Final review quiz
... Declarative and episodic are explicit, and involve which brain structures? ______________________ ...
... Declarative and episodic are explicit, and involve which brain structures? ______________________ ...
Nervous System Cells - Dr. M`s Classes Rock
... Common classification of neurotransmitters: o Function: determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major functional classifications are excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibitory neurotransmitters o Chemical structure: the mechanism by which neurotransmitters cause a change; four main classes; ...
... Common classification of neurotransmitters: o Function: determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major functional classifications are excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibitory neurotransmitters o Chemical structure: the mechanism by which neurotransmitters cause a change; four main classes; ...
demystified Vedic Vision
... Today, it is theoretically possible to test any model of neural function if it can be described by a mathematical formalism and if the resulting equations can be solved numerically. While this is in principle true for nearly all existing models, the computing time needed for this calculations be ...
... Today, it is theoretically possible to test any model of neural function if it can be described by a mathematical formalism and if the resulting equations can be solved numerically. While this is in principle true for nearly all existing models, the computing time needed for this calculations be ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an action potential, or nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! • The membrane will repolarize when K+ ...
... depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes the membrane to become more positive. This starts an action potential, or nerve impulse. They follow the all or none law!!! • The membrane will repolarize when K+ ...
Chapter 29 Nervous and Endocrine System
... from the axon and transmit impulse across synapse by binding to receptor sites on dendrite of adjacent neuron Impulses are self-propagating, like dominos ...
... from the axon and transmit impulse across synapse by binding to receptor sites on dendrite of adjacent neuron Impulses are self-propagating, like dominos ...
Lecture Test 2 2010
... D. It is designed to drain pus away from middle-ear infections. E. It runs from the pharynx to the eardrum (tympanic membrane), through which it opens into the external ear. B 47. In the three-neuron auditory pathway, between the receptor cells in the inner ear and the primary auditory cortex, where ...
... D. It is designed to drain pus away from middle-ear infections. E. It runs from the pharynx to the eardrum (tympanic membrane), through which it opens into the external ear. B 47. In the three-neuron auditory pathway, between the receptor cells in the inner ear and the primary auditory cortex, where ...
Here we can focus directly on the input neurons, the Schaffer
... pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pull synaptic target rather than a p synaptic target. The Schaffer collaterals come in, they re ...
... pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pull synaptic target rather than a p synaptic target. The Schaffer collaterals come in, they re ...
Parieto-prefrontal pathway
... (thought) Why is the hippocampus connected into the parieto-medial temporal pathway? •Much of the processing done by the parieto-medial temporal pathway is focused on navigation and relating ourselves to our environment. •The hippocampus creates cognitive maps, which reduce the cognitive load requi ...
... (thought) Why is the hippocampus connected into the parieto-medial temporal pathway? •Much of the processing done by the parieto-medial temporal pathway is focused on navigation and relating ourselves to our environment. •The hippocampus creates cognitive maps, which reduce the cognitive load requi ...
31.1 The Neuron Functions of the Nervous System and external
... Many drugs cause an increase in the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. The brain reacts to high dopamine levels by reducing the number of receptors. With fewer dopamine receptors available, larger amounts of drugs are required to produce a high. This can result in an addiction. 31.3 The Perip ...
... Many drugs cause an increase in the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. The brain reacts to high dopamine levels by reducing the number of receptors. With fewer dopamine receptors available, larger amounts of drugs are required to produce a high. This can result in an addiction. 31.3 The Perip ...
physio unit 9 [4-20
... Decrease signal transmission when input intensity is too great They travel backwards from cortex to thalamus, medulla, and spinal cord Amplifying Divergence Example Characteristic of corticospinal pathway, which controls skeletal muscles Divergence into multiple tracts Occurs in information transmit ...
... Decrease signal transmission when input intensity is too great They travel backwards from cortex to thalamus, medulla, and spinal cord Amplifying Divergence Example Characteristic of corticospinal pathway, which controls skeletal muscles Divergence into multiple tracts Occurs in information transmit ...
Functional Neural Anatomy
... working memory, the ability to remember recent events, such as how many people ran in vs. out of a building delayed response tasks, in which a stimulus appears, then disappears, and after a delay, the person must respond to the remembered stimulus monitoring recent events, calculating possible actio ...
... working memory, the ability to remember recent events, such as how many people ran in vs. out of a building delayed response tasks, in which a stimulus appears, then disappears, and after a delay, the person must respond to the remembered stimulus monitoring recent events, calculating possible actio ...
Chapter 18 - Austin Community College
... • Caused by an increased fluid volume in the inner ear • Hearing loss and vertigo are both characteristics of this ...
... • Caused by an increased fluid volume in the inner ear • Hearing loss and vertigo are both characteristics of this ...
