Solving Systems of Equations Algebraically LINEAR
... Example 6: Solve a problem involving a quadratic-quadratic system During a basketball game, Tom completes an “alley-oop”. From one side of the hoop, his teammate Ben lobs a perfect pass toward the basket. Tom jumps up, catches the ball and tips it into the basket. The path of the ball thrown by Ben ...
... Example 6: Solve a problem involving a quadratic-quadratic system During a basketball game, Tom completes an “alley-oop”. From one side of the hoop, his teammate Ben lobs a perfect pass toward the basket. Tom jumps up, catches the ball and tips it into the basket. The path of the ball thrown by Ben ...
f(x)
... Use the same methods as in solving equations, with the exception that if you multiply or divide both sides of the inequality by a negative number, it reverses the order of the inequality. ...
... Use the same methods as in solving equations, with the exception that if you multiply or divide both sides of the inequality by a negative number, it reverses the order of the inequality. ...
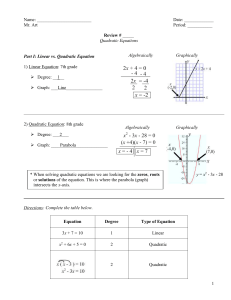
Algebra 1 Test 3 REVIEW
... Constant - a number that is not connected to a variable by multiplication or division. D Difference- subtraction Distributive Property- a(b + c) = ab + ac Domain - the set of all x values. Dependent – the range or y-value for a function. E Expression- something you simplify and does not have an equa ...
... Constant - a number that is not connected to a variable by multiplication or division. D Difference- subtraction Distributive Property- a(b + c) = ab + ac Domain - the set of all x values. Dependent – the range or y-value for a function. E Expression- something you simplify and does not have an equa ...
Section 1-1: Expressions & Formulas
... Solving absolute value equations • First, isolate the absolute value expression. • Set up two equations to solve. • For the first equation, drop the absolute value bars and solve the equation. • For the second equation, drop the bars, negate the opposite side, and solve the equation. • Always check ...
... Solving absolute value equations • First, isolate the absolute value expression. • Set up two equations to solve. • For the first equation, drop the absolute value bars and solve the equation. • For the second equation, drop the bars, negate the opposite side, and solve the equation. • Always check ...
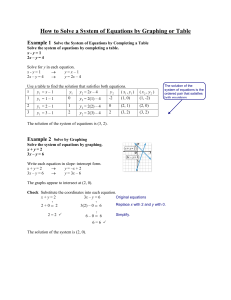
3-1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
... *A linear system in three variables is an equation in the form ax + by + cz = d where a, b, and c are not all zero. A solution of such a system is an ordered __________________ (x, y, z) whose coordinates make each equation true. The graph is a plane in three-dimensional space. See page 178 for exam ...
... *A linear system in three variables is an equation in the form ax + by + cz = d where a, b, and c are not all zero. A solution of such a system is an ordered __________________ (x, y, z) whose coordinates make each equation true. The graph is a plane in three-dimensional space. See page 178 for exam ...