parts of speech packet - Copley
... Indefinite pronouns: refer to persons or things not specifically named. Examples: all, any, anybody, both, each, everyone, everything, few, many, more, neither, nobody, none, no one, one, other, several, some, somebody, someone Ex: One piece of chicken is enough. *Intensive pronouns (pronouns ending ...
... Indefinite pronouns: refer to persons or things not specifically named. Examples: all, any, anybody, both, each, everyone, everything, few, many, more, neither, nobody, none, no one, one, other, several, some, somebody, someone Ex: One piece of chicken is enough. *Intensive pronouns (pronouns ending ...
Eliminating Wordiness
... Example: There are many reasons why I support her election to the School Board. Revision: I support her election to the School Board because she advocates lowering student/teacher ratios and enriching art and music programs. 3. Use active, not passive voice. Verbs are active or passive. In the activ ...
... Example: There are many reasons why I support her election to the School Board. Revision: I support her election to the School Board because she advocates lowering student/teacher ratios and enriching art and music programs. 3. Use active, not passive voice. Verbs are active or passive. In the activ ...
Action Verbs and Direct Objects
... subject of a sentences does, did, or will do. • The verb is the main word of a predicate. It can be action or being. • Many times a sentence with an action verb has a direct object – a word that receives the action. The word is often a noun. The direct object answers the question whom? or what? afte ...
... subject of a sentences does, did, or will do. • The verb is the main word of a predicate. It can be action or being. • Many times a sentence with an action verb has a direct object – a word that receives the action. The word is often a noun. The direct object answers the question whom? or what? afte ...
Blue Border - VirtueVigilance2010
... 1. Indicate location: Sharon is lying in her bed. 2. Indicating location in time: At midnight, Mai sneaked to kitchen and drank a cup of tea. ...
... 1. Indicate location: Sharon is lying in her bed. 2. Indicating location in time: At midnight, Mai sneaked to kitchen and drank a cup of tea. ...
Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... Noun: a person, place, thing, or idea Types of nouns: proper—capitalized; used to identify a particular person, place, or thing, such as “Nova Community College” and “Kleenex tissues.” concrete—has a physical presence, such as “table” and “chair.” abstract—an idea or concept with no physical p ...
... Noun: a person, place, thing, or idea Types of nouns: proper—capitalized; used to identify a particular person, place, or thing, such as “Nova Community College” and “Kleenex tissues.” concrete—has a physical presence, such as “table” and “chair.” abstract—an idea or concept with no physical p ...
Prepositions
... Object He stood in front of Safeway. Subject Verb Object The box is on top of the desk. Subject Verb Object The brown fox jumped over the fence. Subject Verb Object The dog was running over the bridge. Subject Verb Object ...
... Object He stood in front of Safeway. Subject Verb Object The box is on top of the desk. Subject Verb Object The brown fox jumped over the fence. Subject Verb Object The dog was running over the bridge. Subject Verb Object ...
Subject Verb agreement
... The news is on at six. Note: the word dollars is a special case. When talking about an amount of money, it requires a singular verb, but when referring to the dollars themselves, a plural verb is required. Five dollars is a lot of money. Dollars are often used instead of rubles in Russia. 8. Nouns s ...
... The news is on at six. Note: the word dollars is a special case. When talking about an amount of money, it requires a singular verb, but when referring to the dollars themselves, a plural verb is required. Five dollars is a lot of money. Dollars are often used instead of rubles in Russia. 8. Nouns s ...
Phrases and Clauses
... • Absolute -‐ consists of a noun or noun substitute followed by an adjective or participle. Although the phrase refers to the rest of the sentence, it is joined to the main clause by a comma, ...
... • Absolute -‐ consists of a noun or noun substitute followed by an adjective or participle. Although the phrase refers to the rest of the sentence, it is joined to the main clause by a comma, ...
Parts of Speech
... Noun: a person, place, thing, or idea Types of nouns: proper—capitalized; used to identify a particular person, place, or thing, such as “Nova Community College” and “Kleenex tissues.” concrete—has a physical presence, such as “table” and “chair.” abstract—an idea or concept with no physical p ...
... Noun: a person, place, thing, or idea Types of nouns: proper—capitalized; used to identify a particular person, place, or thing, such as “Nova Community College” and “Kleenex tissues.” concrete—has a physical presence, such as “table” and “chair.” abstract—an idea or concept with no physical p ...
Verbs - TeacherWeb
... They were moving slowly through the debris. Did they find Moe’s baseball cap? ...
... They were moving slowly through the debris. Did they find Moe’s baseball cap? ...
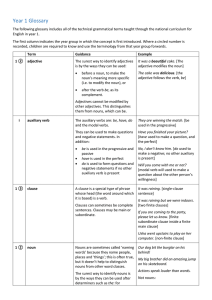
Year 1 Grammar glossary
... A clause is a special type of phrase whose head (the word around which it is based) is a verb. Clauses can sometimes be complete sentences. Clauses may be main or ...
... A clause is a special type of phrase whose head (the word around which it is based) is a verb. Clauses can sometimes be complete sentences. Clauses may be main or ...
