magnitude of these impulses do not depend upon the magnitude of the sensation, rather they follow all-or-none principle. This principle states that the nerve fibers either respond to the limit of their capability or do not get excited at all. A weak stimula ...
Chicurel2001NatureNV..
... Gray and Singer’s experiments motivated many others to turn to multi-unit recordings. The precise significance of the oscillations they saw remains a matter for debate. But dozens of multi-unit studies have since shown that synchronous firing is associated with visual perception and the conscious pr ...
... Gray and Singer’s experiments motivated many others to turn to multi-unit recordings. The precise significance of the oscillations they saw remains a matter for debate. But dozens of multi-unit studies have since shown that synchronous firing is associated with visual perception and the conscious pr ...
Solutions - ISpatula
... triggered it. “They are very sensitive receptor cells” Even one photon can be felt by your eye due to the amplification , and another example is the amplification of sounds as you can hear a very low voice; the pressure associated with sound waves is enhanced by a factor of more that 20 before reach ...
... triggered it. “They are very sensitive receptor cells” Even one photon can be felt by your eye due to the amplification , and another example is the amplification of sounds as you can hear a very low voice; the pressure associated with sound waves is enhanced by a factor of more that 20 before reach ...
Lecture 4 ppt
... WE OBSERVE IS A RESULT OF PROCESSING BY CERTAIN BRAIN STRUCTURES. • THE QUESTION IS HOW THESE STRUCTURES OPERATE? THIS HAS TO BE VERY COMPLEX. CERTAIN BEHAVIORS ARE PROGRAMMED (ANIMALS) BUT THERE IS SIGNIFICANT LEARNING AND ADAPTATION ABILITY. • IT IS KNOWN THAT NEURAL NETWORKS ARE VERY ’PLASTIC’ BU ...
... WE OBSERVE IS A RESULT OF PROCESSING BY CERTAIN BRAIN STRUCTURES. • THE QUESTION IS HOW THESE STRUCTURES OPERATE? THIS HAS TO BE VERY COMPLEX. CERTAIN BEHAVIORS ARE PROGRAMMED (ANIMALS) BUT THERE IS SIGNIFICANT LEARNING AND ADAPTATION ABILITY. • IT IS KNOWN THAT NEURAL NETWORKS ARE VERY ’PLASTIC’ BU ...
1. Which of the following is the component of the limbic system that
... A) was activated by interneurons in her spinal cord. B) did not involve activity in her central nervous system. C) was activated by the rapidly responding brain. D) was activated by her self-regulating autonomic nervous system. E) was controlled by both her nervous system and impulses from her endoc ...
... A) was activated by interneurons in her spinal cord. B) did not involve activity in her central nervous system. C) was activated by the rapidly responding brain. D) was activated by her self-regulating autonomic nervous system. E) was controlled by both her nervous system and impulses from her endoc ...
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Nervous System Notes File
... Nervous tissue contains masses of nerve cells called neurons. Specialized to react to physical and chemical changes. Transmit info in the form of electrochemical changes called nerve impulses. Bundles of axons make nerves. Also contains neuroglial cells that provide physical support, ...
... Nervous tissue contains masses of nerve cells called neurons. Specialized to react to physical and chemical changes. Transmit info in the form of electrochemical changes called nerve impulses. Bundles of axons make nerves. Also contains neuroglial cells that provide physical support, ...
Neuron and Brain Review Handout
... Brainstem: Oldest area of the brain. Also called the reptilian brain. 1. Medulla: the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and Lobes of the Brain breathing. 2. Reticular Formation: A neural network within the brainstem; important in arousal including sleep. Thalamus: Sits on top of the brainste ...
... Brainstem: Oldest area of the brain. Also called the reptilian brain. 1. Medulla: the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and Lobes of the Brain breathing. 2. Reticular Formation: A neural network within the brainstem; important in arousal including sleep. Thalamus: Sits on top of the brainste ...
An octopaminergic system in the CNS of the snails, Lymnaea
... start feeding in sucrose, and the same dose of NC-7 reduced the number of feeding animals by 80-90 percent 1-3 hours after injection. DCDM treatment reduced feeding by 20-60 percent. Additionally, both phentolamine and NC-7 significantly decreased the feeding rate of those animals which still accept ...
... start feeding in sucrose, and the same dose of NC-7 reduced the number of feeding animals by 80-90 percent 1-3 hours after injection. DCDM treatment reduced feeding by 20-60 percent. Additionally, both phentolamine and NC-7 significantly decreased the feeding rate of those animals which still accept ...
Justin Smith - USD Biology
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
... • NPSR mRNA- expressed in stress related areas – Amygdala – BNST – Hypothalamus – Raphe Nucleus – Ventral tegmental area ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... 1. Explain why psychologists are concerned with human biology, and describe the ill-fated phrenology theory. 2. Explain how viewing each person as a biopsychosocial system helps us understand human behavior, and discuss by researchers study other animals in search of clues to human neural processes. ...
... 1. Explain why psychologists are concerned with human biology, and describe the ill-fated phrenology theory. 2. Explain how viewing each person as a biopsychosocial system helps us understand human behavior, and discuss by researchers study other animals in search of clues to human neural processes. ...