Nerve cells (Neurons)
... _________________ or __________________. A group of fibers activated by the same nerve is a ________________. A muscle may be composed of a different number of motor units and each motor units may in turn consist of a different number of fibers. All fibers of a specific motor unit always have ...
... _________________ or __________________. A group of fibers activated by the same nerve is a ________________. A muscle may be composed of a different number of motor units and each motor units may in turn consist of a different number of fibers. All fibers of a specific motor unit always have ...
Study Guide for The Spinal Cord – Chapter 8, Part B Be familiar with
... root ganglion, dura mater, effector, endoneurium, epineurium, ganglion, gray matter, interneuron, lateral gray horn, lumbar enlargement, meninges, monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflex arc, motor neuron (fiber), nerve, nucleus (CNS), perineurium, peripheral nervous system, pia mater, reflex arc, sens ...
... root ganglion, dura mater, effector, endoneurium, epineurium, ganglion, gray matter, interneuron, lateral gray horn, lumbar enlargement, meninges, monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflex arc, motor neuron (fiber), nerve, nucleus (CNS), perineurium, peripheral nervous system, pia mater, reflex arc, sens ...
Chapter 2 Review Notes
... A neural impulse fires when the neuron is stimulated by pressure, heat, light, or chemical messages from adjacent neurons. Received signals trigger an impulse only if the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceeds a minimum intensity called the threshold. The neuron’s reaction is an all ...
... A neural impulse fires when the neuron is stimulated by pressure, heat, light, or chemical messages from adjacent neurons. Received signals trigger an impulse only if the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceeds a minimum intensity called the threshold. The neuron’s reaction is an all ...
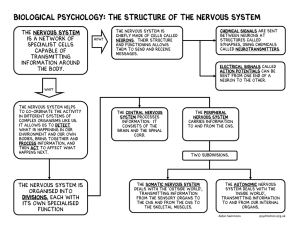
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
The Nervous System
... • Rapid, predictable and involuntary responses to stimuli that occur over neural pathways called reflex arcs. • Autonomic Reflexes – regulate the activity of smooth muscle, the heart, and glands. • Somatic Reflexes – includes all reflexes that stimulate the skeletal muscles. ...
... • Rapid, predictable and involuntary responses to stimuli that occur over neural pathways called reflex arcs. • Autonomic Reflexes – regulate the activity of smooth muscle, the heart, and glands. • Somatic Reflexes – includes all reflexes that stimulate the skeletal muscles. ...
Relating too much information without enough time to
... processed in cell body and sent down axon. Sending Information Information is sent to target neuron. ...
... processed in cell body and sent down axon. Sending Information Information is sent to target neuron. ...
Neuroscience, Genetics, and Behavior
... Close-Up: Left-Handedness—Is Being a Lefty All Right? • Thinking Critically About Left Brain/Right Brain • Summing Up Myers 5e ...
... Close-Up: Left-Handedness—Is Being a Lefty All Right? • Thinking Critically About Left Brain/Right Brain • Summing Up Myers 5e ...
Sense Organs - human anatomy
... Consists of a tangle of knobby nerve endings squeezed into the spaces between the collagen fibers of the tendon The Receptive Field – the area monitored by a single sensory neuron o Any information arriving at the CNS by way of that neuron is interpreted as coming from that sensory field, no matte ...
... Consists of a tangle of knobby nerve endings squeezed into the spaces between the collagen fibers of the tendon The Receptive Field – the area monitored by a single sensory neuron o Any information arriving at the CNS by way of that neuron is interpreted as coming from that sensory field, no matte ...
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... Huntington’s Disease- genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and causes involuntary twitching. Tourette’s Syndrome- irregular movements of the head, neck, or shoulders. They also may be more complex motor behaviors such as snorting, sniffing, and involuntary vocalization ...
... Huntington’s Disease- genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and causes involuntary twitching. Tourette’s Syndrome- irregular movements of the head, neck, or shoulders. They also may be more complex motor behaviors such as snorting, sniffing, and involuntary vocalization ...
Central Nervous System
... • ANS or visceral motor system, regulates smooth and cardiac muscle, and glandular activity ...
... • ANS or visceral motor system, regulates smooth and cardiac muscle, and glandular activity ...
www.sakshieducation.com
... 8) An involuntary response by the nervous system to a stimulus is a A) Synapse B) Reflex C) Motor response D) Smooth muscle ...
... 8) An involuntary response by the nervous system to a stimulus is a A) Synapse B) Reflex C) Motor response D) Smooth muscle ...
Introduction to Neurotransmitters
... • Neurotransmitters fit into receptor sites like a lock-and-key • Because of this, drugs can stimulate or block the neurotransmitter – This can be on purpose with prescription drugs to regulate over or under production or as a result of ...
... • Neurotransmitters fit into receptor sites like a lock-and-key • Because of this, drugs can stimulate or block the neurotransmitter – This can be on purpose with prescription drugs to regulate over or under production or as a result of ...