Nervous System PowerPoint
... heartbeat, and blood _____; reflex center Pons is the relay station between the _____ and the rest of the CNS; may play a role in _____; works with medulla to regulate _____ rate Why do we dream? (6:30) ...
... heartbeat, and blood _____; reflex center Pons is the relay station between the _____ and the rest of the CNS; may play a role in _____; works with medulla to regulate _____ rate Why do we dream? (6:30) ...
Document
... Main Aspects of Sensory Perception • Feature abstraction—identification of more complex aspects and several stimulus properties • Quality discrimination—the ability to identify submodalities of a sensation (e.g., sweet or sour tastes) • Pattern recognition—recognition of familiar or significant pat ...
... Main Aspects of Sensory Perception • Feature abstraction—identification of more complex aspects and several stimulus properties • Quality discrimination—the ability to identify submodalities of a sensation (e.g., sweet or sour tastes) • Pattern recognition—recognition of familiar or significant pat ...
Coming to Attention
... They used a phenomenon called attention blink. In the experiment they once again displayed a series of letters to subjects and observed them with fMRI. This time, however, only a single green letter appeared among rapidly changing black letters, and the subject had to tell at the end of the test wh ...
... They used a phenomenon called attention blink. In the experiment they once again displayed a series of letters to subjects and observed them with fMRI. This time, however, only a single green letter appeared among rapidly changing black letters, and the subject had to tell at the end of the test wh ...
{ How Neurosciences help us to understand some (psycho)therapeutic processes
... Ventral Pre-motor Cortex ...
... Ventral Pre-motor Cortex ...
FIGURE LEGNEDS FIGURE 24.1 A dorsal root ganglion cell is a
... receptor proteins that, through opening of cation channels, produce a depolarization called a generator potential. With sufficient depolarization, voltage-gated Na+ channels open to initiate action potentials. These action potentials are conducted down the axon and into the central branch that inner ...
... receptor proteins that, through opening of cation channels, produce a depolarization called a generator potential. With sufficient depolarization, voltage-gated Na+ channels open to initiate action potentials. These action potentials are conducted down the axon and into the central branch that inner ...
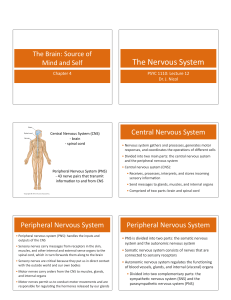
The Nervous System
... acJvity during stress, and neurons involved in learning, memory, dreaming, waking from sleep, and emoJon ...
... acJvity during stress, and neurons involved in learning, memory, dreaming, waking from sleep, and emoJon ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... Definition of Neural Networks • An information processing system that has been developed as a generalization of mathematical models of human cognition or neurobiology, based on the assumptions that – Information processing occurs at many simple elements called neurons. – Signals are passed between ...
... Definition of Neural Networks • An information processing system that has been developed as a generalization of mathematical models of human cognition or neurobiology, based on the assumptions that – Information processing occurs at many simple elements called neurons. – Signals are passed between ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... synaptic cleft • At the postsynaptic mb. The neurotransmitter merges with receptor sites • AP starts at the postsynaptic mb • Neurotransmitters may be broken down by enzymes, washed away, or recycles ...
... synaptic cleft • At the postsynaptic mb. The neurotransmitter merges with receptor sites • AP starts at the postsynaptic mb • Neurotransmitters may be broken down by enzymes, washed away, or recycles ...
PDF
... and R5 photoreceptor precursors independently of ectopic Ato in rough mutants (rough encodes a transcription factor that represses ato) and that Rough normally represses the R8-specific transcription factor senseless (sens) in these two precursors. Because R8 differentiation requires the repression ...
... and R5 photoreceptor precursors independently of ectopic Ato in rough mutants (rough encodes a transcription factor that represses ato) and that Rough normally represses the R8-specific transcription factor senseless (sens) in these two precursors. Because R8 differentiation requires the repression ...
PDF
... and R5 photoreceptor precursors independently of ectopic Ato in rough mutants (rough encodes a transcription factor that represses ato) and that Rough normally represses the R8-specific transcription factor senseless (sens) in these two precursors. Because R8 differentiation requires the repression ...
... and R5 photoreceptor precursors independently of ectopic Ato in rough mutants (rough encodes a transcription factor that represses ato) and that Rough normally represses the R8-specific transcription factor senseless (sens) in these two precursors. Because R8 differentiation requires the repression ...
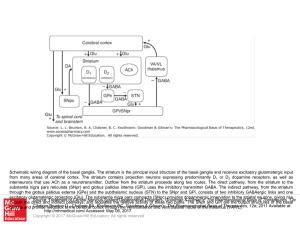
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
... substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNpr) and globus pallidus interna (GPi), uses the inhibitory transmitter GABA. The indirect pathway, from the striatum through the globus pallidus externa (GPe) and the subthalamic nucleus (STN) to the SNpr and GPi, consists of two inhibitory GABAergic links and one ...
... substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNpr) and globus pallidus interna (GPi), uses the inhibitory transmitter GABA. The indirect pathway, from the striatum through the globus pallidus externa (GPe) and the subthalamic nucleus (STN) to the SNpr and GPi, consists of two inhibitory GABAergic links and one ...