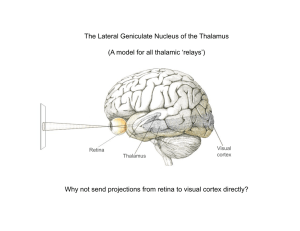
The Lateral Geniculate Nucleus of the Thalamus (A model for all
... Magno cells are ventral, layers 1 + 2. (Fast, no color, no high spatial frequencies, respond strongly to low contrasts, large cell bodes, big, ...
... Magno cells are ventral, layers 1 + 2. (Fast, no color, no high spatial frequencies, respond strongly to low contrasts, large cell bodes, big, ...
How the Brain Pays Attention
... to pinpoint the areas of the brain involved in visual attention and, likewise, where the control occurs. However, although MRI and fMRI scanners show the location of brain activity quite well, they don’t shed light on how the brain is working, at a fine temporal time scale. So we used a technique ca ...
... to pinpoint the areas of the brain involved in visual attention and, likewise, where the control occurs. However, although MRI and fMRI scanners show the location of brain activity quite well, they don’t shed light on how the brain is working, at a fine temporal time scale. So we used a technique ca ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? a Class Objectives a What
... To transmit information to other neurons, a brief electrical current impulses through its axon. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - This current causes the neuron to “fire” ...
... To transmit information to other neurons, a brief electrical current impulses through its axon. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - This current causes the neuron to “fire” ...
psych mod 4 terms
... making proteins. Proteins are chemical building blocks from which all the parts of the brain and body are constructed. 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to pr ...
... making proteins. Proteins are chemical building blocks from which all the parts of the brain and body are constructed. 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to pr ...
Lecture_31_2014_noquiz
... length of your leg. There are many different types of neurons. Some are myelinated, some are not. Smaller nerves branch off of the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve responsible for innervating muscles, skin, etc. in the leg. It contains both motor neurons and sensory neurons (i.e. messages go both wa ...
... length of your leg. There are many different types of neurons. Some are myelinated, some are not. Smaller nerves branch off of the sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve responsible for innervating muscles, skin, etc. in the leg. It contains both motor neurons and sensory neurons (i.e. messages go both wa ...
The Zombie Diaries
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
... What’s the Big Idea?: To understand how information (messages) travel across the brain, and how messages are sent back across the pathways to the rest of the body (neurotransmission). 1.) Choose a partner 2.) Get a Chromebook and a packet from the end of the table 3. ) Review pages 4 - 10 of this Po ...
The Central Nervous System
... transmitted from the retinas of both eyes through the optic nerve The primary visual cortex contains a variety of neurons specialised to respond to specific features of visual information – colour, shape, motion Damage to the occipital lobe may result in visual impairment even if the eyes and th ...
... transmitted from the retinas of both eyes through the optic nerve The primary visual cortex contains a variety of neurons specialised to respond to specific features of visual information – colour, shape, motion Damage to the occipital lobe may result in visual impairment even if the eyes and th ...
I. Functions and Divisions of the Nervous System A. The nervous
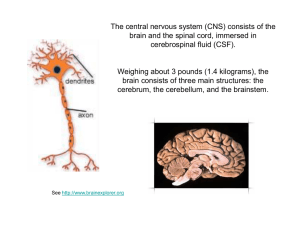
... 2. The neuron cell body, also called the perikaryon or soma, is the major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles. 3. Neurons have armlike processes that extend from the cell body. a. Dendrites are cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell and provid ...
... 2. The neuron cell body, also called the perikaryon or soma, is the major biosynthetic center containing the usual organelles except for centrioles. 3. Neurons have armlike processes that extend from the cell body. a. Dendrites are cell processes that are the receptive regions of the cell and provid ...
1. What are some major differences between
... hypothalamus to PAG. The PANIC system is associated with the anterior cinculate, the BNST, and the preoptic area, as well as the dorsomedial thalamlus and PAG. 4. While there is still much work to be done to understand the brain bases of human emotion, what is the role of the amygdala in emotional p ...
... hypothalamus to PAG. The PANIC system is associated with the anterior cinculate, the BNST, and the preoptic area, as well as the dorsomedial thalamlus and PAG. 4. While there is still much work to be done to understand the brain bases of human emotion, what is the role of the amygdala in emotional p ...
Vision_notes
... one refractive index to another, for example from air to water or from air to glass. Light focusing on retina Light bent as it enters cornea from air (this is the greatest bending that occurs) and as it enters & leaves lens. Lens “fine tunes” the focusing. Far objects: lens stretched relatively fl ...
... one refractive index to another, for example from air to water or from air to glass. Light focusing on retina Light bent as it enters cornea from air (this is the greatest bending that occurs) and as it enters & leaves lens. Lens “fine tunes” the focusing. Far objects: lens stretched relatively fl ...
The Senses
... o The vibrations of the cells, and basilar membrane to which they are attached, generate nerve impulses in neurons that are transmitted through the auditory nerve to the brain, where they are interpreted as sound D. ...
... o The vibrations of the cells, and basilar membrane to which they are attached, generate nerve impulses in neurons that are transmitted through the auditory nerve to the brain, where they are interpreted as sound D. ...
Count the black dots
... Action potentials are measurable events The timings or firing rate of action potentials can encode information - orientation selectivity in visual cortex - coincidence detection for sound localization - place cells in hippocampus ...
... Action potentials are measurable events The timings or firing rate of action potentials can encode information - orientation selectivity in visual cortex - coincidence detection for sound localization - place cells in hippocampus ...