File - Wk 1-2
... insensitive to a stimulus and depolarisation at this time. Repolarisation restores resting electrical conditions, the sodium-potassium pump restores ion distribution. It might appear that large amounts of Na⁺ and K⁺ are exchanged but in reality, it is only a small amount. The axonal membrane has tho ...
... insensitive to a stimulus and depolarisation at this time. Repolarisation restores resting electrical conditions, the sodium-potassium pump restores ion distribution. It might appear that large amounts of Na⁺ and K⁺ are exchanged but in reality, it is only a small amount. The axonal membrane has tho ...
THE NEURON
... The Moving Impulse A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus large enough to start a nerve impulse. The impulse travels quickly down the axon toward the axon terminals. ...
... The Moving Impulse A neuron remains in its resting state until it receives a stimulus large enough to start a nerve impulse. The impulse travels quickly down the axon toward the axon terminals. ...
Second exam study questions
... 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? Ho ...
... 4.What is the functional anatomy of an olfactory receptor cell? How many types of olfactory receptors are there? How is olfactory information carried to and within the brain? 5.What is the functional anatomy of a taste receptor cell? What are the types of taste receptors and what they respond to? Ho ...
In vitro and in vivo Microelectrode Array Recording Techniques
... electrode array which comprises 4225 recording sites (pitch 16 µm) interlaced with 1024 capacitive stimulation sites. The entire array is insulated by a thin, inert and biocompatible oxide layer. Continuous recording of all sensors over several minutes at a sampling rate of 25 kHz is demonstrated. E ...
... electrode array which comprises 4225 recording sites (pitch 16 µm) interlaced with 1024 capacitive stimulation sites. The entire array is insulated by a thin, inert and biocompatible oxide layer. Continuous recording of all sensors over several minutes at a sampling rate of 25 kHz is demonstrated. E ...
Chapter 3
... dopamine neutotransmitter and dopamine neurons in several brain areas. Antipsychotic drugs inhibit the effects of dopamine in the brain, reducing the over- reaction to it. • Depression, probably the most common psychological disturbance, appears to be related to 2 neurotransmitters: norepinephrine a ...
... dopamine neutotransmitter and dopamine neurons in several brain areas. Antipsychotic drugs inhibit the effects of dopamine in the brain, reducing the over- reaction to it. • Depression, probably the most common psychological disturbance, appears to be related to 2 neurotransmitters: norepinephrine a ...
Chapter 9
... 2. List the order of the connective tissue meninges that line the spinal cord. Are they also found around the brain? 3. In the adult does the spinal cord extend through all vertebrae? What is the conus medullaris and caudae equinae? 4. Describe the 2 roots that make up each spinal nerve. What types ...
... 2. List the order of the connective tissue meninges that line the spinal cord. Are they also found around the brain? 3. In the adult does the spinal cord extend through all vertebrae? What is the conus medullaris and caudae equinae? 4. Describe the 2 roots that make up each spinal nerve. What types ...
28.1_Responses
... Sequence What is the correct sequence of the following in response to a stimuli: interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, muscle Review What are two general ways in which nervous systems differ among animal groups Review Give an example of an animal with a very simple sensory system and an example ...
... Sequence What is the correct sequence of the following in response to a stimuli: interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, muscle Review What are two general ways in which nervous systems differ among animal groups Review Give an example of an animal with a very simple sensory system and an example ...
Orexin-A excites rat lateral vestibular nucleus neurons and improves
... lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle weakness without impairment of consciousness. However, most studies so far on th ...
... lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle weakness without impairment of consciousness. However, most studies so far on th ...
KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural
... Any neurotransmitter that does not bind to a receptor successfully, is absorbed back into the terminal button (axon terminal) by the presynaptic neuron in a process called reuptake. ...
... Any neurotransmitter that does not bind to a receptor successfully, is absorbed back into the terminal button (axon terminal) by the presynaptic neuron in a process called reuptake. ...
Instructions (PDF Document)
... Intracellular vs. Extracellular Neural recordings The electrical activity of a neuron can be recorded several different ways. Two common techniques are referred to as intracellular and extracellular recording. Intracellular recordings rely on a microelectrode (typically an ultra sharp glass pipette ...
... Intracellular vs. Extracellular Neural recordings The electrical activity of a neuron can be recorded several different ways. Two common techniques are referred to as intracellular and extracellular recording. Intracellular recordings rely on a microelectrode (typically an ultra sharp glass pipette ...
The Nervous System - Hastings High School
... How neurons work: 1. The neuron is normally at rest. At this point in time, the difference in charge between the outside and the inside of the cell is -70 mV. This difference exists because there are more positive ions outside the cell and fewer positively charged ions inside the cell. 2. Part of th ...
... How neurons work: 1. The neuron is normally at rest. At this point in time, the difference in charge between the outside and the inside of the cell is -70 mV. This difference exists because there are more positive ions outside the cell and fewer positively charged ions inside the cell. 2. Part of th ...
Nervous System
... nervous system regulates peripheral blood flow and sweat glands. Nerves control muscles connected to hair follicles. ...
