the primate amygdala and reinforcement: a
... showed abnormal patterns of food choice, picking up and eating foods not normally eaten such as meat, and picking up and placing in their mouths inedible objects (Murray et al., 1996). These symptoms produced by selective amygdala lesions are classical Klüver-Bucy symptoms. Further evidence relating ...
... showed abnormal patterns of food choice, picking up and eating foods not normally eaten such as meat, and picking up and placing in their mouths inedible objects (Murray et al., 1996). These symptoms produced by selective amygdala lesions are classical Klüver-Bucy symptoms. Further evidence relating ...
Chapter 15: Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic
... 3. Tactile discs, or Merkel’s discs, are fine touch and pressure receptors. They are extremely sensitive to tonic receptors and have very small receptive fields. Figure 15-3c 4. Tactile corpuscles, or Meissner’s corpuscles, perceive sensations of fine touch and pressure and low-frequency vibration. ...
... 3. Tactile discs, or Merkel’s discs, are fine touch and pressure receptors. They are extremely sensitive to tonic receptors and have very small receptive fields. Figure 15-3c 4. Tactile corpuscles, or Meissner’s corpuscles, perceive sensations of fine touch and pressure and low-frequency vibration. ...
Expectation of reward modulates cognitive signals in the basal ganglia
... The modulation of caudate neural activity could instead be considered a kind of attentional modulation. However, this is conceptually different from the type of attention investigated in previous studies. Thus, the previous studies on attention1–3 were based on the ‘attend-versus-ignore’ comparison, ...
... The modulation of caudate neural activity could instead be considered a kind of attentional modulation. However, this is conceptually different from the type of attention investigated in previous studies. Thus, the previous studies on attention1–3 were based on the ‘attend-versus-ignore’ comparison, ...
Signal acquisition and analysis for cortical control of neuroprosthetics
... similar target-directed cursor movements using its brain signals directly, the visual feedback of the braincontrolled cursors enabled the animal to learn to modulate its recorded signals more effectively. A similar maximum likelihood estimation of target location based on neural activity recorded du ...
... similar target-directed cursor movements using its brain signals directly, the visual feedback of the braincontrolled cursors enabled the animal to learn to modulate its recorded signals more effectively. A similar maximum likelihood estimation of target location based on neural activity recorded du ...
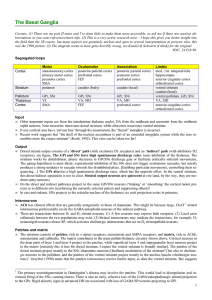
The Basal Ganglia
... and attention-grabbing properties (distinct from the cognitive process of directed/selective attention, which requires a central representation of the target, and distinct from startle responses). Salient stimuli leading to motivational arousal are a large, albeit not comprehensive set of stimuli th ...
... and attention-grabbing properties (distinct from the cognitive process of directed/selective attention, which requires a central representation of the target, and distinct from startle responses). Salient stimuli leading to motivational arousal are a large, albeit not comprehensive set of stimuli th ...
3E-F Worksheet 1. Sensory receptors that are classed by location
... respond to stimuli arising __________body and are found in internal ________and blood________ which are sensitive to chemical changes and ______________changes as well as__________. 3E 1 2. Sensory receptor also classed by location are the Proprioceptors which respond to the degree of ___________of ...
... respond to stimuli arising __________body and are found in internal ________and blood________ which are sensitive to chemical changes and ______________changes as well as__________. 3E 1 2. Sensory receptor also classed by location are the Proprioceptors which respond to the degree of ___________of ...
What can mice tell us about how vision works?
... ipRGCs, the mouse retina harbors eight or more different subtypes of direction-selective RGCs (DSGCs) [31–37]. DSGCs are particularly numerous in mouse retina, and current estimates indicate they comprise at least half of the total number of RGCs [12,33]. Furthermore, one study observed that some mo ...
... ipRGCs, the mouse retina harbors eight or more different subtypes of direction-selective RGCs (DSGCs) [31–37]. DSGCs are particularly numerous in mouse retina, and current estimates indicate they comprise at least half of the total number of RGCs [12,33]. Furthermore, one study observed that some mo ...
