The linguistic basis of a mechanical thesaurus
... A Mechanical Thesaurus whatever the source language, since it is accounting for features that are quite independent of the latter. It is quite clear what this means for the grammar: a formal grammatical analysis which covers the description of the relations between grammar and context to the extent ...
... A Mechanical Thesaurus whatever the source language, since it is accounting for features that are quite independent of the latter. It is quite clear what this means for the grammar: a formal grammatical analysis which covers the description of the relations between grammar and context to the extent ...
Semantic Parsing Based on FrameNet
... for each evaluated frame as well as to (ii) assign a label to it. Both cases can be cast as two different classifications: (1) a classification of the role when its boundaries are known and (2) a classification of the sentence words as either belonging to a role or not1 . ...
... for each evaluated frame as well as to (ii) assign a label to it. Both cases can be cast as two different classifications: (1) a classification of the role when its boundaries are known and (2) a classification of the sentence words as either belonging to a role or not1 . ...
Semantic Parsing Based on FrameNet
... for each evaluated frame as well as to (ii) assign a label to it. Both cases can be cast as two different classifications: (1) a classification of the role when its boundaries are known and (2) a classification of the sentence words as either belonging to a role or not1 . ...
... for each evaluated frame as well as to (ii) assign a label to it. Both cases can be cast as two different classifications: (1) a classification of the role when its boundaries are known and (2) a classification of the sentence words as either belonging to a role or not1 . ...
What is Word Stress?
... two words. Two stresses cannot be one word. It is true that there can be a "secondary" stress in some words. But a secondary stress is much smaller than the main [primary] stress, and is only used in long words.) 2. We can only stress vowels, not consonants. Here are some more, rather complicated, r ...
... two words. Two stresses cannot be one word. It is true that there can be a "secondary" stress in some words. But a secondary stress is much smaller than the main [primary] stress, and is only used in long words.) 2. We can only stress vowels, not consonants. Here are some more, rather complicated, r ...
Sentence Vocabulary Definitions Apostrophe Adjective Adverb
... A word that names a person, animal, place, or thing. ...
... A word that names a person, animal, place, or thing. ...
INF5820 Distributional Semantics
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate’s body. In a human, the cerebral ...
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate’s body. In a human, the cerebral ...
Semantics and Pragmatics - School of Computer Science, University
... • Semantic compositionality is not defeated by lexical or syntactic ambiguity. You just get a different lexico-syntactic meaning for each selection of lexical meanings for the words and syntactic structure for the whole unit. – But you don’t necessarily need to compute all the possibilities explicit ...
... • Semantic compositionality is not defeated by lexical or syntactic ambiguity. You just get a different lexico-syntactic meaning for each selection of lexical meanings for the words and syntactic structure for the whole unit. – But you don’t necessarily need to compute all the possibilities explicit ...
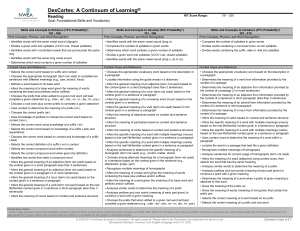
201 - 210
... • Identifies words that mean the opposite of a given word (prepositions) • Infers the meaning of an unknown word using context clues, then selects the word that is the opposite (sentence) ...
... • Identifies words that mean the opposite of a given word (prepositions) • Infers the meaning of an unknown word using context clues, then selects the word that is the opposite (sentence) ...
Dever-clever
... word-cluster, e.g. (to) teach, teacher, teaching. Besides the lexical meaning rootmorphemes possess all other types of meaning proper to morphemes except the part-ofspeech meaning which is not found in roots. Affixational morphemes include inflectional affixes or inflections and derivational affixes ...
... word-cluster, e.g. (to) teach, teacher, teaching. Besides the lexical meaning rootmorphemes possess all other types of meaning proper to morphemes except the part-ofspeech meaning which is not found in roots. Affixational morphemes include inflectional affixes or inflections and derivational affixes ...
Paraphrasing of Synonyms for a Fine
... Paraphrasing is used in many areas of Natural Language Processing – ontology linking, question answering, summarization, machine translation, etc. Paraphrasing between synonyms seems a relatively simple task, but in practice an automatic paraphrasing of synonyms might produce ungrammatical or unnatu ...
... Paraphrasing is used in many areas of Natural Language Processing – ontology linking, question answering, summarization, machine translation, etc. Paraphrasing between synonyms seems a relatively simple task, but in practice an automatic paraphrasing of synonyms might produce ungrammatical or unnatu ...
An auto-indexing method for Arabic text - acc-bc
... selected words are referred to as index words. Manual indexing of text documents is considered to be a cumbersome task in information retrieval. The people who perform indexing are usually well trained and have reasonable linguistic background. Manual indexing requires intensive human effort, since i ...
... selected words are referred to as index words. Manual indexing of text documents is considered to be a cumbersome task in information retrieval. The people who perform indexing are usually well trained and have reasonable linguistic background. Manual indexing requires intensive human effort, since i ...
Words with
... decoding unfamiliar words. New vocabulary words will be introduced each week. A Frayer Model for each word is due every Wednesday to check for completeness. Students should complete and study these words throughout the week in preparation of weekly vocabulary quiz. Words followed by an *(asterick) a ...
... decoding unfamiliar words. New vocabulary words will be introduced each week. A Frayer Model for each word is due every Wednesday to check for completeness. Students should complete and study these words throughout the week in preparation of weekly vocabulary quiz. Words followed by an *(asterick) a ...
