Nervous System - North Mac Schools
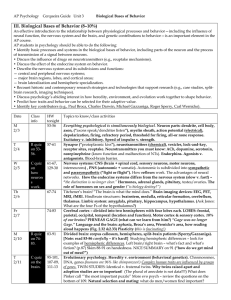
... • Synaptic end bulb- tips of axon terminal • contain synaptic vesicles that store neurotransmitters *Separated by synaptic cleft* • Postsynaptic cell-receives the message ...
... • Synaptic end bulb- tips of axon terminal • contain synaptic vesicles that store neurotransmitters *Separated by synaptic cleft* • Postsynaptic cell-receives the message ...
Unit 3 Cerqueira guide
... • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. • Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms). • Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on be ...
... • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. • Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms). • Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on be ...
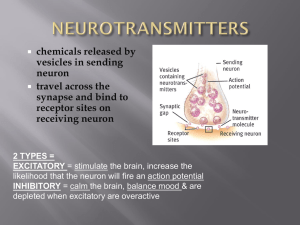
Neurotransmitters
... information enters the brain for processing. The spinal cord consists of the Brainstem which is involved in life sustaining functions. Damage to the brainstem is very often fatal. Other parts of the brainstem include the Medulla Oblongata, which controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, digesti ...
... information enters the brain for processing. The spinal cord consists of the Brainstem which is involved in life sustaining functions. Damage to the brainstem is very often fatal. Other parts of the brainstem include the Medulla Oblongata, which controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, digesti ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 43. What is the major difference between gray matter and white matter in the CNS? Gray matter—contains mostly unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies White matter—consists of dense collections of myelinated fibers (tracts) 44. The __corpus callosum_____ connects the two hemispheres of the brain. 45. The ...
... 43. What is the major difference between gray matter and white matter in the CNS? Gray matter—contains mostly unmyelinated fibers and cell bodies White matter—consists of dense collections of myelinated fibers (tracts) 44. The __corpus callosum_____ connects the two hemispheres of the brain. 45. The ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... neuron, receiving input from other neurons. Dendrites are covered with synapses. Each synapse has many receptors for neurotransmitters of various kinds. Dendritic spines – specialized dendrites that isolate reactions at some synapses. ...
... neuron, receiving input from other neurons. Dendrites are covered with synapses. Each synapse has many receptors for neurotransmitters of various kinds. Dendritic spines – specialized dendrites that isolate reactions at some synapses. ...
NEURONS
... EX- light, gravity, food, etc. *The ability to RESPOND to a stimulus is common to _______ living things !!! ...
... EX- light, gravity, food, etc. *The ability to RESPOND to a stimulus is common to _______ living things !!! ...
Halle Berry as a Computational Brain Abstraction
... The sparse collection or singular grandmother cells must respond to complex objects by connection to neurons at a lower level of abstraction, since sensory input to the visual system is in the form c ...
... The sparse collection or singular grandmother cells must respond to complex objects by connection to neurons at a lower level of abstraction, since sensory input to the visual system is in the form c ...
UNIT 3
... Refractory period During an absolute refractory period, another impulse cannot be generated at all no matter how large the stimulus. A relative refractory period can be triggered by a suprathreshold stimulus. Action potentials cannot be summed. Refractory periods limit the rate at which signals can ...
... Refractory period During an absolute refractory period, another impulse cannot be generated at all no matter how large the stimulus. A relative refractory period can be triggered by a suprathreshold stimulus. Action potentials cannot be summed. Refractory periods limit the rate at which signals can ...
Neuron Stations
... 3) Dendrites: take 2 short pipe cleaners (1/3 length) of the same color and push them through the "cell body" on the side opposite the axon. Dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons! Q4: What would ha ...
... 3) Dendrites: take 2 short pipe cleaners (1/3 length) of the same color and push them through the "cell body" on the side opposite the axon. Dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons! Q4: What would ha ...
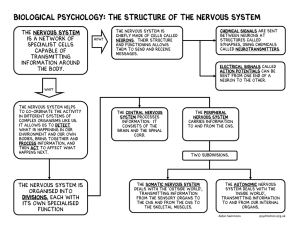
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
... capable of transmitting information around the body. ...
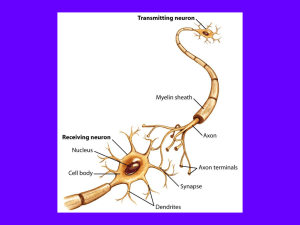
Nervous and Endocrine System
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
... Dendrites – receive the nerve impulse Nucleus – controls all activities of the cell Axon Terminals release neurotransmitters into the synapse Nerve impulses travel from the dendrite through the cell to the axon terminal (one direction only) Nerve impulses travel through the cell as electrica ...
Navigating The Nervous System
... perform thinking and memory functions. c. Sensory- Originates from a sensory organ such as the tongue, eyes, nose, ears, or skin, to the brain. ...
... perform thinking and memory functions. c. Sensory- Originates from a sensory organ such as the tongue, eyes, nose, ears, or skin, to the brain. ...
