Lecture 7. Pronouns I
... whom must always be used when the interrogative pronoun follows the preposition (e.g. To whom did she give the letter?). ...
... whom must always be used when the interrogative pronoun follows the preposition (e.g. To whom did she give the letter?). ...
Lecture 7. Pronouns I
... whom must always be used when the interrogative pronoun follows the preposition (e.g. To whom did she give the letter?). ...
... whom must always be used when the interrogative pronoun follows the preposition (e.g. To whom did she give the letter?). ...
language objectives
... o Using prior knowledge o Setting purposes for reading o Interpreting author’s meaning o Confirming the author’s message o Making generalizations o Interpreting characters’ behaviors 10. Apply strategies to comprehend textual/informational and functional materials. o Using prior knowledge o Setting ...
... o Using prior knowledge o Setting purposes for reading o Interpreting author’s meaning o Confirming the author’s message o Making generalizations o Interpreting characters’ behaviors 10. Apply strategies to comprehend textual/informational and functional materials. o Using prior knowledge o Setting ...
Writing Strategy: Parts of Speech
... Quick Tip of the Week Did you know . . . As a college student I used to cringe when a Professor called on me to answer a question about the different parts of speech. Though it seemed like I should know this information, based on the fact that I was an English major, I only really knew the basics. I ...
... Quick Tip of the Week Did you know . . . As a college student I used to cringe when a Professor called on me to answer a question about the different parts of speech. Though it seemed like I should know this information, based on the fact that I was an English major, I only really knew the basics. I ...
Summer Reading Literary Terms
... 33. Fable--a short story with a moral, especially one in which the characters are animals; a false or improbable account of something 34. Lyric--the words of a song, especially a popular song; singing with a voice that has a light quality and a vocally undramatic delivery 35. Antecedent—the noun or ...
... 33. Fable--a short story with a moral, especially one in which the characters are animals; a false or improbable account of something 34. Lyric--the words of a song, especially a popular song; singing with a voice that has a light quality and a vocally undramatic delivery 35. Antecedent—the noun or ...
Noun, Adjective, and Adverb Clauses
... Arctic winters, which are long and cold, are severe. The arctic is a region where life is difficult. She likes the guy who sits in front of her. ...
... Arctic winters, which are long and cold, are severe. The arctic is a region where life is difficult. She likes the guy who sits in front of her. ...
many students work on the star our school newspaper
... subject describes who or what the sentence is about. It can be made of one or several words. The subject is always a noun Person ...
... subject describes who or what the sentence is about. It can be made of one or several words. The subject is always a noun Person ...
Spanish 1A
... Example: Tengo pelo negro y largo. Tengo ojos cafés. María tiene pelo negro y largo. María tiene ojos cafés. 2. To describe someone’s personality and physical appearance use ‘ser’ (to be) but you also need to conjugate. Use ‘soy’ to talk about yourself and ‘es’ to talk about someone else. Example: S ...
... Example: Tengo pelo negro y largo. Tengo ojos cafés. María tiene pelo negro y largo. María tiene ojos cafés. 2. To describe someone’s personality and physical appearance use ‘ser’ (to be) but you also need to conjugate. Use ‘soy’ to talk about yourself and ‘es’ to talk about someone else. Example: S ...
Neuter dobré dobré
... Animate and Inanimate), and then by their ending in the Nominative -- hard or soft. So a given word might be a “hard masculine noun or “soft feminine adjective” etc. These categories are represented by chosen words called paradigms. How to tell the Gender: Nouns ending in -o and -í are Neuter. Nouns ...
... Animate and Inanimate), and then by their ending in the Nominative -- hard or soft. So a given word might be a “hard masculine noun or “soft feminine adjective” etc. These categories are represented by chosen words called paradigms. How to tell the Gender: Nouns ending in -o and -í are Neuter. Nouns ...
Examples - Cobb Learning
... • Tell me, as a class, what is the difference between a phrase and a clause. • 1, 2, 3…go! ...
... • Tell me, as a class, what is the difference between a phrase and a clause. • 1, 2, 3…go! ...
Lesson 1 (Word Document)
... A pronoun is in Englisc naman spellend, that is, “representing a noun”. The noun it represents depends on how you use it. The modern third person pronoun “he” can represent any single male except the speaker and the person spoken to. It’s unchanged from Englisc, but Englisc could use it for things a ...
... A pronoun is in Englisc naman spellend, that is, “representing a noun”. The noun it represents depends on how you use it. The modern third person pronoun “he” can represent any single male except the speaker and the person spoken to. It’s unchanged from Englisc, but Englisc could use it for things a ...
Lecture 7. Pronouns I
... whom must always be used when the interrogative pronoun follows the preposition (e.g. To whom did she give the letter?). ...
... whom must always be used when the interrogative pronoun follows the preposition (e.g. To whom did she give the letter?). ...
Name: Facilitator: Date: School: 6.08 Simple Sentence Patterns The
... Nominative Case: subjects and predicate nouns Objective Case: direct object, indirect object, and object of preposition ...
... Nominative Case: subjects and predicate nouns Objective Case: direct object, indirect object, and object of preposition ...
An appositive is a noun or pronoun
... An appositive is a noun or pronoun — often with modifiers — set beside another noun or pronoun to explain or identify it. Here are some examples of appositives (the noun or pronoun will be in blue, the appositive will be in red). ...
