Introduction to Bioinformatics
... – string many nouns together in one sequence or – use many noun strings in a passage ...
... – string many nouns together in one sequence or – use many noun strings in a passage ...
unit i (part of speech)
... singular and plural form. Example: two continents, four elements, three dictionaries. 7. UNCOUNTABLE NOUNS: Uncountable nouns (also called mass nouns or noncount nouns) cannot be counted, they are not seperate objects. This means you cannot make them plural by adding -s, because they only have a sin ...
... singular and plural form. Example: two continents, four elements, three dictionaries. 7. UNCOUNTABLE NOUNS: Uncountable nouns (also called mass nouns or noncount nouns) cannot be counted, they are not seperate objects. This means you cannot make them plural by adding -s, because they only have a sin ...
Final Rules Sometimes a prepositional phrase comes between the
... Some nouns that are singular in form name a group of people or things: class, family, team, group, flock, for example. These nouns are called collective nouns. When the subject follows the verb, as in sentences beginning with there, here, or where, be careful to locate the subject and make sure that ...
... Some nouns that are singular in form name a group of people or things: class, family, team, group, flock, for example. These nouns are called collective nouns. When the subject follows the verb, as in sentences beginning with there, here, or where, be careful to locate the subject and make sure that ...
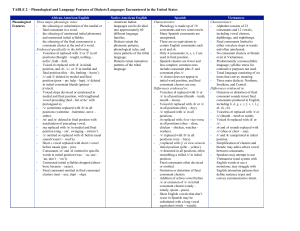
TABLE 2 – Phonological and Language Features of Dialects
... nasalization of preceding vowel. - ing replaced with /n/ in medial and final position (sing – sin’, swinging – swinin’). - /z/ omitted or replaced with /d/ before nasal sound (wasn’t – wud’n). - Short e vowel replaced with short i vowel before nasals (pen – pin). - Consonants /w/ and /d/ omitted in ...
... nasalization of preceding vowel. - ing replaced with /n/ in medial and final position (sing – sin’, swinging – swinin’). - /z/ omitted or replaced with /d/ before nasal sound (wasn’t – wud’n). - Short e vowel replaced with short i vowel before nasals (pen – pin). - Consonants /w/ and /d/ omitted in ...
Verbals
... The general rule is that no word should separate the to of an infinitive from the simple form of the verb that follows. If a word does come between these two components, a split infinitive results. Look at the example that follows: ...
... The general rule is that no word should separate the to of an infinitive from the simple form of the verb that follows. If a word does come between these two components, a split infinitive results. Look at the example that follows: ...
Activity 5 - vsl@online
... conscripserat (line 16) is (1st / 2nd / 3rd) person (singular / plural) (present / imperfect / perfect / pluperfect / future) (active / passive / deponent) (indicative / imperative / subjunctive) of conscribo, -ere, -scripsi, -scriptum which means [ ]; this mood is used because (the action involves ...
... conscripserat (line 16) is (1st / 2nd / 3rd) person (singular / plural) (present / imperfect / perfect / pluperfect / future) (active / passive / deponent) (indicative / imperative / subjunctive) of conscribo, -ere, -scripsi, -scriptum which means [ ]; this mood is used because (the action involves ...
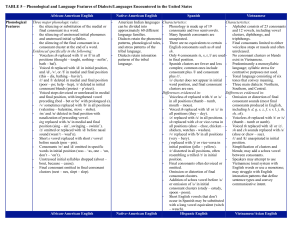
TABLE 5 – Phonological and Language Features of Dialects
... Nonobligatory relative pronouns (He the one did it – omission of who). Reflexive pronouns regularized (hisself, theirself). Demonstrative them or them there substituted for these, those. Use of double/triple negatives permitted. Ain’t used as negative marker. Same form for direct and indirect questi ...
... Nonobligatory relative pronouns (He the one did it – omission of who). Reflexive pronouns regularized (hisself, theirself). Demonstrative them or them there substituted for these, those. Use of double/triple negatives permitted. Ain’t used as negative marker. Same form for direct and indirect questi ...
Year 5 and 6 spelling words The government have set out the
... Exceptions: protein, caffeine, seize (and either and neither if pronounced with an initial deceive, conceive, receive, perceive, ceiling spelt ei after c /i:/ sound). ought, bought, thought, nought, brought, fought Words containing the ough is one of the trickiest spellings in English – it can be us ...
... Exceptions: protein, caffeine, seize (and either and neither if pronounced with an initial deceive, conceive, receive, perceive, ceiling spelt ei after c /i:/ sound). ought, bought, thought, nought, brought, fought Words containing the ough is one of the trickiest spellings in English – it can be us ...
Latin Verbs: the Principal Parts of the Verb
... The verbs listed on the page that explains the principal parts of verbs are all from what is called the first conjugation. This conjugation includes all those verbs whose second principal part ends in -âre. The standard endings for the principal parts of verbs in this conjugation are: -ô, -âre, -âvî ...
... The verbs listed on the page that explains the principal parts of verbs are all from what is called the first conjugation. This conjugation includes all those verbs whose second principal part ends in -âre. The standard endings for the principal parts of verbs in this conjugation are: -ô, -âre, -âvî ...
Grammar Review - Immaculate Conception Catholic School | Denton
... (!) Demonstrative Adjectives: point out definite person/place/thing/idea: this, that, these, those (near/far, singular/plural). Remember that demonstrative adjectives are the same as demonstrative pronouns which replace a noun instead of modifying it.) He bought that book for Christmas. We ate these ...
