Module 3 - socialscienceteacher
... – string-like bundles of axons and dendrites that come from the spinal cord and are held together by connective tissue – carry information from the senses, skin, muscles, and the body’s organs to and from the spinal cord – nerves in the peripheral nervous system have the ability to grow or reattach ...
... – string-like bundles of axons and dendrites that come from the spinal cord and are held together by connective tissue – carry information from the senses, skin, muscles, and the body’s organs to and from the spinal cord – nerves in the peripheral nervous system have the ability to grow or reattach ...
UNIT II: THE HUMAN BRAIN
... stores neurotransmitters. Do not actually touch any neighboring organs, muscles, or cells. ...
... stores neurotransmitters. Do not actually touch any neighboring organs, muscles, or cells. ...
Nervous System The nervous system is divided into two parts: 1
... Cerebral peduncles - carry fibers from the cerebrum through the midbrain. Metencephalon - expands to form the pons and the cerebellum Myelencephalon - forms the medulla oblongata ...
... Cerebral peduncles - carry fibers from the cerebrum through the midbrain. Metencephalon - expands to form the pons and the cerebellum Myelencephalon - forms the medulla oblongata ...
Neural Development - Peoria Public Schools
... • Nerve cells migrate to their final position with amoeba like movement a. Once in their final position, mature neurons do not normally move. ...
... • Nerve cells migrate to their final position with amoeba like movement a. Once in their final position, mature neurons do not normally move. ...
How Antidepressants Work - Rainsville Family Practice
... is caused by, or exacerbated by, a deficiency of seratonins. This may be related to genetic predisposition, chronic stress, or illness, certain medications, or by other factors we do not fully understand. In any event, the first neuron cannot secrete enough messengers to activate the receptor sites ...
... is caused by, or exacerbated by, a deficiency of seratonins. This may be related to genetic predisposition, chronic stress, or illness, certain medications, or by other factors we do not fully understand. In any event, the first neuron cannot secrete enough messengers to activate the receptor sites ...
Brain Anatomy
... friends of him. He died in 1861, thirtheen years after the accident, penniless and epileptic, and no autopsy was performed on his brain. ...
... friends of him. He died in 1861, thirtheen years after the accident, penniless and epileptic, and no autopsy was performed on his brain. ...
Brain Structures
... Most mammalian axons are myelinated. The myelin sheath is provided by oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. Myelin is insulating, preventing passage of ions over the membrane. ...
... Most mammalian axons are myelinated. The myelin sheath is provided by oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells. Myelin is insulating, preventing passage of ions over the membrane. ...
Chapter Outlines - Cengage Learning
... Linkages: Human Development and the Changing Brain Patterns of behavioral development in infants are correlated with plastic changes in activity and structure in the developing brain. During development, the brain overproduces neural connections and, based on experience, establishes which connection ...
... Linkages: Human Development and the Changing Brain Patterns of behavioral development in infants are correlated with plastic changes in activity and structure in the developing brain. During development, the brain overproduces neural connections and, based on experience, establishes which connection ...
Basic Neuroscience Series: Introduction and Series Overview
... • What this course will emphasize: • Overview of basic physiology, cell types, and signaling • Overview of multiple ways the above can fail, leading to ...
... • What this course will emphasize: • Overview of basic physiology, cell types, and signaling • Overview of multiple ways the above can fail, leading to ...
the limbic system
... in the left or the right visual field of a person which fixates a cross in the middle of a computer screen. {180ms is too brief to shift eyes} Due to the pattern of projections within the human visual system, stimuli shown on the right are represented in the left hemisphere and vice versa. If words ...
... in the left or the right visual field of a person which fixates a cross in the middle of a computer screen. {180ms is too brief to shift eyes} Due to the pattern of projections within the human visual system, stimuli shown on the right are represented in the left hemisphere and vice versa. If words ...
Invertebrate nervous systems:
... Seems like we could have energy stored in in the form of voltage differences (batteries) or concentration differences…. In fact cells have both kinds of energy storage mechanisms = electrochemical gradients How much--- what “direction”. ?? etc. For our questions about how neurons will generate time ...
... Seems like we could have energy stored in in the form of voltage differences (batteries) or concentration differences…. In fact cells have both kinds of energy storage mechanisms = electrochemical gradients How much--- what “direction”. ?? etc. For our questions about how neurons will generate time ...
Making Waves With Your Brain!!!!
... • They result from the total average electrical activity inside your brain • You cannot get a shock from them, they are very small voltages • The signals change in size at regular intervals between 1/10 and 60 times a second depending how active the brain is. ...
