Pioneers of cortical plasticity: six classic papers by Wiesel and Hubel
... closed just before eye opening. The kittens were reared in this monocularly deprived condition until they were 3 months old, at which time electrophysiological analyses of afferent retinal axons and neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) contralateral to the deprived eye were undertaken. In ...
... closed just before eye opening. The kittens were reared in this monocularly deprived condition until they were 3 months old, at which time electrophysiological analyses of afferent retinal axons and neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) contralateral to the deprived eye were undertaken. In ...
Exploring Our Senses
... scene (kittens or a romantic couple) or a negative scene (werewolf or dead body) an instant before showing a picture of a person. Participants perceived the kitten or werewolf as a flash of light. The participants gave a more positive rating for the photos associated with the kitten or romantic coup ...
... scene (kittens or a romantic couple) or a negative scene (werewolf or dead body) an instant before showing a picture of a person. Participants perceived the kitten or werewolf as a flash of light. The participants gave a more positive rating for the photos associated with the kitten or romantic coup ...
Chapter 49 Student Guided Notes
... Thalmus Main _______________________ center for information going to the ________________ Main ______________________ center for information leaving the cerebrum Hypothalmus Important in homeostatic regulation Control center including _____________________________ functions (sleep/wake), ...
... Thalmus Main _______________________ center for information going to the ________________ Main ______________________ center for information leaving the cerebrum Hypothalmus Important in homeostatic regulation Control center including _____________________________ functions (sleep/wake), ...
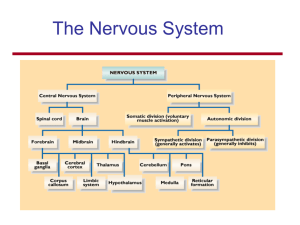
The Nervous System
... • If a portion is stimulated beyond its threshold, it briefly reverses polarity • This polarity reversal travels down the neuron • Neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminals ...
... • If a portion is stimulated beyond its threshold, it briefly reverses polarity • This polarity reversal travels down the neuron • Neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminals ...
Savage Science AP Biology
... Sensory transduction is the conversion of stimulus energy into a change in the membrane potential of a sensory receptor Many sensory receptors are very sensitive: they are able to detect the smallest physical unit of stimulus – For example, most light receptors can detect a photon of light ...
... Sensory transduction is the conversion of stimulus energy into a change in the membrane potential of a sensory receptor Many sensory receptors are very sensitive: they are able to detect the smallest physical unit of stimulus – For example, most light receptors can detect a photon of light ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... 1. Reflexes are simple, involuntary behaviors controlled by spinal cord neurons, without requiring instructions from the brain. 2. Reflexes are controlled by a feedback system. Information about the consequences of an action goes back to the source of the action for further adjustment, if necessary. ...
... 1. Reflexes are simple, involuntary behaviors controlled by spinal cord neurons, without requiring instructions from the brain. 2. Reflexes are controlled by a feedback system. Information about the consequences of an action goes back to the source of the action for further adjustment, if necessary. ...
Types of neurons
... Inputs may number in thousands If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
... Inputs may number in thousands If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
Phenomenology without conscious access is a form of
... bunch of bars arranged on a circle. This is also what we experience when we look at such displays. However, it is well known that subjects have only very limited access to the detailed properties of the individual elements, unless top-down attention is directed to a subset of stimuli using appropria ...
... bunch of bars arranged on a circle. This is also what we experience when we look at such displays. However, it is well known that subjects have only very limited access to the detailed properties of the individual elements, unless top-down attention is directed to a subset of stimuli using appropria ...
Slide 1
... Inputs encoding the movement are sent (upward arrow) through the mossy fibers to the granular layer. These inputs encode the desired and actual position and velocity of each joint along the trajectory and also contextrelated information. Inputs encoding the error are sent (upper downward arrow) thro ...
... Inputs encoding the movement are sent (upward arrow) through the mossy fibers to the granular layer. These inputs encode the desired and actual position and velocity of each joint along the trajectory and also contextrelated information. Inputs encoding the error are sent (upper downward arrow) thro ...
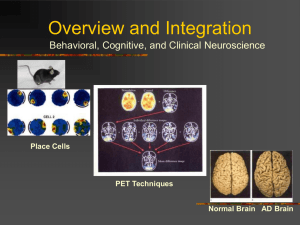
Overview and Integration
... For a history of neuroscienece timeline: neurolab.jsc.nasa.gov/timeline.htm ...
... For a history of neuroscienece timeline: neurolab.jsc.nasa.gov/timeline.htm ...
Types of neurons
... Inputs may number in thousands If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
... Inputs may number in thousands If enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
Biology 118 - Exam 2
... 26. The brain grows most rapidly between the ages of _______ years; this growth is driven by the rapid production of ______. a. 0 to 3 – CSF b. 5 to 10 - myelin c. 0 to 3 – new neurons * d. 5-10 – meninges 27. Vitamin _____ has been added to breads and cereals since 1998 in the U.S. to reduce the r ...
... 26. The brain grows most rapidly between the ages of _______ years; this growth is driven by the rapid production of ______. a. 0 to 3 – CSF b. 5 to 10 - myelin c. 0 to 3 – new neurons * d. 5-10 – meninges 27. Vitamin _____ has been added to breads and cereals since 1998 in the U.S. to reduce the r ...
the biology of awareness
... We use written and spoken language to express abstract ideas and concepts. We also use language to teach one another. Other animals learn only from experience and by imitation. We also pass down our ideas from generation to generation via the social system we call “culture.” Another crucial feature ...
