Impact of Correlated inputs on Simple Neural Models
... correlated but without correlation) Balanced non-specific uncorrelated spike trains (typical of cortical neurons) ...
... correlated but without correlation) Balanced non-specific uncorrelated spike trains (typical of cortical neurons) ...
Neural Coding and Auditory Perception
... We have previously shown that the auditory nerve (AN) contains spatio-temporal cues to the resolved harmonics of a complex tone that are more robust to variations in stimulus level than traditional rate-place cues and could potentially be used in pitch extraction [2]. To investigate whether these cu ...
... We have previously shown that the auditory nerve (AN) contains spatio-temporal cues to the resolved harmonics of a complex tone that are more robust to variations in stimulus level than traditional rate-place cues and could potentially be used in pitch extraction [2]. To investigate whether these cu ...
A multi-level account of selective attention
... Broadbent’s notion that selection must be early, as these basic attributes appeared to be all that was retained from the unattended auditory stream. Not long after Broadbent’s seminal book, Moray (1959) demonstrated that selection was not always implemented by an early filtering mechanism, as he not ...
... Broadbent’s notion that selection must be early, as these basic attributes appeared to be all that was retained from the unattended auditory stream. Not long after Broadbent’s seminal book, Moray (1959) demonstrated that selection was not always implemented by an early filtering mechanism, as he not ...
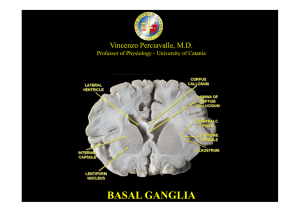
basal ganglia
... On striatal medium spiny neurons of origin of the direct pathway. dopamine binds receptors D1-type, while on those of origin of the indirect pathway binds receptors D2-type. Activation of receptor D1-type induces an increase of cAMP, whereas the activation of receptor D2-type produces a decrease of ...
... On striatal medium spiny neurons of origin of the direct pathway. dopamine binds receptors D1-type, while on those of origin of the indirect pathway binds receptors D2-type. Activation of receptor D1-type induces an increase of cAMP, whereas the activation of receptor D2-type produces a decrease of ...
Parts of the Nervous System
... The neuron is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system, it is the information processing unit, responsible for the generation and conduction of the electrical signals Neurons communicate with one another via chemicals released at the synapse. (neurotransmitters) Neurons are sup ...
... The neuron is the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system, it is the information processing unit, responsible for the generation and conduction of the electrical signals Neurons communicate with one another via chemicals released at the synapse. (neurotransmitters) Neurons are sup ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Synapses and Electroconvulsive
... neurotransmitters, like norepinephrine can be both excitatory or inhibitory. this depends on: – The type of receptors on the post synaptic cell – How the receptors actually work • some receptors directly open an ion channel (like Acetylcholine exciting skeletal muscle cells), but some lead to furthe ...
... neurotransmitters, like norepinephrine can be both excitatory or inhibitory. this depends on: – The type of receptors on the post synaptic cell – How the receptors actually work • some receptors directly open an ion channel (like Acetylcholine exciting skeletal muscle cells), but some lead to furthe ...
Prenatal and postnatal development of laterally
... experience, while retaining the original map shape. The visually driven and internally driven models also differ in many ways besides the source of activity, and thus it has been difficult to determine whether the activity patterns alone account for any differences between the results. In this paper ...
... experience, while retaining the original map shape. The visually driven and internally driven models also differ in many ways besides the source of activity, and thus it has been difficult to determine whether the activity patterns alone account for any differences between the results. In this paper ...
Anatomy of spinal cord
... neuroglia and blood vessels. White color is due to high proportion of myelinated nerve fibers The white matter of the spinal cord is arranged in columns/funiculi; anterior, posterior and lateral. The nerve fibers are arranged as bundles, running vertically through the cord. A group of nerve ...