Transcripts/2_9 2
... a. If an area of cortex does something unique it will have a distinctive architecture i. [S39] Lateral view of a monkey brain 1. If we took a section of tissue from primary visual cortex and stained it with crystal violet you would see something like this – the cortex forms horizontal layers, you wi ...
... a. If an area of cortex does something unique it will have a distinctive architecture i. [S39] Lateral view of a monkey brain 1. If we took a section of tissue from primary visual cortex and stained it with crystal violet you would see something like this – the cortex forms horizontal layers, you wi ...
The Nervous System
... Major regions of neurons Cell body—nucleus and metabolic center of the cell Processes—fibers that extend from the cell body ...
... Major regions of neurons Cell body—nucleus and metabolic center of the cell Processes—fibers that extend from the cell body ...
Overlapping representation of primary tastes in a defined
... to bregma to 1.5 mm posterior to bregma (Figure 1E). We also found consistent tasteevoked (QHCl) c-fos labeling in regions containing labeled thalamic fibers, further demonstrating the labeled area is GC (Figure 1G). As previous imaging studies focused on an anatomically defined region of GC delinea ...
... to bregma to 1.5 mm posterior to bregma (Figure 1E). We also found consistent tasteevoked (QHCl) c-fos labeling in regions containing labeled thalamic fibers, further demonstrating the labeled area is GC (Figure 1G). As previous imaging studies focused on an anatomically defined region of GC delinea ...
Retinal diseases
... EPIRETINAL AND SUBRETINAL MICROIMPLANT: PROS AND CONS As illustrated in this research both approaches, epiretinal and subretinal, have advantages and disadvantages. The epiretinal design, for example, does not rely on the presence of intact neurons for signal processing when imposing spike patterns ...
... EPIRETINAL AND SUBRETINAL MICROIMPLANT: PROS AND CONS As illustrated in this research both approaches, epiretinal and subretinal, have advantages and disadvantages. The epiretinal design, for example, does not rely on the presence of intact neurons for signal processing when imposing spike patterns ...
Neuroanatomy 6-12
... • Did the CEN Outreach volunteer teach the student objectives? • Did the CEN Outreach program reach the goals of the teacher? • Did the CEN Outreach program reach it’s own goals/objectives? Resources: • http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Homeostasis NGSS Description: MS-LS1-1 Conduct an invest ...
... • Did the CEN Outreach volunteer teach the student objectives? • Did the CEN Outreach program reach the goals of the teacher? • Did the CEN Outreach program reach it’s own goals/objectives? Resources: • http://www.biology-online.org/dictionary/Homeostasis NGSS Description: MS-LS1-1 Conduct an invest ...
Application of MEMS in Optobionics: Artificial Silicon Retina
... EPIRETINAL AND SUBRETINAL MICROIMPLANT: PROS AND CONS As illustrated in this research both approaches, epiretinal and subretinal, have advantages and disadvantages. The epiretinal design, for example, does not rely on the presence of intact neurons for signal processing when imposing spike patterns ...
... EPIRETINAL AND SUBRETINAL MICROIMPLANT: PROS AND CONS As illustrated in this research both approaches, epiretinal and subretinal, have advantages and disadvantages. The epiretinal design, for example, does not rely on the presence of intact neurons for signal processing when imposing spike patterns ...
The Somatic Senses - Appoquinimink High School
... feeling to seem to come from the stimulated receptors. This is at the same time the sensation forms. Basically the brain projects the sensation back to its apparent source. This allows to pinpoint the region of stimulation. ...
... feeling to seem to come from the stimulated receptors. This is at the same time the sensation forms. Basically the brain projects the sensation back to its apparent source. This allows to pinpoint the region of stimulation. ...
Computational Models of Neural Auditory Processing
... when they impinge upon your ears. There are many layers of acoustic, mechanical, electrochemical, and neural processes that can be examined and modeled from the front in, or as bottom-up, data-driven algorithms. As each layer is modeled by an algorithm, experimented with, and compared with what is k ...
... when they impinge upon your ears. There are many layers of acoustic, mechanical, electrochemical, and neural processes that can be examined and modeled from the front in, or as bottom-up, data-driven algorithms. As each layer is modeled by an algorithm, experimented with, and compared with what is k ...
