Document
... • Change in potential is proportional to the intensity of the stimulation. • Stimulation + more stimulation before initial stimulation subsides is called summation. • Once the threshold is reached, an action potential occurs. ...
... • Change in potential is proportional to the intensity of the stimulation. • Stimulation + more stimulation before initial stimulation subsides is called summation. • Once the threshold is reached, an action potential occurs. ...
Neuron & Synapse Quiz
... (b) The outside of a neuron is more negatively charged than the inside. (c) The inside and outside of a neuron have the ...
... (b) The outside of a neuron is more negatively charged than the inside. (c) The inside and outside of a neuron have the ...
1. Cell body
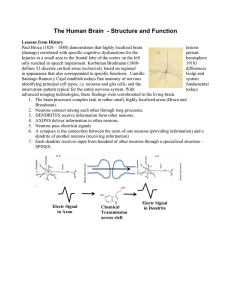
... 4. Neurotransmitters enter into the space between the 2 neurons, called the synaptic cleft. 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on dendrites of the next neuron thereby passing on the signal. ...
... 4. Neurotransmitters enter into the space between the 2 neurons, called the synaptic cleft. 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on dendrites of the next neuron thereby passing on the signal. ...
Anatomy of a Neuron
... In many ways, a neuron is like an electric wire. Although electric wires and neurons carry signals in different ways, their basic jobs are the same; to carry electricity. An electric wire in a radio, for example, may carry signals from a transistor to a speaker, where the signals are changed into so ...
... In many ways, a neuron is like an electric wire. Although electric wires and neurons carry signals in different ways, their basic jobs are the same; to carry electricity. An electric wire in a radio, for example, may carry signals from a transistor to a speaker, where the signals are changed into so ...
Drug and Alcohol Abuse
... • (1) Neurons release neurotransmitters from their axon terminals. • (2) The neurotransmitter can excite or inhibit the neighbor neuron – Excite: causes the neighbor neuron to release neurotransmitter to ...
... • (1) Neurons release neurotransmitters from their axon terminals. • (2) The neurotransmitter can excite or inhibit the neighbor neuron – Excite: causes the neighbor neuron to release neurotransmitter to ...
Chapter Outline
... Cessation & Modification of the Signal • Mechanisms to turn off stimulation – diffusion of neurotransmitter away from synapse into ECF where astrocytes return it to the neurons – synaptic knob reabsorbs amino acids and monoamines by endocytosis & breaks them down with monoamine oxidase – acetylcholi ...
... Cessation & Modification of the Signal • Mechanisms to turn off stimulation – diffusion of neurotransmitter away from synapse into ECF where astrocytes return it to the neurons – synaptic knob reabsorbs amino acids and monoamines by endocytosis & breaks them down with monoamine oxidase – acetylcholi ...
No Slide Title
... - Chemicals from other neurons - Chemicals from endocrine glands - Chemicals from outside sources (e.g., Drugs) ...
... - Chemicals from other neurons - Chemicals from endocrine glands - Chemicals from outside sources (e.g., Drugs) ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... of depolarization, an action potential occurs. VISUAL: Hold up Electrical wire—similarities to axon (insulation, send electrical impulse) and the main difference: no continuous signals/bursts of activity with periods to reset the chemicals involved Student activity—complete the map of the neuron by ...
... of depolarization, an action potential occurs. VISUAL: Hold up Electrical wire—similarities to axon (insulation, send electrical impulse) and the main difference: no continuous signals/bursts of activity with periods to reset the chemicals involved Student activity—complete the map of the neuron by ...
Nervous System Nervous System
... Biology Content Standards 4. Anatomy and Physiology Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to pe ...
... Biology Content Standards 4. Anatomy and Physiology Broad Concept: There is a relationship between the organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to pe ...
