Principles of Neural Science - Weizmann Institute of Science
... The superior colliculus is a structure of alternating gray cellular and white (axonal) layers lying on the roof of the midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells project directly to the superficial layers and form a map of the contralateral visual field. Cells in the superficial layers in turn project through ...
... The superior colliculus is a structure of alternating gray cellular and white (axonal) layers lying on the roof of the midbrain. Retinal ganglion cells project directly to the superficial layers and form a map of the contralateral visual field. Cells in the superficial layers in turn project through ...
Full text PDF - Bosnian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences
... myelin depositing, which is formed from repeated coiling of Schwan cells membrane around the axon. Myelin sheath which surrounds nerve fibres in spinal-cord has a very different origin, as it is formed from oligodentroglial cells. Although myelinisation of nerve fibres in spinal-cord starts approximat ...
... myelin depositing, which is formed from repeated coiling of Schwan cells membrane around the axon. Myelin sheath which surrounds nerve fibres in spinal-cord has a very different origin, as it is formed from oligodentroglial cells. Although myelinisation of nerve fibres in spinal-cord starts approximat ...
Primary afferent neurons of the gut
... EC cells “taste” luminal contents and release their mediators across the basolateral membrane to generate action potentials in the afferent nerve endings. Stimulus intensity is encoded in the amount of mediator release and represents the balance between the mechanisms causing releasing and the u ...
... EC cells “taste” luminal contents and release their mediators across the basolateral membrane to generate action potentials in the afferent nerve endings. Stimulus intensity is encoded in the amount of mediator release and represents the balance between the mechanisms causing releasing and the u ...
Ear25 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... auditory pathways in cortex resemble VISUAL pathways in that there is increasingly complex processing of auditory information along them. organized in two general paths (like visual pathways): 1. Dorsal-parietal pathway concerned with sound localization ("where" pathway). 2. Ventral-temporal pat ...
... auditory pathways in cortex resemble VISUAL pathways in that there is increasingly complex processing of auditory information along them. organized in two general paths (like visual pathways): 1. Dorsal-parietal pathway concerned with sound localization ("where" pathway). 2. Ventral-temporal pat ...
Specific Projection of the Sensory Crypt Cells in
... mitral cells whose axons make up the lMOT. This finding is in accordance with our previous studies showing that microvillous ORNs project to the lateral olfactory tract, which mediates feeding behavior, and that ciliated ORNs project to the medial bundle of the medial olfactory tract mediating alarm ...
... mitral cells whose axons make up the lMOT. This finding is in accordance with our previous studies showing that microvillous ORNs project to the lateral olfactory tract, which mediates feeding behavior, and that ciliated ORNs project to the medial bundle of the medial olfactory tract mediating alarm ...
The cytoarchitectonic and neuronal structure of the red nucleus in
... general, they lie above the magnocellular part. Its medial side adjoins the oculomotor nerve III, and the retroflexus fascicle in front, whereas its ventral side adjoins strictly the medial lemniscus. The posterior portion of RN is constituted of RNm, which is in the form of a circular, well disting ...
... general, they lie above the magnocellular part. Its medial side adjoins the oculomotor nerve III, and the retroflexus fascicle in front, whereas its ventral side adjoins strictly the medial lemniscus. The posterior portion of RN is constituted of RNm, which is in the form of a circular, well disting ...
Controlling the Elements: An Optogenetic Approach to
... revealed a great deal about the neural mechanisms of fear learning (1–7,11–13). Despite this progress, much remains to be understood about the fundamental principles by which fear conditioning is implemented at the level of defined neural circuits. In addition, information processing by neurons in t ...
... revealed a great deal about the neural mechanisms of fear learning (1–7,11–13). Despite this progress, much remains to be understood about the fundamental principles by which fear conditioning is implemented at the level of defined neural circuits. In addition, information processing by neurons in t ...
Dynamics of extraclassical surround modulation in three types of V1
... where Rn is the responses to the jth stimulus, Fn is the predicted value, and R0 is the mean response of the actual data (Freeman et al. 2002). Across the population, the mean R2 for 2-s stimuli is 0.86 ⫾ 0.09. Definition of modulatory cell types and their CRF. In our study, cells with suppressive, ...
... where Rn is the responses to the jth stimulus, Fn is the predicted value, and R0 is the mean response of the actual data (Freeman et al. 2002). Across the population, the mean R2 for 2-s stimuli is 0.86 ⫾ 0.09. Definition of modulatory cell types and their CRF. In our study, cells with suppressive, ...