... We use written and spoken language to express abstract ideas and concepts. We also use language to teach one another. Other animals learn only from experience and by imitation. We also pass down our ideas from generation to generation via the social system we call “culture.” Another crucial feature ...
Vestibulospinal Tract - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... The vestibulospinal tract arises from the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters nucleus) and descends ipsilaterally in the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord. Vestibulospinal neurons synapse in laminae VII, VIII, and IX of the spinal cord. Several vestibulospinal fibers synapse directly with α and ϒ ...
... The vestibulospinal tract arises from the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters nucleus) and descends ipsilaterally in the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord. Vestibulospinal neurons synapse in laminae VII, VIII, and IX of the spinal cord. Several vestibulospinal fibers synapse directly with α and ϒ ...
3DeterDiff
... (see Fig 7A). B) Separation of neuronal and glial sublineages in progenitor 6-4. The glial regulatory protein, Gmc, is expressed in 6-4. When this cell ...
... (see Fig 7A). B) Separation of neuronal and glial sublineages in progenitor 6-4. The glial regulatory protein, Gmc, is expressed in 6-4. When this cell ...
The Nervous System
... neurons in your hand, and you pull your hand away As you pull your hand away, nerve impulses travel to your brain. You feel the pain ...
... neurons in your hand, and you pull your hand away As you pull your hand away, nerve impulses travel to your brain. You feel the pain ...
The Nervous System
... to a section of your nerves called the autonomic nervous system (ANS) which then activates the adrenal glands in the kidneys to secrete chemicals, such as adrenaline and noradrenaline, which key up the body for fight or flight. ...
... to a section of your nerves called the autonomic nervous system (ANS) which then activates the adrenal glands in the kidneys to secrete chemicals, such as adrenaline and noradrenaline, which key up the body for fight or flight. ...
Neurons & Transmission of Information
... •Synapse = junction where the axon terminal of the sending neuron communicates with a receiving neuron across the synaptic cleft •Neurotransmitters = chemical that is released into the synaptic cleft from the axon terminal of the sending neuron, crosses the synapse, & binds to appropriate receptor s ...
... •Synapse = junction where the axon terminal of the sending neuron communicates with a receiving neuron across the synaptic cleft •Neurotransmitters = chemical that is released into the synaptic cleft from the axon terminal of the sending neuron, crosses the synapse, & binds to appropriate receptor s ...
Dynamic Equilibrium Review 1. Describe the structure and function
... signal onto the next cell 2. When looking at the relative ion levels inside and outside a cell, what do we notice? How does this important to a neuron? The outside of the cell is more positive, relative to the inside. This assists in ion exchange (Na+ in, K+ out) that is the process of neuron firing ...
... signal onto the next cell 2. When looking at the relative ion levels inside and outside a cell, what do we notice? How does this important to a neuron? The outside of the cell is more positive, relative to the inside. This assists in ion exchange (Na+ in, K+ out) that is the process of neuron firing ...
Cerebral Cortex
... Executive areas: Receive input from other areas of cortex and non-specific thalamic nuclei Organize behavior in accordance with goals, conventions, emotions and current conditions. Choose behavior and motor strategy to navigate current situation Send output to motor planning cortex and other cortica ...
... Executive areas: Receive input from other areas of cortex and non-specific thalamic nuclei Organize behavior in accordance with goals, conventions, emotions and current conditions. Choose behavior and motor strategy to navigate current situation Send output to motor planning cortex and other cortica ...
TalkHumaine_grandjean
... Apparently time is less important in the generation of responses of the multimodal neurons than spatial occurrences. The amplitude of the increase of response decreases with the increase of asynchrony. The maximum of responses is related to the overlap of pattern activity through the time (binding p ...
... Apparently time is less important in the generation of responses of the multimodal neurons than spatial occurrences. The amplitude of the increase of response decreases with the increase of asynchrony. The maximum of responses is related to the overlap of pattern activity through the time (binding p ...
Hasan_PressRelease_2008 - Max Planck Institute for Medical
... indicator that colours the cells in the brain of a living mouse. Image: Max Planck Institute for Medical Research Yellow and blue fluorescent proteins This situation could be set to change. As part of an intensive international cooperation project, Mazahir Hasan has made nerve cells, which release a ...
... indicator that colours the cells in the brain of a living mouse. Image: Max Planck Institute for Medical Research Yellow and blue fluorescent proteins This situation could be set to change. As part of an intensive international cooperation project, Mazahir Hasan has made nerve cells, which release a ...
Therapeutic Cell Replacement - McLoon Lab
... Therapeutic Neuron Replacement - iPSCs IPSCs can be generated (possibly) from any differentiated cell type, but usually is done with skin cells. ...
... Therapeutic Neuron Replacement - iPSCs IPSCs can be generated (possibly) from any differentiated cell type, but usually is done with skin cells. ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... module concludes with a discussion of plasticity. In general, what are the functions of the various cortex regions? ...
... module concludes with a discussion of plasticity. In general, what are the functions of the various cortex regions? ...