Slide 1
... A conducting sphere initially has no net charge. A positively charged rod is then brought close to the sphere. The sphere is then connected to ground. The rod is then removed, and then the connection to ground is broken. After these steps, what is the net charge on the sphere? ...
... A conducting sphere initially has no net charge. A positively charged rod is then brought close to the sphere. The sphere is then connected to ground. The rod is then removed, and then the connection to ground is broken. After these steps, what is the net charge on the sphere? ...
The Rutherford Model
... indicated the nucleus was no larger than 3 x 10-14m. The atom is ________________ by comparison at 1.0 x 10-10 m. ...
... indicated the nucleus was no larger than 3 x 10-14m. The atom is ________________ by comparison at 1.0 x 10-10 m. ...
is the accelerating voltage of 1000 V)
... A proton passes undeflected through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. The electric field strength is 120 N/C and the magnetic field strength is 0.45 T. What is the speed of the proton? ...
... A proton passes undeflected through perpendicular electric and magnetic fields. The electric field strength is 120 N/C and the magnetic field strength is 0.45 T. What is the speed of the proton? ...
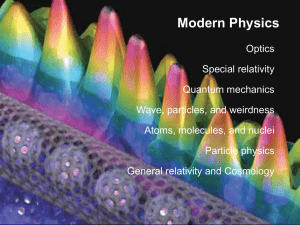
Modern Physics - Tarleton State University
... The probability density for the hydrogen atom for three different electron states. ...
... The probability density for the hydrogen atom for three different electron states. ...
Recitation Week 7
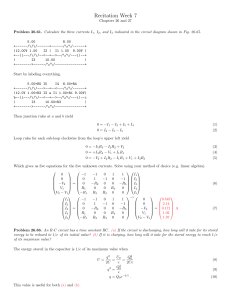
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
Atoms
... The work of J.J. Thomson, E. Rutherford and others toward the end of the 19th century and into the beginning of the 20th century established that atoms consist of a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons. In a neutral atom, the positive charge on the nucleus exactly balances the ...
... The work of J.J. Thomson, E. Rutherford and others toward the end of the 19th century and into the beginning of the 20th century established that atoms consist of a positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons. In a neutral atom, the positive charge on the nucleus exactly balances the ...
Slide 1
... separated by a distance d. The particles are surrounded by empty space. Are there any points in space, besides at infinity, at which the electric potential, due to the pair, is zero? a) Yes b) No ...
... separated by a distance d. The particles are surrounded by empty space. Are there any points in space, besides at infinity, at which the electric potential, due to the pair, is zero? a) Yes b) No ...
Old Physics GRE Problems Based on content from Chapter 2 of your
... A. The electric field transforms completely into a magnetic field. B. If initially there is only an electric field, after the transformation there may be both an electric and magnetic field. C. The electric field is unaltered. D. The magnetic field is unaltered. E. It cannot be determined unless a g ...
... A. The electric field transforms completely into a magnetic field. B. If initially there is only an electric field, after the transformation there may be both an electric and magnetic field. C. The electric field is unaltered. D. The magnetic field is unaltered. E. It cannot be determined unless a g ...
Lesson 1 Assignment - Rocky View Schools
... b. Use the charge-to-mass ratio of the particle to determine whether it is an alpha particle, electron, or proton. Hint: Check your physics data sheet for the charges and masses. ...
... b. Use the charge-to-mass ratio of the particle to determine whether it is an alpha particle, electron, or proton. Hint: Check your physics data sheet for the charges and masses. ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... charged particles that respond to an applied magnetic field. – used by Thomson to discover electron, first subatomic particle and measure its charge/mass ratio, led to Plum pudding model – used in CRT televisions Tiny oil drop exposed to radiation to give it a charge. Size of charge measured by bala ...
... charged particles that respond to an applied magnetic field. – used by Thomson to discover electron, first subatomic particle and measure its charge/mass ratio, led to Plum pudding model – used in CRT televisions Tiny oil drop exposed to radiation to give it a charge. Size of charge measured by bala ...
Ex10
... 2. Consider a Millikan type experiment to measure the charge e of a particle with mass m. The particle is in an electric field E in the z direction, produced by a capacitor whose plates are distance d apart. The experiment is at temperature T and in a poor vacuum, i.e. col is short. (col is the av ...