Teacher Guide
... times it tapped. Ask the class to explain why the number of muscle flexes does not match the number of taps. Once the class understands that some of the students only pass a message for every 2, 3, or 4 incoming messages, introduce the idea of threshold – that a cell body must add up all incoming me ...
... times it tapped. Ask the class to explain why the number of muscle flexes does not match the number of taps. Once the class understands that some of the students only pass a message for every 2, 3, or 4 incoming messages, introduce the idea of threshold – that a cell body must add up all incoming me ...
Overview of the Brain
... functions on several levels that can be broken down into both a micro and macroscopic regions. • At the microscopic level we have the basic nerve cell, the neuron, which is interconnected into a network of neurons that transects, crisscrosses, and connects every cell and sensory organs to the brain. ...
... functions on several levels that can be broken down into both a micro and macroscopic regions. • At the microscopic level we have the basic nerve cell, the neuron, which is interconnected into a network of neurons that transects, crisscrosses, and connects every cell and sensory organs to the brain. ...
Self Organizing Maps: Fundamentals
... We now turn to unsupervised training, in which the networks learn to form their own classifications of the training data without external help. To do this we have to assume that class membership is broadly defined by the input patterns sharing common features, and that the network will be able to id ...
... We now turn to unsupervised training, in which the networks learn to form their own classifications of the training data without external help. To do this we have to assume that class membership is broadly defined by the input patterns sharing common features, and that the network will be able to id ...
System Architecture of ERS/ERD
... • 1970s - Research that developed algorithms to reconstruct movements from motor cortex neurons, which control movement. • 1980s - Johns Hopkins researchers found a mathematical relationship between electrical responses of single motor-cortex neurons in rhesus macaque monkeys and the direction that ...
... • 1970s - Research that developed algorithms to reconstruct movements from motor cortex neurons, which control movement. • 1980s - Johns Hopkins researchers found a mathematical relationship between electrical responses of single motor-cortex neurons in rhesus macaque monkeys and the direction that ...
SOMATOSENSORY PATHWAYS
... anterolateral pathway, if you step on a tack with you foot, your spinothalamic tract enables you to realize “something sharp is puncturing the sole of my foot”; your spinothalamic intralaminar projections and spinoreticular tract cause you to feel “ouch! That hurts!”; and your spinomesencephalic tra ...
... anterolateral pathway, if you step on a tack with you foot, your spinothalamic tract enables you to realize “something sharp is puncturing the sole of my foot”; your spinothalamic intralaminar projections and spinoreticular tract cause you to feel “ouch! That hurts!”; and your spinomesencephalic tra ...
LESSON 3.3 WORKBOOK
... neurons experience enough IPSPs they won’t fire an action potential and will experience neural inhibition. But what effect will this have on your head? In fact if these neurons are inhibited, i.e. prevented from functioning, they will no longer be able to prevent your head falling onto your chest. T ...
... neurons experience enough IPSPs they won’t fire an action potential and will experience neural inhibition. But what effect will this have on your head? In fact if these neurons are inhibited, i.e. prevented from functioning, they will no longer be able to prevent your head falling onto your chest. T ...
Brain Day Volunteer Instructor Manual
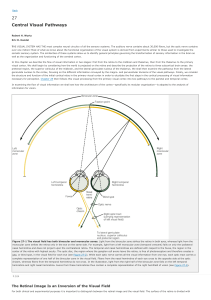
... The human eye is ~2.5cm in length and weighs about 7g (less than three pennies!). Muscles control the movement of the eye. The eyelid protects the surface of the eye. Tears clean the eye’s surface. The surface of the eye, the cornea, acts like a filter. The iris and pupil adjust to the amount of lig ...
... The human eye is ~2.5cm in length and weighs about 7g (less than three pennies!). Muscles control the movement of the eye. The eyelid protects the surface of the eye. Tears clean the eye’s surface. The surface of the eye, the cornea, acts like a filter. The iris and pupil adjust to the amount of lig ...
The Brain.
... The main motor area controls the main skeletal muscles of the body and the main sensory area receives input from the various skin receptors all over the body. The areas are duplicated onto the two cerebral hemispheres, which control opposite sides of the body. Therefore, those situated on the ...
... The main motor area controls the main skeletal muscles of the body and the main sensory area receives input from the various skin receptors all over the body. The areas are duplicated onto the two cerebral hemispheres, which control opposite sides of the body. Therefore, those situated on the ...
