The GPS toolkit - Fishburn Primary School
... If they answer the question: “What is it like?” - they are adjectives, and will be telling you more about a specific noun. Examples: Life is hard. (adjective) Kim works hard. (adverb) The train arrived early. (adverb) I took an early train. (adjective) ...
... If they answer the question: “What is it like?” - they are adjectives, and will be telling you more about a specific noun. Examples: Life is hard. (adjective) Kim works hard. (adverb) The train arrived early. (adverb) I took an early train. (adjective) ...
Grammar Study Sheet
... The pronouns I, he, she, we, and they are used as subjects of sentences. The pronouns me, him, her, us, and them are used after action verbs. The pronouns you and it can be used anywhere in a sentence. Kevin has cheese. He shares it. The pronoun he is the subject of the sentence. The pronoun it is ...
... The pronouns I, he, she, we, and they are used as subjects of sentences. The pronouns me, him, her, us, and them are used after action verbs. The pronouns you and it can be used anywhere in a sentence. Kevin has cheese. He shares it. The pronoun he is the subject of the sentence. The pronoun it is ...
Year 6 Grammar Glossary - Henry Cavendish Primary School
... table, person, car school of fish table, car, Janet anger, happiness, John kicked the ball. Sam and Emma (his oldest children) are coming to visit him next weekend. Margaret is generally happy – she sings in the mornings! - but responsibility weighs her down. Sarah is, I believe, our best student. ...
... table, person, car school of fish table, car, Janet anger, happiness, John kicked the ball. Sam and Emma (his oldest children) are coming to visit him next weekend. Margaret is generally happy – she sings in the mornings! - but responsibility weighs her down. Sarah is, I believe, our best student. ...
word-formation-processes
... -is the study of meaningful forms in the language, or of internal structures of words. MORPHEME-is a minimal unit of meaning or (grammatical function) in the language (element such as –s,-er,-ed,-ing) eg. reopened=3 morphemes re+open+ed -the smallest meaningful unit in language. LEXEME-is a family ...
... -is the study of meaningful forms in the language, or of internal structures of words. MORPHEME-is a minimal unit of meaning or (grammatical function) in the language (element such as –s,-er,-ed,-ing) eg. reopened=3 morphemes re+open+ed -the smallest meaningful unit in language. LEXEME-is a family ...
Maths Renewed Framework Objectives - Year 1
... Most prefixes are added to the beginning of root words without any ...
... Most prefixes are added to the beginning of root words without any ...
vice – vicious, grace – gracious, space – spacious, malice – malicious.
... Most prefixes are added to the beginning of root words without any ...
... Most prefixes are added to the beginning of root words without any ...
Using Sentence Structure and Part of Speech
... Identifying Parts of Speech Identifying Verbs • Verbs, which show action, may end several ways: – -ed – -s – -ing ...
... Identifying Parts of Speech Identifying Verbs • Verbs, which show action, may end several ways: – -ed – -s – -ing ...
WORD CLASSES, SENTENCE STRUCTURE and TERMINOLOGY
... Agreeing Plurals and Singulars If you want to write proper English, you have to follow a rule called “subject-verb agreement.” – That means that if the subject is plural (ducks), then the verb needs to be plural (quack). If the subject is singular (duck) then the verb needs to be singular (quacks). ...
... Agreeing Plurals and Singulars If you want to write proper English, you have to follow a rule called “subject-verb agreement.” – That means that if the subject is plural (ducks), then the verb needs to be plural (quack). If the subject is singular (duck) then the verb needs to be singular (quacks). ...
Glossary Literacy L3 - Skills for Life Network
... standard English, I am, not I is). alliteration Using the same sound to begin two or more neighbouring words. blend Combining two or more sounds for fluent reading: tr and str are blends. case Some English pronouns change case according to function in the clause: so She saw me but I saw her. checkin ...
... standard English, I am, not I is). alliteration Using the same sound to begin two or more neighbouring words. blend Combining two or more sounds for fluent reading: tr and str are blends. case Some English pronouns change case according to function in the clause: so She saw me but I saw her. checkin ...
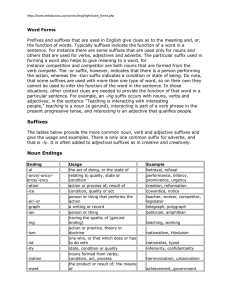
Word Forms - Professor Catherine Hatzakos
... others that are used for verbs, adjectives and adverbs. The particular suffix used in forming a word also helps to give meaning to a word, for instance competition and competitor are both nouns that are formed from the verb compete. The -or suffix, however, indicates that there is a person performin ...
... others that are used for verbs, adjectives and adverbs. The particular suffix used in forming a word also helps to give meaning to a word, for instance competition and competitor are both nouns that are formed from the verb compete. The -or suffix, however, indicates that there is a person performin ...