... neuroglia and blood vessels. White color is due to high proportion of myelinated nerve fibers The white matter of the spinal cord is arranged in columns/funiculi; anterior, posterior and lateral. The nerve fibers are arranged as bundles, running vertically through the cord. A group of nerve ...
Ch12 notes Martini 9e
... • The sodium–potassium exchange pump ejects 3 Na+ ions for every 2 K+ ions that it brings into the cell • It serves to stabilize the resting potential when the ratio of Na+ entry to K+ loss through passive channels is 3:2 • At the normal resting potential, these passive and active mechanisms are in ...
... • The sodium–potassium exchange pump ejects 3 Na+ ions for every 2 K+ ions that it brings into the cell • It serves to stabilize the resting potential when the ratio of Na+ entry to K+ loss through passive channels is 3:2 • At the normal resting potential, these passive and active mechanisms are in ...
Nerves, structures, and organs of the head 1. Left cerebral
... Dura mater (21) A sheath of dense fibrous elastic tissue which lines the inner surfaces of the cranium and the vertebrae, Fornix (6) An arch of fold found in the cerebral hemispheres of man, Medulla oblongata (15) Composed primarily of white matter, the medulla communicates between the higher brain ...
... Dura mater (21) A sheath of dense fibrous elastic tissue which lines the inner surfaces of the cranium and the vertebrae, Fornix (6) An arch of fold found in the cerebral hemispheres of man, Medulla oblongata (15) Composed primarily of white matter, the medulla communicates between the higher brain ...
Objectives: The student shall know the facts, understand the
... Active transport (primary & secondary); application to the resting neuron membrane and intestinal absorption of sodium, glucose, and water Water transport; definitions of solution osmolarity and tonicity Vesicular transport; endocytosis and exocytosis Components of electrochemical (passive) driving ...
... Active transport (primary & secondary); application to the resting neuron membrane and intestinal absorption of sodium, glucose, and water Water transport; definitions of solution osmolarity and tonicity Vesicular transport; endocytosis and exocytosis Components of electrochemical (passive) driving ...
Nervous and Muscle Tissue - White Plains Public Schools
... • Epithelial, bone, areolar, dense irregular and blood tissues regenerate. • Smooth muscle and dense regular connective tissue have a moderate capacity to regenerate while skeletal muscle and cartilage are weak. • Cardiac and nervous tissues have none. ...
... • Epithelial, bone, areolar, dense irregular and blood tissues regenerate. • Smooth muscle and dense regular connective tissue have a moderate capacity to regenerate while skeletal muscle and cartilage are weak. • Cardiac and nervous tissues have none. ...
Powerpoint version
... Signal at the synapse excites or inhibits the postsynaptic neuron Excitatory synapse: Causes an influx of Na+ into postsynaptic neuron. This produces an EPSP and depolarizes the neuron. ...
... Signal at the synapse excites or inhibits the postsynaptic neuron Excitatory synapse: Causes an influx of Na+ into postsynaptic neuron. This produces an EPSP and depolarizes the neuron. ...
Electroconvulsive therapy - a shocking topic
... neurotransmitters, like norepinephrine can be both excitatory or inhibitory. this depends on: – The type of receptors on the post synaptic cell – How the receptors actually work • some receptors directly open an ion channel (like Acetylcholine exciting skeletal muscle cells), but some lead to furthe ...
... neurotransmitters, like norepinephrine can be both excitatory or inhibitory. this depends on: – The type of receptors on the post synaptic cell – How the receptors actually work • some receptors directly open an ion channel (like Acetylcholine exciting skeletal muscle cells), but some lead to furthe ...
15. Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
... NE to these alpha receptors causes vasoconstriction. Beta receptors are found in bronchioles of the lungs and blood vessels that serve the heart and skeletal muscles. Binding of NE to these beta receptors causes dilation. Beta receptors on cardiac muscle cause increases in heart rate and strength of ...
... NE to these alpha receptors causes vasoconstriction. Beta receptors are found in bronchioles of the lungs and blood vessels that serve the heart and skeletal muscles. Binding of NE to these beta receptors causes dilation. Beta receptors on cardiac muscle cause increases in heart rate and strength of ...