... (!) Demonstrative Adjectives: point out definite person/place/thing/idea: this, that, these, those (near/far, singular/plural). Remember that demonstrative adjectives are the same as demonstrative pronouns which replace a noun instead of modifying it.) He bought that book for Christmas. We ate these ...
Verbal Adjectives PPT
... – captus = masc. sg. = the captured man – captae = fem. pl. = the captured women – capta = neut. pl. = the captured things ...
... – captus = masc. sg. = the captured man – captae = fem. pl. = the captured women – capta = neut. pl. = the captured things ...
Reading Unit 4 Study Guide
... o main idea – the most important or central thought of a paragraph or story/text, which tells the read what the text is about o details – ideas that support the topic or main idea sentence in a paragraph or text Generalize – a general statement or concept obtained by inference from specific cases. ...
... o main idea – the most important or central thought of a paragraph or story/text, which tells the read what the text is about o details – ideas that support the topic or main idea sentence in a paragraph or text Generalize – a general statement or concept obtained by inference from specific cases. ...
Correct Agreement of Subject and Verb
... The following indefinite pronouns are singular: each, either, neither, one, everyone, every one, no one, one, someone, anyone, nobody, anybody, somebody, everybody, something, nothing, anything, everything, much Neither parent is there. Neither is there. Everyone on both teams has to follow th ...
... The following indefinite pronouns are singular: each, either, neither, one, everyone, every one, no one, one, someone, anyone, nobody, anybody, somebody, everybody, something, nothing, anything, everything, much Neither parent is there. Neither is there. Everyone on both teams has to follow th ...
english grammar without tears
... advocates of Modern Grammar are inclined to scoff at Traditional Grammarians with statements like ‘The Adverb is a literary ragbag into which words that cannot be classified are thrown’. Just as T.S. Eliot requires every new aspirating poet to have an awareness of the history of poetry from Homer to ...
... advocates of Modern Grammar are inclined to scoff at Traditional Grammarians with statements like ‘The Adverb is a literary ragbag into which words that cannot be classified are thrown’. Just as T.S. Eliot requires every new aspirating poet to have an awareness of the history of poetry from Homer to ...
Chapter 1(b)
... Greek, verb endings change depending on the person (1st, 2nd, 3rd) and number (singular or plural) of the verb. Regular will follow the form: λυ-̄́ “loosen, loose” (3rd person sing.): λυ-̄́ ει Contract will follow the form: ϕιλε- “love” (3rd person sing.): ϕιλέ-ει>ϕιλει̉̑ Irregular doesn’t follow a ...
... Greek, verb endings change depending on the person (1st, 2nd, 3rd) and number (singular or plural) of the verb. Regular will follow the form: λυ-̄́ “loosen, loose” (3rd person sing.): λυ-̄́ ει Contract will follow the form: ϕιλε- “love” (3rd person sing.): ϕιλέ-ει>ϕιλει̉̑ Irregular doesn’t follow a ...
CASE/USAGE ROUND-UP JENNEY`S LESSONS 1
... ADDENDUM -The PASSIVE VOICE of MaNiaCC verbs can function as a simple COPULA! e.g. Priamus erat dominus Troiae. Priamus vocabatur dominus Troiae. In these two sentences, erat and vocabatur analogous: both are copulas! GENITIVE 1. Gen./POSSESSION - the Genitive case answers the question "whose?" - En ...
... ADDENDUM -The PASSIVE VOICE of MaNiaCC verbs can function as a simple COPULA! e.g. Priamus erat dominus Troiae. Priamus vocabatur dominus Troiae. In these two sentences, erat and vocabatur analogous: both are copulas! GENITIVE 1. Gen./POSSESSION - the Genitive case answers the question "whose?" - En ...
Conjugating Reflexive Verbs
... A reflexive verb infinitive is identified by its reflexive pronoun se, which is placed before the infinitive and that serves as a direct or indirect object pronoun. A reflexive verb shows that the subject is performing the action upon itself and, therefore, the subject and the reflexive pronoun refe ...
... A reflexive verb infinitive is identified by its reflexive pronoun se, which is placed before the infinitive and that serves as a direct or indirect object pronoun. A reflexive verb shows that the subject is performing the action upon itself and, therefore, the subject and the reflexive pronoun refe ...
helping verb
... The future tense of a verb names an action that will take place in the future. In the future tense, the word will is used with the verb. **Sometimes shall is used when the pronouns I or we is the ...
... The future tense of a verb names an action that will take place in the future. In the future tense, the word will is used with the verb. **Sometimes shall is used when the pronouns I or we is the ...
Parts of Speech Activity ()
... feelings. Nouns can be a subject or an object of a verb, can be modified by an adjective and can take an article or determiner. Nouns may be divided into two groups: countable nouns have plural forms and uncountable nouns do not. 3. pronoun- a word that substitutes a noun or noun phrase. There are a ...
... feelings. Nouns can be a subject or an object of a verb, can be modified by an adjective and can take an article or determiner. Nouns may be divided into two groups: countable nouns have plural forms and uncountable nouns do not. 3. pronoun- a word that substitutes a noun or noun phrase. There are a ...
Pronoun: a word used in place of one or more nouns. We use
... QUESTION 2: When is a word a pronoun? When is a word an adjective? These demonstrative pronouns can be used as adjectives: that, these, this, and those. These interrogative pronouns can be used as adjectives: what and which. These indefinite pronouns can be used as adjectives: all, another, any, bo ...
... QUESTION 2: When is a word a pronoun? When is a word an adjective? These demonstrative pronouns can be used as adjectives: that, these, this, and those. These interrogative pronouns can be used as adjectives: what and which. These indefinite pronouns can be used as adjectives: all, another, any, bo ...