... 2. Consider a Millikan type experiment to measure the charge e of a particle with mass m. The particle is in an electric field E in the z direction, produced by a capacitor whose plates are distance d apart. The experiment is at temperature T and in a poor vacuum, i.e. col is short. (col is the av ...
Periodic Table
... Newton’s Laws, Coulomb’s Law, gravity…Quantum mechanics deals with the forces on objects of very small mass (like the electron or an atom). In QM things behave in ways that seem “odd” as they are by their nature not following the “rules” of classical mechanics. ...
... Newton’s Laws, Coulomb’s Law, gravity…Quantum mechanics deals with the forces on objects of very small mass (like the electron or an atom). In QM things behave in ways that seem “odd” as they are by their nature not following the “rules” of classical mechanics. ...
Rutherford gold foil abstract
... and found to hold within the limit of experimental error. From a consideration of general results on scattering by different materials, the central charge of the atom is found to be very nearly proportional to its atomic weight. The exact value of the central charge has not been determined, but for ...
... and found to hold within the limit of experimental error. From a consideration of general results on scattering by different materials, the central charge of the atom is found to be very nearly proportional to its atomic weight. The exact value of the central charge has not been determined, but for ...
Quantum Mechanics II, Ex 4730
... Given a spherical shell with radius R and a particle with mass M and charge e. Notice that the standard variables which show the particle are (θ, φ, Lx, Ly, Lz) In this question we have to assume that the particle can be excited from ground state to first energy level but not beyond so the state spa ...
... Given a spherical shell with radius R and a particle with mass M and charge e. Notice that the standard variables which show the particle are (θ, φ, Lx, Ly, Lz) In this question we have to assume that the particle can be excited from ground state to first energy level but not beyond so the state spa ...
穨 Ams1a
... radiation : stream of fast moving electron travelling with speed of light. The electron is emitted by splitting a neutron in radioactive decay. Ionize gas through which they pass. ...
... radiation : stream of fast moving electron travelling with speed of light. The electron is emitted by splitting a neutron in radioactive decay. Ionize gas through which they pass. ...
Ask a scientist answers
... Q11: “Since beta decay is when …” A11: Good question. The weak force is responsible for changing one quark into another, in this case a d-quark into a u-quark. Because the electric charge must conserved one needs to emit a negative charge (the neutron is neutral, the proton is +1, so you need a -1ty ...
... Q11: “Since beta decay is when …” A11: Good question. The weak force is responsible for changing one quark into another, in this case a d-quark into a u-quark. Because the electric charge must conserved one needs to emit a negative charge (the neutron is neutral, the proton is +1, so you need a -1ty ...
SI Physics 221
... 1) True/False. An uncharged particle that enters an electric field will not experience a force from that field. ...
... 1) True/False. An uncharged particle that enters an electric field will not experience a force from that field. ...
Week 1: Nuclear timeline (pdf, 233 KB)
... The reader must understand that this is not a total outline of the development of physics but what I deem is the line of discoveries that leads directly to the development of atomic energy. As an example I offer thermodynamics. For this, I could develop a separate trail with some similar names such ...
... The reader must understand that this is not a total outline of the development of physics but what I deem is the line of discoveries that leads directly to the development of atomic energy. As an example I offer thermodynamics. For this, I could develop a separate trail with some similar names such ...
History of subatomic physics
.jpg?width=300)
The idea that matter consists of smaller particles and that there exists a limited number of sorts of primary, smallest particles in nature has existed in natural philosophy since time immemorial. Such ideas gained physical credibility beginning in the 19th century, but the concept of ""elementary particle"" underwent some changes in its meaning: notably, modern physics no longer deems elementary particles indestructible. Even elementary particles can decay or collide destructively; they can cease to exist and create (other) particles in result.Increasingly small particles have been discovered and researched: they include molecules, which are constructed of atoms, that in turn consist of subatomic particles, namely atomic nuclei and electrons. Many more types of subatomic particles have been found. Most such particles (but not electrons) were eventually found to be composed of even smaller particles such as quarks. Particle physics studies these smallest particles and their behaviour under high energies, whereas nuclear physics studies atomic nuclei and their (immediate) constituents: protons and neutrons.