Cooperation and biased competition model can explain attentional
... neurons that are selective for the target object. The origin of this signal is not explicitly modelled, but it might originate from a workingmemory module that encodes and memorizes context in terms of rules. The second top±down signal, the attention bias, facilitates neurons that have the cued loca ...
... neurons that are selective for the target object. The origin of this signal is not explicitly modelled, but it might originate from a workingmemory module that encodes and memorizes context in terms of rules. The second top±down signal, the attention bias, facilitates neurons that have the cued loca ...
Fifty years of CPGs: two neuroethological papers that shaped BEHAVIORAL NEUROSCIENCE
... M. Hughes, visiting from Cambridge, found that the deafferented crayfish abdominal nerve cord sometimes continued to produce coordinated bursts of spikes in motor axons that innervated different swimmerets (Hughes and Wiersma, 1960), a motor pattern that drives coordinated swimmeret beating during n ...
... M. Hughes, visiting from Cambridge, found that the deafferented crayfish abdominal nerve cord sometimes continued to produce coordinated bursts of spikes in motor axons that innervated different swimmerets (Hughes and Wiersma, 1960), a motor pattern that drives coordinated swimmeret beating during n ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... All sensory information reaching the neocortex is conveyed through a sub-cortical (below the cortex) structure called the thalamus. Other signals, thought to be primarily ‘control’ signals that modulate cortical activity, also come into the neocortex from approximately 20 sub-cortical regions of the ...
... All sensory information reaching the neocortex is conveyed through a sub-cortical (below the cortex) structure called the thalamus. Other signals, thought to be primarily ‘control’ signals that modulate cortical activity, also come into the neocortex from approximately 20 sub-cortical regions of the ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... All sensory information reaching the neocortex is conveyed through a sub-cortical (below the cortex) structure called the thalamus. Other signals, thought to be primarily ‘control’ signals that modulate cortical activity, also come into the neocortex from approximately 20 sub-cortical regions of the ...
... All sensory information reaching the neocortex is conveyed through a sub-cortical (below the cortex) structure called the thalamus. Other signals, thought to be primarily ‘control’ signals that modulate cortical activity, also come into the neocortex from approximately 20 sub-cortical regions of the ...
emboj2008265-sup
... Supplementary Figure 7. Identity of cortactin bands labeled by the cortactin antibody. (A) Western analysis showing cortactin antibody specificity in 293 cells transfected with HA-cortactin-myc (+) and control cells (-). Endogenous cortactin is already expressed by this cell line (Ctn band). The co ...
... Supplementary Figure 7. Identity of cortactin bands labeled by the cortactin antibody. (A) Western analysis showing cortactin antibody specificity in 293 cells transfected with HA-cortactin-myc (+) and control cells (-). Endogenous cortactin is already expressed by this cell line (Ctn band). The co ...
High-performance genetically targetable optical neural silencing by
... The ability to silence the activity of genetically specified neurons in a temporally precise fashion would open up the ability to investigate the causal role of specific cell classes in neural computations, behaviors, and pathologies. Here we show that members of the class of light-driven outward pr ...
... The ability to silence the activity of genetically specified neurons in a temporally precise fashion would open up the ability to investigate the causal role of specific cell classes in neural computations, behaviors, and pathologies. Here we show that members of the class of light-driven outward pr ...
2.1 Resonding for change
... 1. Your ........ system carries fast....... impulses. Changes in the .............. are picked up by your................ 2. Complete: Receptor ___ CNS ___ Effector 3. Explain what happens in your nervous system when you see a piece of chocolate and eat it. ...
... 1. Your ........ system carries fast....... impulses. Changes in the .............. are picked up by your................ 2. Complete: Receptor ___ CNS ___ Effector 3. Explain what happens in your nervous system when you see a piece of chocolate and eat it. ...
A soft-wired hypothalamus
... and can also be affected by other peripheral metabolic signals, such as include two distinct lateral hypothalamic orexigenic neuronal popughrelin, glucose, insulin and peptide YY, a putative satiety signal released lations producing either melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH)29 from the gastrointesti ...
