Sub and Elimination
... There are three possible outcomes that you may encounter when working with these systems: 1.) one solution 2.) no solution 1.infinite solutions ...
... There are three possible outcomes that you may encounter when working with these systems: 1.) one solution 2.) no solution 1.infinite solutions ...
1st Semester Exam Algebra 2 Page 1 1. Solve 2. Write the standard
... 32. Which of the following is equivalent to x 3 ? 22. Graph: y = | x + 3| 33. Factor: 27x3 – 8 23. Graph: y = (x – 4)2 + 3 34. Factor: 9x2 – 42x + 49: 24. Graph : f(x) = x3 – 5x2 + 4x = 0 ...
... 32. Which of the following is equivalent to x 3 ? 22. Graph: y = | x + 3| 33. Factor: 27x3 – 8 23. Graph: y = (x – 4)2 + 3 34. Factor: 9x2 – 42x + 49: 24. Graph : f(x) = x3 – 5x2 + 4x = 0 ...
Topic 3: Solving two simultaneous linear equations
... Plot these two lines (see graph paper) The solution lies where these two lines intersect Solution is x = 2, y = 5 Simultaneous equations with no solution Sometimes when the straight lines corresponding to the two simultaneous equations are drawn, the lines are parallel so they do not intersect. This ...
... Plot these two lines (see graph paper) The solution lies where these two lines intersect Solution is x = 2, y = 5 Simultaneous equations with no solution Sometimes when the straight lines corresponding to the two simultaneous equations are drawn, the lines are parallel so they do not intersect. This ...
a Microsoft Word format document
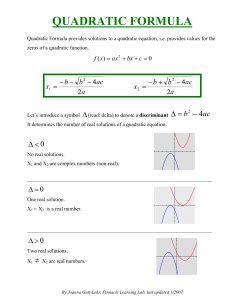
... Find the square root of a number, and make a reasonable interpretation of the displayed value for a given situation, using a calculator. Express the square root of a whole number less than 1,000 in simplest radical form. Solve quadratic equations algebraically by factoring, quadratic formula or by u ...
... Find the square root of a number, and make a reasonable interpretation of the displayed value for a given situation, using a calculator. Express the square root of a whole number less than 1,000 in simplest radical form. Solve quadratic equations algebraically by factoring, quadratic formula or by u ...