Document
... A. Conduction in an unmyelinated fiber. Na+ flows in depolarizing adjacent sections of membrane. Self propagating B. Saltatory conduction in myelinated fibers. Myelin insulates and blocks current across membrane Depolarization occurs at Nodes of Ranvier Current jumps from node to node Faster and mo ...
... A. Conduction in an unmyelinated fiber. Na+ flows in depolarizing adjacent sections of membrane. Self propagating B. Saltatory conduction in myelinated fibers. Myelin insulates and blocks current across membrane Depolarization occurs at Nodes of Ranvier Current jumps from node to node Faster and mo ...
Chapter 3
... Generation of an Action Potential • Action potential = sequence of rapidly occurring events that briefly reverse membrane potential due to rapid changes in membrane permeability – depolarization = membrane becomes less negative inside – repolarization = restoration of RMP (-70 mV) – threshold poten ...
... Generation of an Action Potential • Action potential = sequence of rapidly occurring events that briefly reverse membrane potential due to rapid changes in membrane permeability – depolarization = membrane becomes less negative inside – repolarization = restoration of RMP (-70 mV) – threshold poten ...
02biologya
... Neurotransmitters • Glial cells – Cells that help to make the brain more efficient by holding neurons together, removing waste products such as dead neurons, making the myelin coating for the axons, and performing other manufacturing, nourishing, and cleanup tasks – Synapse – The junction where the ...
... Neurotransmitters • Glial cells – Cells that help to make the brain more efficient by holding neurons together, removing waste products such as dead neurons, making the myelin coating for the axons, and performing other manufacturing, nourishing, and cleanup tasks – Synapse – The junction where the ...
Psych 11Nervous System Overview
... The sympathetic branch of the ANS prepares the body for "fight or flight". This involves several involuntary responses to a stressful situation such as increases in heart rate (effector is cardiac muscle) and respiratory rate, dilation of the pupils (effector is smooth muscle), shunting of blood a ...
... The sympathetic branch of the ANS prepares the body for "fight or flight". This involves several involuntary responses to a stressful situation such as increases in heart rate (effector is cardiac muscle) and respiratory rate, dilation of the pupils (effector is smooth muscle), shunting of blood a ...
ElectroEncephaloGram (EEG) - MIT Biology
... The aim of this session is to provide an introduction to the electroencephalogram and to explore the electrical activity of the brain. In this laboratory class you will record electroencephalograms from a volunteer, look at interfering signals, and examine the effects of visual activity on alpha wav ...
... The aim of this session is to provide an introduction to the electroencephalogram and to explore the electrical activity of the brain. In this laboratory class you will record electroencephalograms from a volunteer, look at interfering signals, and examine the effects of visual activity on alpha wav ...
EEG - mitbrain
... The aim of this session is to provide an introduction to the electroencephalogram and to explore the electrical activity of the brain. In this laboratory class you will record electroencephalograms from a volunteer, look at interfering signals, and examine the effects of visual activity on alpha wav ...
... The aim of this session is to provide an introduction to the electroencephalogram and to explore the electrical activity of the brain. In this laboratory class you will record electroencephalograms from a volunteer, look at interfering signals, and examine the effects of visual activity on alpha wav ...
Supplementary material 4 – Unified probability of spike
... spike variability values from our dataset. This was done to avoid needing to explicitly model the distribution of average spike variability values. Only biphasic spikes were included. In an actual recording, neurons within a brain region may have more similar biological characteristics than occurs b ...
... spike variability values from our dataset. This was done to avoid needing to explicitly model the distribution of average spike variability values. Only biphasic spikes were included. In an actual recording, neurons within a brain region may have more similar biological characteristics than occurs b ...
File
... 12. Sir Charles Sherrington observed that impulses took more time to travel a neural pathway than he might have anticipated. His observation provided evidence for the existence of: A) association areas. B) synaptic gaps. C) interneurons. D) neural networks. ...
... 12. Sir Charles Sherrington observed that impulses took more time to travel a neural pathway than he might have anticipated. His observation provided evidence for the existence of: A) association areas. B) synaptic gaps. C) interneurons. D) neural networks. ...
STRUCTURE OF NEURON AND NEUROGLIA NERVOUS SYSTEM
... STRUCTURE OF NEURON AND NEUROGLIA NERVOUS SYSTEM Has three overlapping functions – Sensory - receptors monitor changes (stimuli) and gathers information inside and outside the body – Integrative - prrocesses and interprets sensory input, makes decisions – Motor - dictates a response by activating ef ...
... STRUCTURE OF NEURON AND NEUROGLIA NERVOUS SYSTEM Has three overlapping functions – Sensory - receptors monitor changes (stimuli) and gathers information inside and outside the body – Integrative - prrocesses and interprets sensory input, makes decisions – Motor - dictates a response by activating ef ...
Nerve cord
... Allows animals to detect and process signals to react to them Stimulus: a signal that causes an animal to react Example: touch, sound, smells, tastes Response: an animal’s reaction to a stimulus ...
... Allows animals to detect and process signals to react to them Stimulus: a signal that causes an animal to react Example: touch, sound, smells, tastes Response: an animal’s reaction to a stimulus ...