... and can also be affected by other peripheral metabolic signals, such as include two distinct lateral hypothalamic orexigenic neuronal popughrelin, glucose, insulin and peptide YY, a putative satiety signal released lations producing either melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH)29 from the gastrointesti ...
Nucleus Accumbens Medium Spiny Neurons Target Non
... receptor-mediated IPSC (n ⫽ 24) (Fig. 3A), although electrical stimulation clearly evokes a frequency-dependent slow GABAB IPSC in VTA neurons (n ⫽ 5) (Fig. 3B). Although these data imply that the NAc input is exclusively mediated by GABAA receptors, one possible explanation for the lack of an obser ...
... receptor-mediated IPSC (n ⫽ 24) (Fig. 3A), although electrical stimulation clearly evokes a frequency-dependent slow GABAB IPSC in VTA neurons (n ⫽ 5) (Fig. 3B). Although these data imply that the NAc input is exclusively mediated by GABAA receptors, one possible explanation for the lack of an obser ...
Regulation of Action-Potential Firing in Spiny Neurons of the Rat
... biocytin. The threshold for action-potential firing was measured under three different conditions: 1) electrical stimulation of the contralateral cerebral cortex, 2) brief directly applied current pulses, and 3) spontaneous action-potentials occurring during spontaneous episodes of depolarization ( ...
... biocytin. The threshold for action-potential firing was measured under three different conditions: 1) electrical stimulation of the contralateral cerebral cortex, 2) brief directly applied current pulses, and 3) spontaneous action-potentials occurring during spontaneous episodes of depolarization ( ...
Synaptic inhibition is caused by:
... Which of the following is not true regarding a group of end bulbs which affect one post-synaptic site of another neuron: a. each causes a potential of 1mV b. they will be from endings of more than one axon c. only EPSP or IPSP types will be present d. both spatial and temporal methods will be utiliz ...
... Which of the following is not true regarding a group of end bulbs which affect one post-synaptic site of another neuron: a. each causes a potential of 1mV b. they will be from endings of more than one axon c. only EPSP or IPSP types will be present d. both spatial and temporal methods will be utiliz ...
Izabella Battonyai
... order to resolve the fine structural organization, and 5-HT immunoreactive innervation of the PC. Data have also been sporadic on the presence, distribution and cellular localization of ion channels, especially the K +channels in the snail CNS. To have a better insight in the distribution of K +chan ...
... order to resolve the fine structural organization, and 5-HT immunoreactive innervation of the PC. Data have also been sporadic on the presence, distribution and cellular localization of ion channels, especially the K +channels in the snail CNS. To have a better insight in the distribution of K +chan ...
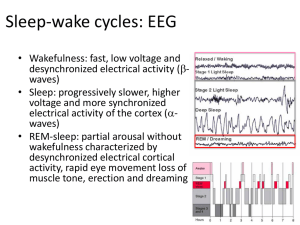
Modulation of Cortical Activation and Behavioral Arousal by
... and atonia on the EMG. Neurons that are active during waking (red symbols) include cells with ascending projections toward the cortex, which stimulate fast cortical activity, and cells with descending projections toward the spinal cord, which stimulate postural muscle tone and behavioral arousal. Th ...
... and atonia on the EMG. Neurons that are active during waking (red symbols) include cells with ascending projections toward the cortex, which stimulate fast cortical activity, and cells with descending projections toward the spinal cord, which stimulate postural muscle tone and behavioral arousal. Th ...
Lange Physiology > Section II
... As noted above, axons conduct impulses in either direction. However, conduction at synapses procedes in only one direction, ie, orthodromic, because the neurotransmitter at the synapse is in the presynaptic and not in the postsynaptic cell. The one-way gate at the synapses is necessary for orderly ...
... As noted above, axons conduct impulses in either direction. However, conduction at synapses procedes in only one direction, ie, orthodromic, because the neurotransmitter at the synapse is in the presynaptic and not in the postsynaptic cell. The one-way gate at the synapses is necessary for orderly ...