... • They result from the total average electrical activity inside your brain • You cannot get a shock from them, they are very small voltages • The signals change in size at regular intervals between 1/10 and 60 times a second depending how active the brain is. ...
the nervous system
... Describe the structural and functional organization of the nervous system into Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System (Afferent and Efferent Divisions). b. Describe the functional organization of the Efferent Division of the Peripheral Nervous System into Autonomic Nervous System and S ...
... Describe the structural and functional organization of the nervous system into Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System (Afferent and Efferent Divisions). b. Describe the functional organization of the Efferent Division of the Peripheral Nervous System into Autonomic Nervous System and S ...
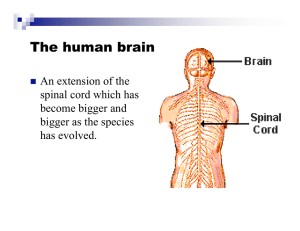
The human brain
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
... Defined the cerebral cortex into 52 distinct regions on the basis of their cytoarchitectonic characteristics. ...
The Nervous System
... Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episo ...
... Parkinson’s Disease – degeneration of nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine; leads to uncoordinated muscular movement Multiple Sclerosis – auto-immune disease; destruction of nerve cell insulation Alzheimer’s – mental deterioration usually associated with age Epilepsy – sudden episo ...
Chapter 5 Gases - LCMR School District
... their plasma membrane – their cytoplasm is more negatively charged than the interstitial fluid outside the cell • Negatively charged proteins and active transport of Na+ and K+ ions maintain voltage difference across a cell membrane, called the membrane potential • An unstimulated neuron has a resti ...
... their plasma membrane – their cytoplasm is more negatively charged than the interstitial fluid outside the cell • Negatively charged proteins and active transport of Na+ and K+ ions maintain voltage difference across a cell membrane, called the membrane potential • An unstimulated neuron has a resti ...
Chapter 5 Gases - Bethel Local Schools
... their plasma membrane – their cytoplasm is more negatively charged than the interstitial fluid outside the cell • Negatively charged proteins and active transport of Na+ and K+ ions maintain voltage difference across a cell membrane, called the membrane potential • An unstimulated neuron has a resti ...
... their plasma membrane – their cytoplasm is more negatively charged than the interstitial fluid outside the cell • Negatively charged proteins and active transport of Na+ and K+ ions maintain voltage difference across a cell membrane, called the membrane potential • An unstimulated neuron has a resti ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... b. Anionic proteins balance the cations inside the cell, while chloride ions mostly balance cations outside of the cell. c. Potassium ions (K+) play the most important role in generating a resting membrane potential, since the membrane is roughly 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. D. Membrane P ...
... b. Anionic proteins balance the cations inside the cell, while chloride ions mostly balance cations outside of the cell. c. Potassium ions (K+) play the most important role in generating a resting membrane potential, since the membrane is roughly 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. D. Membrane P ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... b. Anionic proteins balance the cations inside the cell, while chloride ions mostly balance cations outside of the cell. c. Potassium ions (K+) play the most important role in generating a resting membrane potential, since the membrane is roughly 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. D. Membrane P ...
... b. Anionic proteins balance the cations inside the cell, while chloride ions mostly balance cations outside of the cell. c. Potassium ions (K+) play the most important role in generating a resting membrane potential, since the membrane is roughly 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. D. Membrane P ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Module 4 – Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - division of the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the ______________________ muscles, organs, and glands sensory pathway nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS consisting of sensory neurons. ...
... Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - division of the PNS consisting of nerves that control all of the ______________________ muscles, organs, and glands sensory pathway nerves coming from the sensory organs to the CNS consisting of sensory neurons. ...
Student Guide Chapter 11
... b. Anionic proteins balance the cations inside the cell, while chloride ions mostly balance cations outside of the cell. c. Potassium ions (K+) play the most important role in generating a resting membrane potential, since the membrane is roughly 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. D. Membrane P ...
... b. Anionic proteins balance the cations inside the cell, while chloride ions mostly balance cations outside of the cell. c. Potassium ions (K+) play the most important role in generating a resting membrane potential, since the membrane is roughly 25 times more permeable to K+ than Na+. D. Membrane P ...
Neuron, Impulse Generation, and Reflex Arc
... Evidence on the mechanism of an impulse comes from measuring the electrochemical potential across the membrane of a neuronal axon. (the axomembrane) two electrodes required: one is inserted into the cell; the other is on the surface. ...
... Evidence on the mechanism of an impulse comes from measuring the electrochemical potential across the membrane of a neuronal axon. (the axomembrane) two electrodes required: one is inserted into the cell; the other is on the surface. ...
Lect5
... • Iion is ionic current • gion is ionic conductance • emfion is the electromotive force acting on an ion • emfion = Vm - Eion Total membrane potential ...
... • Iion is ionic current • gion is ionic conductance • emfion is the electromotive force acting on an ion • emfion = Vm - Eion Total membrane potential ...