PDF
... network behaviour. Pyramidal neurons, the most widespread excitatory neuron of the neocortex have multiple spike initiation zones, which interact via dendritic and somatic spikes actively propagating in all directions within the dendritic tree. For these neurons, therefore, both the location and tim ...
... network behaviour. Pyramidal neurons, the most widespread excitatory neuron of the neocortex have multiple spike initiation zones, which interact via dendritic and somatic spikes actively propagating in all directions within the dendritic tree. For these neurons, therefore, both the location and tim ...
a study of axonal protein trafficking in neuronal networks via the
... express fluorescent proteins in neurons. Preliminary results show that the neurons can be polarized with their soma and axons being compartmentalized into different fluidically isolated microenvironments. When chemical stimulation was applied to axonal chamber, anterograde migration of expressed flu ...
... express fluorescent proteins in neurons. Preliminary results show that the neurons can be polarized with their soma and axons being compartmentalized into different fluidically isolated microenvironments. When chemical stimulation was applied to axonal chamber, anterograde migration of expressed flu ...
The Nervous System
... Functions of the major parts of the eye: Sclera or Scleroid Layer – (white of eye) a tough protective layer of connective tissue that helps maintain the shape of the eye and provides an attachment for the muscles that move the eye Cornea - the clear, dome-shaped part of the sclera covering the front ...
... Functions of the major parts of the eye: Sclera or Scleroid Layer – (white of eye) a tough protective layer of connective tissue that helps maintain the shape of the eye and provides an attachment for the muscles that move the eye Cornea - the clear, dome-shaped part of the sclera covering the front ...
Electrical Synapses between Dopaminergic Neurons of the
... an intercellular communication. Recent studies report the expression of connexins (Cx) in DA neurons in juvenile rats (Leung et al., 2002) but also an absence of dye coupling in these cells (Lin et al., 2003). Thus, gap junctional communication between DA neurons remains to be clarified. Furthermore ...
... an intercellular communication. Recent studies report the expression of connexins (Cx) in DA neurons in juvenile rats (Leung et al., 2002) but also an absence of dye coupling in these cells (Lin et al., 2003). Thus, gap junctional communication between DA neurons remains to be clarified. Furthermore ...
Dissociation of Mnemonic Coding and Other Functional Neuronal
... its hands and legs and to put pieces of food into its mouth, after which also chewing and licking could be observed. If the neuron responded to more than one type of sensory stimulation it was classified as polysensory. If the neuron did not respond to any of the afore mentioned stimuli it was class ...
... its hands and legs and to put pieces of food into its mouth, after which also chewing and licking could be observed. If the neuron responded to more than one type of sensory stimulation it was classified as polysensory. If the neuron did not respond to any of the afore mentioned stimuli it was class ...
Transcript
... wonderful classical history of the idea of regional localization. That history is evident at very early embryonic stages. So on the left-hand side here we're looking at an embryo perhaps at an early stage of neural development and what this small group of cells has to transform itself into is the br ...
... wonderful classical history of the idea of regional localization. That history is evident at very early embryonic stages. So on the left-hand side here we're looking at an embryo perhaps at an early stage of neural development and what this small group of cells has to transform itself into is the br ...
Chapter 15 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Visceral Reflex to High BP • High blood pressure detected by arterial stretch receptors (1), afferent neuron (2) carries signal to CNS, efferent (3) signals travel to the heart (4), heart slows reducing BP ...
... Visceral Reflex to High BP • High blood pressure detected by arterial stretch receptors (1), afferent neuron (2) carries signal to CNS, efferent (3) signals travel to the heart (4), heart slows reducing BP ...
Synaptic receptors, neurotransmitters and brain modulators
... involuntary. (However, breathing, for example, can be in part consciously controlled.) ...
... involuntary. (However, breathing, for example, can be in part consciously controlled.) ...
nervous system
... activities necessary to life by allowing us to receive stimuli (sensory information) from various sensory receptors and then processing them into appropriate responses made by body organs (effectors). ...
... activities necessary to life by allowing us to receive stimuli (sensory information) from various sensory receptors and then processing them into appropriate responses made by body organs (effectors). ...