1 Given a base word form, the task is to assign the appropriate
... How to tell? The easy case is when the word is modifying a noun. In general, these are adjectives if there is a corresponding adjective sense in WordNet. Such adjective senses exist for frightening and working. However, this is not the case for “clicking” and “playing”, so that in the following sent ...
... How to tell? The easy case is when the word is modifying a noun. In general, these are adjectives if there is a corresponding adjective sense in WordNet. Such adjective senses exist for frightening and working. However, this is not the case for “clicking” and “playing”, so that in the following sent ...
Lecture 2: What`s in a word? Morphological structure of the word 1
... distribution. Allomorphs also occur among prefixes. Their form may depend on the initial letters with which they will assimilate, e.g. in: im occurs before bilabials impossible; ir occurs before г - irregular; il occurs before 1 - illegal; in occurs before other consonants and vowels - inability, in ...
... distribution. Allomorphs also occur among prefixes. Their form may depend on the initial letters with which they will assimilate, e.g. in: im occurs before bilabials impossible; ir occurs before г - irregular; il occurs before 1 - illegal; in occurs before other consonants and vowels - inability, in ...
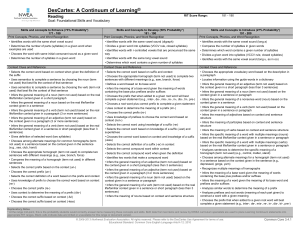
181 - 190
... * At the range mid-point, this is the probability students would correctly answer items measuring these concepts and skills. Both data from test items and review by NWEA curriculum specialists are used to place Learning Continuum statements into appropriate RIT ranges. Blank cells indicate data are ...
... * At the range mid-point, this is the probability students would correctly answer items measuring these concepts and skills. Both data from test items and review by NWEA curriculum specialists are used to place Learning Continuum statements into appropriate RIT ranges. Blank cells indicate data are ...
Document
... Module/Week 15 - Word Work 9 - Making an adjective stronger by adding -er or -est Comparative adjectives compare one thing or quality against or with another, e.g. ‘That boy is funnier than you.’ Superlative adjectives select the best, or worst, of more than two, e.g. ‘He is the funniest boy.’ Many ...
... Module/Week 15 - Word Work 9 - Making an adjective stronger by adding -er or -est Comparative adjectives compare one thing or quality against or with another, e.g. ‘That boy is funnier than you.’ Superlative adjectives select the best, or worst, of more than two, e.g. ‘He is the funniest boy.’ Many ...
Superhero Grammar Test - stmarys.brighton
... As he had, forgotten his cape, Superman borrowed one from his friend. As he had forgotten, his cape, Superman borrowed one from his friend. As he had forgotten his cape, Superman borrowed one from his friend. As he had forgotten his trainers Superman borrowed one, from his friend. ...
... As he had, forgotten his cape, Superman borrowed one from his friend. As he had forgotten, his cape, Superman borrowed one from his friend. As he had forgotten his cape, Superman borrowed one from his friend. As he had forgotten his trainers Superman borrowed one, from his friend. ...
Noisy-context surprisal as a human sentence - TedLab
... Richard Futrell & Roger Levy (MIT) [email protected] Models of human sentence processing difficulty can be broadly divided into two kinds, expectation-based and memory-based. Expectation-based models such as surprisal theory (Hale, 2001; Levy, 2008; Smith & Levy, 2013) have good coverage of many phen ...
... Richard Futrell & Roger Levy (MIT) [email protected] Models of human sentence processing difficulty can be broadly divided into two kinds, expectation-based and memory-based. Expectation-based models such as surprisal theory (Hale, 2001; Levy, 2008; Smith & Levy, 2013) have good coverage of many phen ...
this PDF file - Journal of Teaching English for Specific
... use. There are several possible explanations which, however, should not be considered competing but rather complementary. One explanation is the 'amount of knowledge' explanation which says that productive learning is considered more difficult because it requires extra learning of new spoken or writ ...
... use. There are several possible explanations which, however, should not be considered competing but rather complementary. One explanation is the 'amount of knowledge' explanation which says that productive learning is considered more difficult because it requires extra learning of new spoken or writ ...
BrainGene: computational creativity algorithm that invents novel
... Even drastically simplified representations of lexical and semantic knowledge are useful for applications in word games, query precisiation, medical applications, common sense. Brain processes analyzed at different levels are great inspiration! Fruitful approach: approximations to knowledge reps in ...
... Even drastically simplified representations of lexical and semantic knowledge are useful for applications in word games, query precisiation, medical applications, common sense. Brain processes analyzed at different levels are great inspiration! Fruitful approach: approximations to knowledge reps in ...
Processes of Word Formation
... fusing together elements from two other words and whose meaning shares or combines the meanings of the source words. The elements are normally the beginning of one and the end of the other. ...
... fusing together elements from two other words and whose meaning shares or combines the meanings of the source words. The elements are normally the beginning of one and the end of the other. ...
1 What is morphology? CHAPTER OUTLINE
... On the other hand, we sometimes use morphology even when we don’t need new lexemes. For example, we saw that each lexeme can have a number of word forms. The lexeme WALK has forms like walk, walks, walked, walking that can be used in different grammatical contexts. When we change the form of a word ...
... On the other hand, we sometimes use morphology even when we don’t need new lexemes. For example, we saw that each lexeme can have a number of word forms. The lexeme WALK has forms like walk, walks, walked, walking that can be used in different grammatical contexts. When we change the form of a word ...