21-1
... • First cell body in DRG with synapses in cord • 2nd cell body in gray matter of cord, sends fibers to other side of cord & up through white matter to synapse in thalamus • 3rd cell body in thalamus projects to cerebral cortex ...
... • First cell body in DRG with synapses in cord • 2nd cell body in gray matter of cord, sends fibers to other side of cord & up through white matter to synapse in thalamus • 3rd cell body in thalamus projects to cerebral cortex ...
PDF
... about the molecular mechanisms underlying their formation. To investigate the involvement of motoneurons in sensory neuron development, Hirohide Takebayashi and colleagues analyse sensory neuron phenotypes in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of Olig2 knockout mouse embryos, which lack motoneurons (see ...
... about the molecular mechanisms underlying their formation. To investigate the involvement of motoneurons in sensory neuron development, Hirohide Takebayashi and colleagues analyse sensory neuron phenotypes in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of Olig2 knockout mouse embryos, which lack motoneurons (see ...
NIPS/Dec99/notebook3
... elicit bursting activity (1). This is possible because these fibers possess large presynaptic knobs containing round glutamatergic vesicles. The synaptic contacts are so powerful that a single primary afferent fiber can generate pairs or triplets of output spikes from several target DCN neurons (8) ...
... elicit bursting activity (1). This is possible because these fibers possess large presynaptic knobs containing round glutamatergic vesicles. The synaptic contacts are so powerful that a single primary afferent fiber can generate pairs or triplets of output spikes from several target DCN neurons (8) ...
Anat 1: Ch 17 (SS99)
... C. Neuron #1 releases Ach, usually neuron #2 releases NE D. Prepares for emergency action, excitatory to many organs, inhibitory to others ( digestive for example) E. Effects very widespread and somewhat persistent ...
... C. Neuron #1 releases Ach, usually neuron #2 releases NE D. Prepares for emergency action, excitatory to many organs, inhibitory to others ( digestive for example) E. Effects very widespread and somewhat persistent ...
Chapter 49 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... 1. External ear: pinna and auditory canal in some vertebrates. 2. Middle ear: tympanic membrane and auditory bones. 3. Inner ear: semicircular canals, vestibule and cochlea. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear with the pharynx and equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the atmosph ...
... 1. External ear: pinna and auditory canal in some vertebrates. 2. Middle ear: tympanic membrane and auditory bones. 3. Inner ear: semicircular canals, vestibule and cochlea. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear with the pharynx and equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the atmosph ...
Neuronal activity in dorsomedial frontal cortex and prefrontal cortex
... stimulus location in nonspatially guided tasks because spatial factors controlled responding in other tasks. The present experiment overcame that problem because stimulus location was never a differential discriminative stimulus for responding. We found that stimulus location was nevertheless encode ...
... stimulus location in nonspatially guided tasks because spatial factors controlled responding in other tasks. The present experiment overcame that problem because stimulus location was never a differential discriminative stimulus for responding. We found that stimulus location was nevertheless encode ...
Olfactory network dynamics and the coding of multidimensional
... and active shortening of the integration window, as found here, is a solution to this problem. ...
... and active shortening of the integration window, as found here, is a solution to this problem. ...
Dear Notetaker:
... o Posterior parietal lobe is where the dorsal pathway ends o Post central sulcus divides the anterior part of parietal lobe from posterior part of parietal lobe Posterior portion of parietal lobe is posterior to sulcus o Posterior portion of parietal lobe has a superior lobule and inferior lobule ...
... o Posterior parietal lobe is where the dorsal pathway ends o Post central sulcus divides the anterior part of parietal lobe from posterior part of parietal lobe Posterior portion of parietal lobe is posterior to sulcus o Posterior portion of parietal lobe has a superior lobule and inferior lobule ...
1 1. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the A. brain and
... usually caused by damage to the cerebrum during gestation or birth trauma but can also be hereditary. A. Conjunctivitis B. Epilepsy C. Multiple sclerosis D. Cerebral palsy E. Parkinson disease ...
... usually caused by damage to the cerebrum during gestation or birth trauma but can also be hereditary. A. Conjunctivitis B. Epilepsy C. Multiple sclerosis D. Cerebral palsy E. Parkinson disease ...
Slide 1
... the stimulus causes channels to open and there must be enough of them opened to depolarize the membrane increasing a stimulus above threshold does not result in a larger response - this is all-or-nothing. If all stimuli above threshold cause a neuron to fire, how do we detect different intensities o ...
... the stimulus causes channels to open and there must be enough of them opened to depolarize the membrane increasing a stimulus above threshold does not result in a larger response - this is all-or-nothing. If all stimuli above threshold cause a neuron to fire, how do we detect different intensities o ...
Nervous System Notes
... the stimulus causes channels to open and there must be enough of them opened to depolarize the membrane increasing a stimulus above threshold does not result in a larger response - this is all-or-nothing. If all stimuli above threshold cause a neuron to fire, how do we detect different intensities o ...
... the stimulus causes channels to open and there must be enough of them opened to depolarize the membrane increasing a stimulus above threshold does not result in a larger response - this is all-or-nothing. If all stimuli above threshold cause a neuron to fire, how do we detect different intensities o ...