No Slide Title
... What properties make some cells electrically excitable? Cells such as muscle and nerve cells have >#... ...
... What properties make some cells electrically excitable? Cells such as muscle and nerve cells have >#... ...
MAC: Electrophysiology Lecture
... Otoacoustic emissions, a low-level sound emitted by the cochlea, so not an AEP… • Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials • Middle latency potentials • Later latency potentials ...
... Otoacoustic emissions, a low-level sound emitted by the cochlea, so not an AEP… • Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials • Middle latency potentials • Later latency potentials ...
somatosensory area i
... – Sensory signals from all modalities - Posterior – Anterior half parietal Lobe – Somatosensory signals – Reception and Interpretation – Posterior half – Still higher levels of interpretation ...
... – Sensory signals from all modalities - Posterior – Anterior half parietal Lobe – Somatosensory signals – Reception and Interpretation – Posterior half – Still higher levels of interpretation ...
BOLD signal - Department of Psychology
... measure blood flow in area of peripheral visual cortex – away from foveal representation of fixation point – on some trials visual stimuli were presented to activate the measured area ...
... measure blood flow in area of peripheral visual cortex – away from foveal representation of fixation point – on some trials visual stimuli were presented to activate the measured area ...
Somatic senses
... Rapidly transferred to CNS by small myelinated fibeers Slow pain – more diffused pain Carried by small unmyelinated fibers ...
... Rapidly transferred to CNS by small myelinated fibeers Slow pain – more diffused pain Carried by small unmyelinated fibers ...
Nervous System
... A. Dura mater: tough outer covering of brain and s.c. B. Arachnoid mater: middle layer C. Pia mater: inner surface which clings tightly to surface of brain and s.c. • Subarachnoid space: separates the arachnoid and pia maters; filled with CSF ...
... A. Dura mater: tough outer covering of brain and s.c. B. Arachnoid mater: middle layer C. Pia mater: inner surface which clings tightly to surface of brain and s.c. • Subarachnoid space: separates the arachnoid and pia maters; filled with CSF ...
Class 10- Control and Coordination
... The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. a) Receptors :- These are the sense organs which receive the stimuli and pass the message to the brain or spinal cord through the sensory nerves. Eg :- Photoreceptors in the eyes to detect light. Phonoreceptors in the ears to detect s ...
... The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord and nerves. a) Receptors :- These are the sense organs which receive the stimuli and pass the message to the brain or spinal cord through the sensory nerves. Eg :- Photoreceptors in the eyes to detect light. Phonoreceptors in the ears to detect s ...
How is the stimulus represented in the nervous system?
... 1. Distances between spike trains are computed. 2. From the distances a cluster analysis can be done. 3. The result is a confusion matrix from which the MI can be calculated. ...
... 1. Distances between spike trains are computed. 2. From the distances a cluster analysis can be done. 3. The result is a confusion matrix from which the MI can be calculated. ...
Dorsolateral Prefrontal Association Cortex
... ◦ Association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest i.e from general goals (cortical level) to specific details of action (lower levels). ◦ Parallel structure – signals flow between levels over multiple paths ◦ Information flow is down, while in the Sensory system informtion flows throu ...
... ◦ Association cortex at the highest level, muscles at the lowest i.e from general goals (cortical level) to specific details of action (lower levels). ◦ Parallel structure – signals flow between levels over multiple paths ◦ Information flow is down, while in the Sensory system informtion flows throu ...
Chapter 15
... • Transduction is the conversion of a stimulus into an electrical event or potential • A potential is a change in the membrane’s electrical condition • There are graded potentials which are localized, variable in amplitude and fade with distance • They can “sum” (or result in summation) • If there i ...
... • Transduction is the conversion of a stimulus into an electrical event or potential • A potential is a change in the membrane’s electrical condition • There are graded potentials which are localized, variable in amplitude and fade with distance • They can “sum” (or result in summation) • If there i ...
