File - teacherver.com
... TIP: Turn the sentence into two sentences. The director rode with Jerry and I. The director rode with Jerry The director rode with me (not I). Belle and him are going to the company picnic. Belle is going to the company picnic. He (not him) is going to the company picnic. ...
... TIP: Turn the sentence into two sentences. The director rode with Jerry and I. The director rode with Jerry The director rode with me (not I). Belle and him are going to the company picnic. Belle is going to the company picnic. He (not him) is going to the company picnic. ...
Reading and Language Arts Study Guide
... Ex: These kites’ tails are made of place, thing, or animal rags. Plural Nouns name more than one Pronouns person, place, thing, or animal. A word that takes the place of a noun. *Add –s or –es to make most nouns plural. For nouns that end in a Singular/Plural consonant and y, change y to I and Singu ...
... Ex: These kites’ tails are made of place, thing, or animal rags. Plural Nouns name more than one Pronouns person, place, thing, or animal. A word that takes the place of a noun. *Add –s or –es to make most nouns plural. For nouns that end in a Singular/Plural consonant and y, change y to I and Singu ...
transitive and intransitive verbs
... He stopped to smell the flower. Or it can be [I], as in: The flower smelled nice. ...
... He stopped to smell the flower. Or it can be [I], as in: The flower smelled nice. ...
El presente progresivo - Hoffman Estates High School
... The present progressive tense is used to talk about actions taking place at a given time. The action has to be taking place at the time it is used in the sentence (Ahora-now). Equivalent to the English -ING It is formed by combining a form of the verb ESTAR with the present participle. ...
... The present progressive tense is used to talk about actions taking place at a given time. The action has to be taking place at the time it is used in the sentence (Ahora-now). Equivalent to the English -ING It is formed by combining a form of the verb ESTAR with the present participle. ...
study notes episode 26 urban archaeology
... beginning with a gerund (- To learn another language is important. ing form) or infinitive - singular 4. expressions of time, Three years is the length of the program. money, weight or Two thousand dollars is the fee required for measurement - singu ...
... beginning with a gerund (- To learn another language is important. ing form) or infinitive - singular 4. expressions of time, Three years is the length of the program. money, weight or Two thousand dollars is the fee required for measurement - singu ...
Morphology
... only suffix is (-ish) , meaning ( some what x ) e.g. greenish , smallish , remotish • By contrast, the prefix (un-)meaning not is extremely widely spread, e.g.:- unhappy, unsure, unreliable, undiscovered however ,this does not mean that (un-) can be prefixed to all adjectives quite freely . ...
... only suffix is (-ish) , meaning ( some what x ) e.g. greenish , smallish , remotish • By contrast, the prefix (un-)meaning not is extremely widely spread, e.g.:- unhappy, unsure, unreliable, undiscovered however ,this does not mean that (un-) can be prefixed to all adjectives quite freely . ...
Morphology
... only suffix is (-ish) , meaning ( some what x ) e.g. greenish , smallish , remotish • By contrast, the prefix (un-)meaning not is extremely widely spread, e.g.:- unhappy, unsure, unreliable, undiscovered however ,this does not mean that (un-) can be prefixed to all adjectives quite freely . ...
... only suffix is (-ish) , meaning ( some what x ) e.g. greenish , smallish , remotish • By contrast, the prefix (un-)meaning not is extremely widely spread, e.g.:- unhappy, unsure, unreliable, undiscovered however ,this does not mean that (un-) can be prefixed to all adjectives quite freely . ...
Verbs are usually defined as "action" words or "doing" words. The
... The plane arrived. The intransitive verb, arrived, takes no direct object. If we add modifiers to this arrived verb, these modifiers ARE NOT DIRECT OBJECTS: The plane from Los Angeles arrived LATER THAN USUAL. Later than usual modifies arrived, but it is NOT the object of arrived. To repeat: We have ...
... The plane arrived. The intransitive verb, arrived, takes no direct object. If we add modifiers to this arrived verb, these modifiers ARE NOT DIRECT OBJECTS: The plane from Los Angeles arrived LATER THAN USUAL. Later than usual modifies arrived, but it is NOT the object of arrived. To repeat: We have ...
The Preposition - Jessore Govt City College
... (a) Do you sleep on your back or your front?(b) The boy rode on the elephant’s back.(c) We were sitting in the back row.(d) He ran away through the back door.(e) We got seats at the back. (f) He came back home last night. (g) She stepped back to let her brother pass. (h) The barbed wire kept the pro ...
... (a) Do you sleep on your back or your front?(b) The boy rode on the elephant’s back.(c) We were sitting in the back row.(d) He ran away through the back door.(e) We got seats at the back. (f) He came back home last night. (g) She stepped back to let her brother pass. (h) The barbed wire kept the pro ...
Useful Grammatical Terms - VCC Library
... Independent clauses can stand alone as complete sentences. Dependent clauses are not complete sentences; they connect to an independent clause with a subordinating conjunction or a relative pronoun. Dependent clauses function as a noun, adjective or adverb in a sentence. Examples: She walks to work ...
... Independent clauses can stand alone as complete sentences. Dependent clauses are not complete sentences; they connect to an independent clause with a subordinating conjunction or a relative pronoun. Dependent clauses function as a noun, adjective or adverb in a sentence. Examples: She walks to work ...
parts of speech presentation
... action or a state of being. Verbs can be telling about something that happened in the past, is happening in the present, or will happen in the future. They can even be used to explain that one thing happened before another in the past (Past Perfect Tense) ...
... action or a state of being. Verbs can be telling about something that happened in the past, is happening in the present, or will happen in the future. They can even be used to explain that one thing happened before another in the past (Past Perfect Tense) ...