How to determine the part of speech of a word
... 2. Other parts of speech The nice aspect of the other parts of speech is that they are closed-class words. This means, first, that there aren’t all that many of them. More important, they constitute a complete list, which cannot be added to (except by the long-term process of grammar change). So, if ...
... 2. Other parts of speech The nice aspect of the other parts of speech is that they are closed-class words. This means, first, that there aren’t all that many of them. More important, they constitute a complete list, which cannot be added to (except by the long-term process of grammar change). So, if ...
Principle 2: We can make our writing more vigorous and
... also’, the verb tends to agree with the subject nearest to it. Neither the lecturer nor the students want to reschedule the class. (want agrees with students). 7. ‘There is’ and ‘there are’ agree with the noun that follows. There is flexibility in this kind of management structure. There are many ad ...
... also’, the verb tends to agree with the subject nearest to it. Neither the lecturer nor the students want to reschedule the class. (want agrees with students). 7. ‘There is’ and ‘there are’ agree with the noun that follows. There is flexibility in this kind of management structure. There are many ad ...
Verb Errors
... change. They also don’t know how to make the right variation in verbs. But we can see there are some kinds of changes in it, such as the tense we should know how to use the regular or irregular verbs. But for the beginners, they will use one rule in any kinds of situations. But actually the verbs ha ...
... change. They also don’t know how to make the right variation in verbs. But we can see there are some kinds of changes in it, such as the tense we should know how to use the regular or irregular verbs. But for the beginners, they will use one rule in any kinds of situations. But actually the verbs ha ...
English Notes
... *Are words that can be substituted for nouns in naming people, places, and things. *Personal pronouns refer to people or animals: I, you, she, he, it, we, they, me, him, her, us, them *Possessive pronouns are personal pronouns used to show possession: my, mine, your(s), his, her(s), our(s), their(s) ...
... *Are words that can be substituted for nouns in naming people, places, and things. *Personal pronouns refer to people or animals: I, you, she, he, it, we, they, me, him, her, us, them *Possessive pronouns are personal pronouns used to show possession: my, mine, your(s), his, her(s), our(s), their(s) ...
Making Subjects and Verbs Agree
... The book or the pen is in the drawer. 3. When a compound subject contains both a singular and a plural noun or pronoun joined by or or nor, the verb should agree with the part of the subject that is nearer the verb. The boy or his friends run every day. His friends or the boy runs every day. 4. Does ...
... The book or the pen is in the drawer. 3. When a compound subject contains both a singular and a plural noun or pronoun joined by or or nor, the verb should agree with the part of the subject that is nearer the verb. The boy or his friends run every day. His friends or the boy runs every day. 4. Does ...
document
... and is used with most other verbs. Well as an adjective means "healthy." He pitches well. ...
... and is used with most other verbs. Well as an adjective means "healthy." He pitches well. ...
Year 2 Grammar Glossary
... A vowel letter is one that you make by just changing the shape of your open mouth. You don't use your teeth, tongue or lips. • The letters a, e, i, o and u are vowels. They can be spoken or written. • Letter y can also be used to represent a vowel sound. ...
... A vowel letter is one that you make by just changing the shape of your open mouth. You don't use your teeth, tongue or lips. • The letters a, e, i, o and u are vowels. They can be spoken or written. • Letter y can also be used to represent a vowel sound. ...
Noun Clauses - Montgomery College
... A noun clause is a dependent clause; it is a clause used as the Subject or the Object of a verb. As such, it plays the same role as a noun. Noun clauses are regularly introduced by pronouns such as whatever, whichever, who, whom, whoever, whomever, that, what , etc. You must be able to ask t ...
... A noun clause is a dependent clause; it is a clause used as the Subject or the Object of a verb. As such, it plays the same role as a noun. Noun clauses are regularly introduced by pronouns such as whatever, whichever, who, whom, whoever, whomever, that, what , etc. You must be able to ask t ...
Chapter 11 - EduVenture
... A prepositional phrase is introduced by a preposition and modifies a noun/pronoun or verb A participle phrase modifies a noun A gerund phrase acts as a noun An infinitive phrase can act as a noun or modify a noun or verb ...
... A prepositional phrase is introduced by a preposition and modifies a noun/pronoun or verb A participle phrase modifies a noun A gerund phrase acts as a noun An infinitive phrase can act as a noun or modify a noun or verb ...
VerbalsTo
... They are formed by taking “to” plus a verb To go, to run, to fly, to swim Infinitives are verbals that can be adjectives, ...
... They are formed by taking “to” plus a verb To go, to run, to fly, to swim Infinitives are verbals that can be adjectives, ...
Mrs. Ray*s TAG Language Arts Class
... That, which, who, whom, whose Indefinite pronouns refer to a person, place, thing, or idea that my not be specifically named. Examples: all, another, both, each, few, many, most, much, neither, nobody, other, several. ...
... That, which, who, whom, whose Indefinite pronouns refer to a person, place, thing, or idea that my not be specifically named. Examples: all, another, both, each, few, many, most, much, neither, nobody, other, several. ...