... An appositive is a noun or pronoun — often with modifiers — set beside another noun or pronoun to explain or identify it. Here are some examples of appositives (the noun or pronoun will be in blue, the appositive will be in red). ...
Notes-Gerunds and Infinitives Key
... When a noun looks like a verb with the word “to” in front of it, it is called a infinitive. To + the base form of a verb. For example: ...
... When a noun looks like a verb with the word “to” in front of it, it is called a infinitive. To + the base form of a verb. For example: ...
2016 - ielanguages.com
... Nouns and Gender All nouns have a gender in Dutch, either common (de words) or neuter (het words). It is hard to guess which gender a noun is, so it is best to memorize the genders when memorizing vocabulary. However, two-thirds of Dutch words are common gender (because the common gender has combine ...
... Nouns and Gender All nouns have a gender in Dutch, either common (de words) or neuter (het words). It is hard to guess which gender a noun is, so it is best to memorize the genders when memorizing vocabulary. However, two-thirds of Dutch words are common gender (because the common gender has combine ...
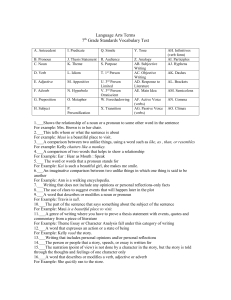
Language Arts Terms
... 3.___A comparison between two unlike things, using a word such as like, as , than, or resembles For example: Kelly chatters like a monkey. 4.___A comparison of two words that helps to show a relationship For Example: Ear : Hear as Mouth : Speak 5.___ The word or words that a pronoun stands for For E ...
... 3.___A comparison between two unlike things, using a word such as like, as , than, or resembles For example: Kelly chatters like a monkey. 4.___A comparison of two words that helps to show a relationship For Example: Ear : Hear as Mouth : Speak 5.___ The word or words that a pronoun stands for For E ...
Introduction to Linguistics and its role in Natural Language Processing
... Semantics: the study of the meaning of language. Can be decomposed into: Lexical semantics: the study of meaning of individual words Global semantics: how the meaning of individual words are combined into meaning of sentences (or more). One approach to lexical semantics is to study how word meanings ...
... Semantics: the study of the meaning of language. Can be decomposed into: Lexical semantics: the study of meaning of individual words Global semantics: how the meaning of individual words are combined into meaning of sentences (or more). One approach to lexical semantics is to study how word meanings ...
Elements of Poetry
... identify, explain, or supplement its meaning. Appositives may be restrictive-(set off by commas) or nonrestrictive. Auxiliary- a form of be, have or do (or a modal, such as will, should) used with a verb. They regularly indicate tense but may also indicate voice, mood, person, or number. Case-the fo ...
... identify, explain, or supplement its meaning. Appositives may be restrictive-(set off by commas) or nonrestrictive. Auxiliary- a form of be, have or do (or a modal, such as will, should) used with a verb. They regularly indicate tense but may also indicate voice, mood, person, or number. Case-the fo ...
Editing your writing for grammar mistakes
... and a balance sheet as at 30/6/96 for three separate accounting systems. The singular article “a” can only be followed by the singular form of a countable noun. Countable nouns must be in the plural form if they are referring to more than one. ...
... and a balance sheet as at 30/6/96 for three separate accounting systems. The singular article “a” can only be followed by the singular form of a countable noun. Countable nouns must be in the plural form if they are referring to more than one. ...
AQA Subject terminology mat
... make the meaning of a verb, adjective, or other adverb stronger or weaker, and often appear between the subject and its verb (She nearly lost everything.) Pronoun - used in place of a noun that has already been mentioned, often to avoid repeating the noun. For example: Laura left early because she w ...
... make the meaning of a verb, adjective, or other adverb stronger or weaker, and often appear between the subject and its verb (She nearly lost everything.) Pronoun - used in place of a noun that has already been mentioned, often to avoid repeating the noun. For example: Laura left early because she w ...
Fixing your grammar errors
... Object = The noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that receives or is affected by the action of a verb Most often, the basic sentence order in English is subjectverb-object (SVO). Adding on parts of speech to the basic sentence creates ...
... Object = The noun, pronoun, or noun phrase that receives or is affected by the action of a verb Most often, the basic sentence order in English is subjectverb-object (SVO). Adding on parts of speech to the basic sentence creates ...
verbal phrases - Montville.net
... • The past participle is formed by adding –d or –ed to the verb. • For example: walk – walked, smile – smiled, and ring – rung. Examples: The tired artist did not complete the painting. - tired is the past participle modifying artist ...
... • The past participle is formed by adding –d or –ed to the verb. • For example: walk – walked, smile – smiled, and ring – rung. Examples: The tired artist did not complete the painting. - tired is the past participle modifying artist ...
Grammar Guide - Dundee and Angus College
... I and me If you are having difficulty deciding whether to use I or me in your sentence, rewrite it without mentioning the other person to see if I or me sounds correct. Sam and I are going to the new restaurant for lunch tomorrow I am going to the restaurant for lunch tomorrow. Me going to the ne ...
... I and me If you are having difficulty deciding whether to use I or me in your sentence, rewrite it without mentioning the other person to see if I or me sounds correct. Sam and I are going to the new restaurant for lunch tomorrow I am going to the restaurant for lunch tomorrow. Me going to the ne ...