Non-action verbs
... o words that describe the verb are not verbs (usually, sometimes, never, seldom, always) o words that end in ly are not verbs (slowly, quickly, ...
... o words that describe the verb are not verbs (usually, sometimes, never, seldom, always) o words that end in ly are not verbs (slowly, quickly, ...
ELA Study Guide
... Plural Nouns- more than one person, place, or thing. Most of the time we just add –s or –es, but there are some exceptions! If it is an irregular plural noun, it may change altogether or stay the same. ...
... Plural Nouns- more than one person, place, or thing. Most of the time we just add –s or –es, but there are some exceptions! If it is an irregular plural noun, it may change altogether or stay the same. ...
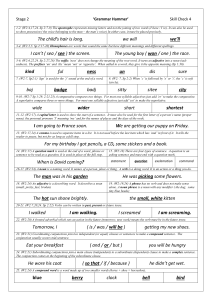
Stage 2 Check 4 – Answers
... 5-6. (W2:6,22,24. Sp 2:27,28) The suffix ‘ness’ does not change the meaning of the root word. It turns an adjective into a noun (sadsadness). The prefixes ‘un’ and ‘dis’ mean ‘not’ or ‘opposite’. When added to a word, they give it the opposite meaning (Sp 1:30). ...
... 5-6. (W2:6,22,24. Sp 2:27,28) The suffix ‘ness’ does not change the meaning of the root word. It turns an adjective into a noun (sadsadness). The prefixes ‘un’ and ‘dis’ mean ‘not’ or ‘opposite’. When added to a word, they give it the opposite meaning (Sp 1:30). ...
Document
... • Neither the cat nor the dogs likes the new food. • The mayor as well as his brothers are going to jail. • Nobody wants to dance. • The paper or the ruler are in the desk. ...
... • Neither the cat nor the dogs likes the new food. • The mayor as well as his brothers are going to jail. • Nobody wants to dance. • The paper or the ruler are in the desk. ...
HS4 – LOS USOS DIFERENTES DEL PRONOMBRE “SE” Perhaps
... occurrence. Many times it is used to remove the element of blame from the person who did the action so that (s)he does not have to claim responsibility. An indirect object pronoun will be used to refer to the person involved in the occurrence and the verb will match the subject (thing or things) inv ...
... occurrence. Many times it is used to remove the element of blame from the person who did the action so that (s)he does not have to claim responsibility. An indirect object pronoun will be used to refer to the person involved in the occurrence and the verb will match the subject (thing or things) inv ...
Sibusiso Nyembezi. lsichazimazwi Sanamuhla Nangomuso.
... some nouns undergo a structural change to perform a qualificative function, m,any Zulu nouns are inherently qualificative in nature. They do not co-occur with other nouns used qualificatively in the sentence. An intriguing question is whether or not these·"nouns" should be c1assified under the relat ...
... some nouns undergo a structural change to perform a qualificative function, m,any Zulu nouns are inherently qualificative in nature. They do not co-occur with other nouns used qualificatively in the sentence. An intriguing question is whether or not these·"nouns" should be c1assified under the relat ...
Parts of Speech - Ohio County Schools
... Words as Different Parts of Speech • The way a word is used in a sentence determines what part of speech it is. DIFFERENT USES OF A WORD As a noun: I purchased a FM radio. As a verb: In an emergency, radio for help. As an adjective: I will use a radio transmission. ...
... Words as Different Parts of Speech • The way a word is used in a sentence determines what part of speech it is. DIFFERENT USES OF A WORD As a noun: I purchased a FM radio. As a verb: In an emergency, radio for help. As an adjective: I will use a radio transmission. ...
Noun – names a person, place, thing, or idea.
... another, anybody, anyone, anything, each, either, everybody, everything, much, neither, nobody, no one, nothing, one, other, somebody, someone, something ...
... another, anybody, anyone, anything, each, either, everybody, everything, much, neither, nobody, no one, nothing, one, other, somebody, someone, something ...
Slide 1
... anybody, anything, anyone, each, either, everyone, everybody, everything, neither, nobody, no one, one, someone, something Plural all, both, few, most, none, some If none means “not one,” it is singular. ...
... anybody, anything, anyone, each, either, everyone, everybody, everything, neither, nobody, no one, one, someone, something Plural all, both, few, most, none, some If none means “not one,” it is singular. ...
Subject-Verb Agreement Identifying the Subject
... Identifying the Subject In all of the examples listed above, the subject noun is placed directly next to its verb, and so it is rather simple to determine which type of verb to use. However, in some sentences, the subject is separated from its verb by additional phrases or clauses. To find the subje ...
... Identifying the Subject In all of the examples listed above, the subject noun is placed directly next to its verb, and so it is rather simple to determine which type of verb to use. However, in some sentences, the subject is separated from its verb by additional phrases or clauses. To find the subje ...
Parts of Speech
... sentence – there will always be at least one word between a reflexive pronoun and its antecedent. – Ex. Luke Skywalker made himself a lightsaber. ...
... sentence – there will always be at least one word between a reflexive pronoun and its antecedent. – Ex. Luke Skywalker made himself a lightsaber. ...
Article
... The noun or pronoun that receives the action of the preceding verb. For Example: Please call him tomorrow. Call is the VERB, who or what is receiving the action of the VERB CALL. Ask the question who/what are you going to call? The answer is HIM and therefore it is the direct object. ...
... The noun or pronoun that receives the action of the preceding verb. For Example: Please call him tomorrow. Call is the VERB, who or what is receiving the action of the VERB CALL. Ask the question who/what are you going to call? The answer is HIM and therefore it is the direct object. ...