An Introduction to the ANS and Higher
... • If nerve is inactive under normal conditions, can only increase activity • If nerve maintains background level of activity, can increase or decrease activity • Autonomic motor neurons • Maintain resting level of spontaneous activity • Background level of activation determines autonomic tone • Sign ...
... • If nerve is inactive under normal conditions, can only increase activity • If nerve maintains background level of activity, can increase or decrease activity • Autonomic motor neurons • Maintain resting level of spontaneous activity • Background level of activation determines autonomic tone • Sign ...
Wiring optimization can relate neuronal structure and function
... solution predicts the position of most neurons along the anterior– posterior (AP) body axis of the nematode worm. This result suggests that wiring minimization is a good general description of the relationship between connectivity and neuron placement. A comparison of the cost-minimized layout with ...
... solution predicts the position of most neurons along the anterior– posterior (AP) body axis of the nematode worm. This result suggests that wiring minimization is a good general description of the relationship between connectivity and neuron placement. A comparison of the cost-minimized layout with ...
Transgenic Targeting of Recombinant Rabies Virus Reveals
... Generation of biological reagents. EnvA-pseudotyped lentivirus was produced as previously described (Wickersham et al., 2007a) but with the VSV glycoprotein expression vector replaced with the plasmid pCMMPEnvARGCD-IRES-EGFP (Wickersham et al., 2007b) encoding the EnvA envelope glycoprotein with the ...
... Generation of biological reagents. EnvA-pseudotyped lentivirus was produced as previously described (Wickersham et al., 2007a) but with the VSV glycoprotein expression vector replaced with the plasmid pCMMPEnvARGCD-IRES-EGFP (Wickersham et al., 2007b) encoding the EnvA envelope glycoprotein with the ...
Regulation of Action-Potential Firing in Spiny Neurons of the Rat
... biocytin. The threshold for action-potential firing was measured under three different conditions: 1) electrical stimulation of the contralateral cerebral cortex, 2) brief directly applied current pulses, and 3) spontaneous action-potentials occurring during spontaneous episodes of depolarization ( ...
... biocytin. The threshold for action-potential firing was measured under three different conditions: 1) electrical stimulation of the contralateral cerebral cortex, 2) brief directly applied current pulses, and 3) spontaneous action-potentials occurring during spontaneous episodes of depolarization ( ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... neurons. They travel somewhere between 2 (in nonmyelinated neurons) and 225 miles per hour (in myelinated neurons). Messages can travel from your toe to your brain in about 1/50 of a second. Neurons carry information in one direction only: From dendrites to cell body to axon to terminal buttons. Mes ...
... neurons. They travel somewhere between 2 (in nonmyelinated neurons) and 225 miles per hour (in myelinated neurons). Messages can travel from your toe to your brain in about 1/50 of a second. Neurons carry information in one direction only: From dendrites to cell body to axon to terminal buttons. Mes ...
Pre-Bötzinger complex

The pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC) is a cluster of interneurons in the ventrolateral medulla of the brainstem. This complex has been proven to be essential for the generation of respiratory rhythm in mammals. The exact mechanism of the rhythm generation and transmission to motor nuclei remains controversial and the topic of much present research.Several synthetic compounds have been shown to act on neurons specific to the preBötC, most being selective agonists or antagonists to receptor subtypes on neurons in the vicinity. Since many of these neurons express GABA, glutamate, serotonin and adenosine receptors, chemicals custom tailored to bind at these sites are most effective at altering respiratory rhythm.Adenosine modulates the preBötC output via activation of the A1 and A2A receptor subtypes. An adenosine A1 receptor agonist has been shown to depress preBötC rhythmogenesis independent of the neurotransmitters GABA and glycine in ""in vitro"" preparations from 0-7 day old mice. Another synthetic drug specific to the adenosine A2A receptor subtype is CGS-21680 that has been shown to cause apneas in 14-21 day old rat pups in vivo. For this reason, it has been used as a model to study pathological conditions such as apnea of prematurity and SIDS in neonatal infants.