... nervous system regulates peripheral blood flow and sweat glands. Nerves control muscles connected to hair follicles. ...
Section: Nervous system
... 7. Nerve cells specialized to receive and conduct electrical impulses are called _______________. 8. Electrical messages, called __________________--, may travel as fast as 150 m/s or as slow as 0.2 m/s. Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ___ ...
... 7. Nerve cells specialized to receive and conduct electrical impulses are called _______________. 8. Electrical messages, called __________________--, may travel as fast as 150 m/s or as slow as 0.2 m/s. Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ___ ...
31.1 Really Neurons
... Homework Name and describe the three types of neurons Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs. Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. Interneurons process the information from sensory neurons and send commands to other interneurons or motor ...
... Homework Name and describe the three types of neurons Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs. Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. Interneurons process the information from sensory neurons and send commands to other interneurons or motor ...
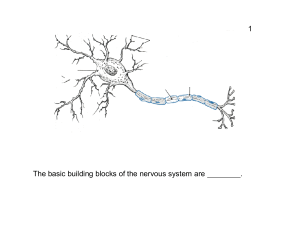
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... The peripheral nervous system is connect to your brain and your brainstem, which is also known as ...
... The peripheral nervous system is connect to your brain and your brainstem, which is also known as ...
Nervous System - wondersofscience
... B) Peripheral Nervous system • Connects different parts of the body to the central nervous system • Nerves are structures that help transmit information between the central nervous system and various regions of the body • There are two main types of nerves: ...
... B) Peripheral Nervous system • Connects different parts of the body to the central nervous system • Nerves are structures that help transmit information between the central nervous system and various regions of the body • There are two main types of nerves: ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... neuron travels to the spinal cord, enters the dorsal horn, and continues to ventral horn where it synapses onto a motor neuron. This synapse is excitatory and causes the motor neuron to fire action potentials that travel in the axon of that motor neuron back out to the quadriceps, causing it to cont ...
... neuron travels to the spinal cord, enters the dorsal horn, and continues to ventral horn where it synapses onto a motor neuron. This synapse is excitatory and causes the motor neuron to fire action potentials that travel in the axon of that motor neuron back out to the quadriceps, causing it to cont ...
Lesson 1
... whenever an electrical current is present there is an accompanying magnetic field, MEG detects neural activity too brief to be detected by PET or MRI. This technique has been used to locate seizure-producing regions in epileptic patients. C. PRONG--parallel recording of neural groups Electrodes that ...
... whenever an electrical current is present there is an accompanying magnetic field, MEG detects neural activity too brief to be detected by PET or MRI. This technique has been used to locate seizure-producing regions in epileptic patients. C. PRONG--parallel recording of neural groups Electrodes that ...
Lesson 1
... whenever an electrical current is present there is an accompanying magnetic field, MEG detects neural activity too brief to be detected by PET or MRI. This technique has been used to locate seizure-producing regions in epileptic patients. C. PRONG--parallel recording of neural groups Electrodes that ...
... whenever an electrical current is present there is an accompanying magnetic field, MEG detects neural activity too brief to be detected by PET or MRI. This technique has been used to locate seizure-producing regions in epileptic patients. C. PRONG--parallel recording of neural groups Electrodes that ...
Bad Fish
... If a cell starts at resting potential (-70mv), and then is stimulated: A. The membrane voltage will become < -70mV, because Na+ will move OUT of the cell B. The membrane voltage will become >-70mV, because Na+ will move OUT of the cell. C. The membrane voltage will become < -70mV because Na+ will m ...
... If a cell starts at resting potential (-70mv), and then is stimulated: A. The membrane voltage will become < -70mV, because Na+ will move OUT of the cell B. The membrane voltage will become >-70mV, because Na+ will move OUT of the cell. C. The membrane voltage will become < -70mV because Na+ will m ...
Biology of the Mind Neural and Hormonal Systems
... ▪ a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon ▪ generated by the movement of positively charged ions in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane ...
... ▪ a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon ▪ generated by the movement of positively charged ions in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane ...
p. A5 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... general phenomenon - seen in all types of effector cells: 1) skeletal muscle (muscle also atrophies) 2) smooth muscle (muscle does not atrophy!) 3) exocrine glands (except for sweat glands). 4) lower nervous system centers (after higher centers are destroyed) – hyperactivity is called "release phe ...
... general phenomenon - seen in all types of effector cells: 1) skeletal muscle (muscle also atrophies) 2) smooth muscle (muscle does not atrophy!) 3) exocrine glands (except for sweat glands). 4) lower nervous system centers (after higher centers are destroyed) – hyperactivity is called "release phe ...
Topic 5
... electrical synapses BIDIRECTIONAL. This difference means that neural circuits with electrical synapses can perform quite differently than those with chemical synapses. Typically the channel created by the grouping of proteins is called a connexon. However, as shown here, the term connexon can also b ...
... electrical synapses BIDIRECTIONAL. This difference means that neural circuits with electrical synapses can perform quite differently than those with chemical synapses. Typically the channel created by the grouping of proteins is called a connexon. However, as shown here, the term connexon can also b ...