Overview of Addiction Related Brain Regions Nucleus Accumbens
... memory (procedural memory) and different brain regions. And there is evidence (e.g., O'Kane et al 2004) to suggest that patient HM (who had his medial temporal lobes removed bilaterally as a treatment for epilepsy) can form new semantic memories. Role in spatial memory and navigation Some evidence i ...
... memory (procedural memory) and different brain regions. And there is evidence (e.g., O'Kane et al 2004) to suggest that patient HM (who had his medial temporal lobes removed bilaterally as a treatment for epilepsy) can form new semantic memories. Role in spatial memory and navigation Some evidence i ...
12 The Central Nervous System Part A Central Nervous System
... Exhibits spatial discrimination Somatosensory homunculus – caricature of relative amounts of cortical tissue devoted to each sensory function Primary Somatosensory Cortex Somatosensory Association Cortex Located posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex Integrates sensory information Forms compr ...
... Exhibits spatial discrimination Somatosensory homunculus – caricature of relative amounts of cortical tissue devoted to each sensory function Primary Somatosensory Cortex Somatosensory Association Cortex Located posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex Integrates sensory information Forms compr ...
From autism to ADHD: computational simulations
... Other: Grossberg ART model. At which level can we understand not just correlations, but real mechanisms responsible for behavioral symptoms? (genes, proteins, biochemistry, ion channels, synapses, membranes) (neural properties, networks) (behavior, syndromes, disease). ...
... Other: Grossberg ART model. At which level can we understand not just correlations, but real mechanisms responsible for behavioral symptoms? (genes, proteins, biochemistry, ion channels, synapses, membranes) (neural properties, networks) (behavior, syndromes, disease). ...
Functional Organization of Ferret Auditory Cortex
... according to their preferred or ‘best’ frequency. In contrast, neurons in non-primary areas can differ in their frequency organization, response latencies, and spatial and spectral integration properties. Indeed, systematic variations in these response properties have been used as a basis for segreg ...
... according to their preferred or ‘best’ frequency. In contrast, neurons in non-primary areas can differ in their frequency organization, response latencies, and spatial and spectral integration properties. Indeed, systematic variations in these response properties have been used as a basis for segreg ...
The Distribution and Morphological Characteristics of
... nucleus. The soma were spherical with 3–4 primary dendrites. Dorsal to this group and located entirely within the periaqueductal gray matter was the A10dc group. The cells of this group were found along the midline of the periaqueductal gray, dorsal to the oculomotor nucleus, adjacent to the floor o ...
... nucleus. The soma were spherical with 3–4 primary dendrites. Dorsal to this group and located entirely within the periaqueductal gray matter was the A10dc group. The cells of this group were found along the midline of the periaqueductal gray, dorsal to the oculomotor nucleus, adjacent to the floor o ...
Nerve Cells, Neural Circuitry, and Behavior
... formation of networks. Rather each cell makes specific connections—at particular contact points—with certain postsynaptic target cells but not with others. The principles of dynamic polarization and connectional specificity are the basis of the modern connectionist approach to studying the brain. Ra ...
... formation of networks. Rather each cell makes specific connections—at particular contact points—with certain postsynaptic target cells but not with others. The principles of dynamic polarization and connectional specificity are the basis of the modern connectionist approach to studying the brain. Ra ...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Sensory Pathway (PNS
... Cylinder of nerve tissue within the vertebral canal (thick as a finger) vertebral column grows faster so in an adult the spinal cord only extends to L1 ...
... Cylinder of nerve tissue within the vertebral canal (thick as a finger) vertebral column grows faster so in an adult the spinal cord only extends to L1 ...
chapter2 (new window)
... – Rods are destroyed first – Foveal cones can also be attacked – Severe cases result in complete blindness ...
... – Rods are destroyed first – Foveal cones can also be attacked – Severe cases result in complete blindness ...