Neurofeedback
... prone complexity and robust predictable oscillatory synchrony… “…this switching behavior is the most efficient way for the brain to detect changes in the body and the surrounding physical world, while preserving its autonomous internal organization.” -Gyorgy Buzsaki Rhythms of the Brain ...
... prone complexity and robust predictable oscillatory synchrony… “…this switching behavior is the most efficient way for the brain to detect changes in the body and the surrounding physical world, while preserving its autonomous internal organization.” -Gyorgy Buzsaki Rhythms of the Brain ...
23. Parasympathetic nervous system
... Basic anatomical difference between the motor pathways of the voluntary somatic nervous system (to skeletal muscles) and those of the autonomic nervous system ...
... Basic anatomical difference between the motor pathways of the voluntary somatic nervous system (to skeletal muscles) and those of the autonomic nervous system ...
Turtle Dorsal Cortex Pyramidal Neurons Comprise Two Distinct Cell
... hypothesis that cellular individuality represents a smaller computational role within the context of the larger network. These competing hypotheses raise the important question to what extent the computational function of a neuron is determined by its individual type or by its circuit connections. W ...
... hypothesis that cellular individuality represents a smaller computational role within the context of the larger network. These competing hypotheses raise the important question to what extent the computational function of a neuron is determined by its individual type or by its circuit connections. W ...
Key Transmitters - Sinauer Associates
... Several auxilliary synaptic proteins regulate this trafficking.49 It allows rapid changes in the numbers and subunit composition of synaptic receptors during neural activity, providing the basis for many forms of synaptic plasticity (see Chapter 16). The NMDA receptors are made up of GluN1–3 subunit ...
... Several auxilliary synaptic proteins regulate this trafficking.49 It allows rapid changes in the numbers and subunit composition of synaptic receptors during neural activity, providing the basis for many forms of synaptic plasticity (see Chapter 16). The NMDA receptors are made up of GluN1–3 subunit ...
The Impact of Prior Experience With Cross-Modal
... sound) or cross-modal (light and sound) stimulation, as well as from rats with and without prior exposure to cross-modal stimuli. The tissue was processed for c-fos, which is a protein indicating neural activity evoked by stimulation. Data collection involved counting c-fos positive bipolar and mult ...
... sound) or cross-modal (light and sound) stimulation, as well as from rats with and without prior exposure to cross-modal stimuli. The tissue was processed for c-fos, which is a protein indicating neural activity evoked by stimulation. Data collection involved counting c-fos positive bipolar and mult ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology I
... Monitors internal conditions- blood gasses, viscera operation, etc ...
... Monitors internal conditions- blood gasses, viscera operation, etc ...
Chapter 48 - cloudfront.net
... neighboring region, region B. The depolarization of region B will soon be large enough for it to reach the threshold, causing the original potential action to be reinitiated in there, similar to the passing of the baton. By then, region B will be its rising phase and it will cause depolarization of ...
... neighboring region, region B. The depolarization of region B will soon be large enough for it to reach the threshold, causing the original potential action to be reinitiated in there, similar to the passing of the baton. By then, region B will be its rising phase and it will cause depolarization of ...
J Neurophysiol - University of Connecticut
... would thus be 1/8 octaves by 5 ms. If we require that the peak rise at least twice as high as the noise threshold (a conservative criterion), then the minimum size for a robust STRF feature is 0.095 octaves by 3.8 ms. By this measure, 223 of 240 (93%) thalamic single units and 164 of 267 (61%) corti ...
... would thus be 1/8 octaves by 5 ms. If we require that the peak rise at least twice as high as the noise threshold (a conservative criterion), then the minimum size for a robust STRF feature is 0.095 octaves by 3.8 ms. By this measure, 223 of 240 (93%) thalamic single units and 164 of 267 (61%) corti ...
Joint EuroSPIN/NeuroTime Meeting 2013, January 14
... addition, the number of electrodes driven over threshold during activity is distributed approximately like a power law with an exponent of -3/2 for event sizes suggesting a critical dynamics. Neural avalanches have been shown to provide: optimal information transmission, maximal information capacity ...
... addition, the number of electrodes driven over threshold during activity is distributed approximately like a power law with an exponent of -3/2 for event sizes suggesting a critical dynamics. Neural avalanches have been shown to provide: optimal information transmission, maximal information capacity ...