A noun is a person, place, thing, or idea. Persons: teacher, Beyonce
... swarm, class, family, team ...
... swarm, class, family, team ...
100 Commonly Misspelled Words
... Pronouns (she, yourself, her, he, it, they, who, etc.) need to be clear about the word or words they are replacing. (INCORRECT:The restaurant prohibitted smoking, which many customers resented.) Do the customers resent the restaurant or smoking? Use a comma after an introductory phrase. (Determined ...
... Pronouns (she, yourself, her, he, it, they, who, etc.) need to be clear about the word or words they are replacing. (INCORRECT:The restaurant prohibitted smoking, which many customers resented.) Do the customers resent the restaurant or smoking? Use a comma after an introductory phrase. (Determined ...
Parts of Speech
... Relative pronouns: that, which, who, whom, whose Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those Indefinite pronouns: all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, ...
... Relative pronouns: that, which, who, whom, whose Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those Indefinite pronouns: all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, ...
Curriculum Map for Progression in Vocabulary, Grammar and
... Use conjunctions to express time, place and cause (eg. When, before, after, while, so because) adverbs (eg.then, next, soon therefore) prepositions (eg. Before after, during in because of) Noun phrases expanded by the addition of modifying adjectives, nouns and prepositional phrases (the strict math ...
... Use conjunctions to express time, place and cause (eg. When, before, after, while, so because) adverbs (eg.then, next, soon therefore) prepositions (eg. Before after, during in because of) Noun phrases expanded by the addition of modifying adjectives, nouns and prepositional phrases (the strict math ...
The Eight Parts of Speech
... • The word that a pronoun replaces is called its antecedent. – EX: Elena read a book and returned it to the library. – EX: The models bought themselves new dresses. ...
... • The word that a pronoun replaces is called its antecedent. – EX: Elena read a book and returned it to the library. – EX: The models bought themselves new dresses. ...
The Eight Parts of Speech
... • The word that a pronoun replaces is called its antecedent. – EX: Elena read a book and returned it to the library. – EX: The models bought themselves new dresses. ...
... • The word that a pronoun replaces is called its antecedent. – EX: Elena read a book and returned it to the library. – EX: The models bought themselves new dresses. ...
All our dreams can come true – if we have the courage to pursue them.
... Monday, September 23, 2013 ...
... Monday, September 23, 2013 ...
Diction
... The speaker may want the audience to know only a certain amount about a subject so may choose to use vague phrases. If a speaker wishes to expound in great detail he or she will use words that are specific and precise. ...
... The speaker may want the audience to know only a certain amount about a subject so may choose to use vague phrases. If a speaker wishes to expound in great detail he or she will use words that are specific and precise. ...
NOTE TO TEACHERS: The following is not meant as a handout for
... The following is not meant as a handout for your students! It is meant solely as an educational resource for teachers needing to review this particular grammar topic before teaching their lessons! NOTE TO TEACHERS: ...
... The following is not meant as a handout for your students! It is meant solely as an educational resource for teachers needing to review this particular grammar topic before teaching their lessons! NOTE TO TEACHERS: ...
6. Supporting Grammar - Parent Guide to
... An adjective is a ‘describing’ word: it is a word used to describe (or tell you more about) a noun. The burglar was wearing a black jacket, a furry hat and a large mask over his face. (The words in pink tell us more about the noun that follows) An adjective usually comes before a noun but sometimes ...
... An adjective is a ‘describing’ word: it is a word used to describe (or tell you more about) a noun. The burglar was wearing a black jacket, a furry hat and a large mask over his face. (The words in pink tell us more about the noun that follows) An adjective usually comes before a noun but sometimes ...
Aim: How can the study of the parts of speech help us understand
... • Pronoun. A word that takes the place of one or more nouns. • Example: Do all men kill the things they do not love? (The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare). • Personal pronoun. Refers to a particular person, place, thing, or idea. • Example: I, me, we, us, you, he, him, she, her, it, they, ...
... • Pronoun. A word that takes the place of one or more nouns. • Example: Do all men kill the things they do not love? (The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare). • Personal pronoun. Refers to a particular person, place, thing, or idea. • Example: I, me, we, us, you, he, him, she, her, it, they, ...
Statistical Natural Language Procesing: linguistic
... (e.g. ‘the’, ‘a’) and adjectives describe the properties of nouns (e.g. ‘red’, ‘long’, ‘intelligent’). Verbs are used to describe actions, activities and states ...
... (e.g. ‘the’, ‘a’) and adjectives describe the properties of nouns (e.g. ‘red’, ‘long’, ‘intelligent’). Verbs are used to describe actions, activities and states ...