Review 3 ____ 1. The cells that provide structural support and
... 8. Bradley is deeply relaxed and his muscles are not moving at all. This suggests that, for Bradley's motor neurons a. sodium ions are concentrated inside the neurons and potassium ions are concentrated outside the neurons b. sodium ions and potassium ions are both concentrated inside the neurons c. ...
... 8. Bradley is deeply relaxed and his muscles are not moving at all. This suggests that, for Bradley's motor neurons a. sodium ions are concentrated inside the neurons and potassium ions are concentrated outside the neurons b. sodium ions and potassium ions are both concentrated inside the neurons c. ...
The Nervous System and Neurons
... 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they include? 4. Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. How is resting potential reached? 5. What is a ...
... 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they include? 4. Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. How is resting potential reached? 5. What is a ...
the nervous system
... Types of Neurons • Sensory neurons carry impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS • Have long dendrites • Motor neurons carry impulses from the CNS to an effector (muscle or gland) • Have long axons • Interneurons connect other neurons to the CNS ...
... Types of Neurons • Sensory neurons carry impulses from sensory receptors to the CNS • Have long dendrites • Motor neurons carry impulses from the CNS to an effector (muscle or gland) • Have long axons • Interneurons connect other neurons to the CNS ...
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal establish todays fine anatomy of nervous system identifying principal cell types, i.e. neurons and glia cells, and the fundamental innervation pattern typical for the entire nervous system. With toda ...
... in appearance that also corresponded to specific functions. Camillo Golgi and Santiago Ramon y Cajal establish todays fine anatomy of nervous system identifying principal cell types, i.e. neurons and glia cells, and the fundamental innervation pattern typical for the entire nervous system. With toda ...
Nerves and the brain
... The importance of the brain in the coordination of animal behaviour is highlighted when parts of it are damaged. The paralysis that follows a stroke, or the shaking movements of people with Parkinson’s disease, are signs of damage to the brain. In people with these conditions, muscular contractions ...
... The importance of the brain in the coordination of animal behaviour is highlighted when parts of it are damaged. The paralysis that follows a stroke, or the shaking movements of people with Parkinson’s disease, are signs of damage to the brain. In people with these conditions, muscular contractions ...
Nervous System Test Review
... Cerebrum Controls It regulates all your thoughts and actions. There are many sections of the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
... Cerebrum Controls It regulates all your thoughts and actions. There are many sections of the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
Nervous System - mr-youssef-mci
... Contains two main nerve types: 1. somatic nerves involved with voluntary movement senses / movement 2. autonomic nerves involved with involuntary movement sympathetic / parasympathetic systems ...
... Contains two main nerve types: 1. somatic nerves involved with voluntary movement senses / movement 2. autonomic nerves involved with involuntary movement sympathetic / parasympathetic systems ...
The Nervous System
... Also similar to muscle contraction, all action potentials on one neuron are the same strength. So a stronger stimulation doesn’t create a stronger action potential, it creates more action potentials. ...
... Also similar to muscle contraction, all action potentials on one neuron are the same strength. So a stronger stimulation doesn’t create a stronger action potential, it creates more action potentials. ...
The Nervous System
... • Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose ...
... • Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception • High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose ...
Document
... – Glia – structural support and insulation – Neurons – communication – Soma – cell body – Dendrites – receive – Axon – transmit away ...
... – Glia – structural support and insulation – Neurons – communication – Soma – cell body – Dendrites – receive – Axon – transmit away ...
No Slide Title
... • Neurons may have different thresholds of excitation but all obey the rule that once the threshold is reached, an action potential is triggered – this is called the ‘all-or-none rule’. • Following the action potential, the sodium gates remain closed for around 1ms and so further action potentials c ...
... • Neurons may have different thresholds of excitation but all obey the rule that once the threshold is reached, an action potential is triggered – this is called the ‘all-or-none rule’. • Following the action potential, the sodium gates remain closed for around 1ms and so further action potentials c ...
4/12 - bio.utexas.edu
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. Fig 46.1 ...
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. Fig 46.1 ...