CHAPTER 6 PRINCIPLES OF NEURAL CIRCUITS.
... receptor array contains a topographic representation or “map” of sound frequency, visual space; or other stimulus dimension. Generation of temporal patterns. Sensory stimuli are distributed in time, and receptors and nerve fibers are active at times that are correlated with the temporal pattern of t ...
... receptor array contains a topographic representation or “map” of sound frequency, visual space; or other stimulus dimension. Generation of temporal patterns. Sensory stimuli are distributed in time, and receptors and nerve fibers are active at times that are correlated with the temporal pattern of t ...
Reflexes and Brain - Sinoe Medical Association
... • Gland , smooth muscle, cardiac muscles=Îautonomic reflex ...
... • Gland , smooth muscle, cardiac muscles=Îautonomic reflex ...
Introductory chapter
... and Hartline have formed the paradigm for subsequent exploration of the nervous system. On the one hand this must mean that their early experiments captured essential and universal features of the neural code. On the other hand one must worry that, in following this single line of ideas, some crucia ...
... and Hartline have formed the paradigm for subsequent exploration of the nervous system. On the one hand this must mean that their early experiments captured essential and universal features of the neural code. On the other hand one must worry that, in following this single line of ideas, some crucia ...
My Reaction Test Score = Neural Transmission
... neuron action potential as a signal moves down the axon. This wave of changing electrical charge flows down the axon until it reaches the terminal button. At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of t ...
... neuron action potential as a signal moves down the axon. This wave of changing electrical charge flows down the axon until it reaches the terminal button. At the end (terminal button) of the axon the signal causes small sacks (vesicles) of chemicals to be released into the space between the end of t ...
Ear to Auditory Cortex
... • Young children born with hearing loss are the best candidates for this implant. ...
... • Young children born with hearing loss are the best candidates for this implant. ...
Motor neuron
... prepares body for fight or flight situations Parasympathetic – prepares body for resting and digesting activities • _______________ ...
... prepares body for fight or flight situations Parasympathetic – prepares body for resting and digesting activities • _______________ ...
Chapter 5: sensation PAGE 1 Table 1: Sensing the World: Some
... (a) Phantom Limb- This is when a person feels pain in a limb that is not existing, or when the brain misinterprets the spontaneous central nervous system activity that occurs in the absence of normal sensory input. This may be cause because pain is not only a sense but also from the brain. (b) Gate ...
... (a) Phantom Limb- This is when a person feels pain in a limb that is not existing, or when the brain misinterprets the spontaneous central nervous system activity that occurs in the absence of normal sensory input. This may be cause because pain is not only a sense but also from the brain. (b) Gate ...
SHEEP BRAIN DISSECTION GUIDE
... the retina transmit light information to other retinal neurons which process the information and send the output to the rest of the brain via the optic nerve which projects from the back of the eyeball. The right and left optic nerves cross at the optic chiasm, forming a distinctive "X" on the ventr ...
... the retina transmit light information to other retinal neurons which process the information and send the output to the rest of the brain via the optic nerve which projects from the back of the eyeball. The right and left optic nerves cross at the optic chiasm, forming a distinctive "X" on the ventr ...
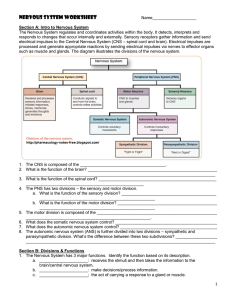
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... connected to sensory receptors and the axons are connected to other neurons. The receptors change information from external sources, such as light waves or sound vibrations, into electrical impulses. In motor neurons, the dendrites are connected to other neurons, and the axons to effectors (muscles ...
... connected to sensory receptors and the axons are connected to other neurons. The receptors change information from external sources, such as light waves or sound vibrations, into electrical impulses. In motor neurons, the dendrites are connected to other neurons, and the axons to effectors (muscles ...