The Parts of Speech
... an adverb. The preposition along with its noun or pronoun (as well as any modifiers of that noun or pronoun if there are any) is called a prepositional phrase. So therefore every prepositional phrase is working as a modifier, either as an adjective or as an adverb. I’m including a list of the common ...
... an adverb. The preposition along with its noun or pronoun (as well as any modifiers of that noun or pronoun if there are any) is called a prepositional phrase. So therefore every prepositional phrase is working as a modifier, either as an adjective or as an adverb. I’m including a list of the common ...
Transitive vs. Intransitive Verbs Transitive verbs direct action toward
... 7. Charlie combed his hair nervously before the dance. 8. We bought paper napkins for the picnic. 9. Zelda smiled at the thought of a parade in the snow. 10. Fish and potatoes sizzled in the pan. ...
... 7. Charlie combed his hair nervously before the dance. 8. We bought paper napkins for the picnic. 9. Zelda smiled at the thought of a parade in the snow. 10. Fish and potatoes sizzled in the pan. ...
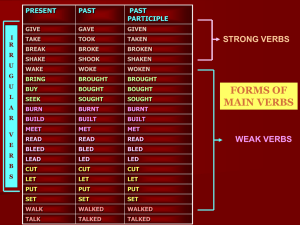
Strong and Weak Verbs
... What is a weak verb? Generally a main verb that needs a ‘t’ or ‘d’ to give its past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb • A main verb that loses an ‘e’ from its usual form to give the past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb e.g. read - read - read , bleed – bled- bled ...
... What is a weak verb? Generally a main verb that needs a ‘t’ or ‘d’ to give its past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb • A main verb that loses an ‘e’ from its usual form to give the past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb e.g. read - read - read , bleed – bled- bled ...
Writing 2 (Identifying sentences errors)
... past tense belonged. To be consistent, that last verb needs to be changed to the present tense belong. 2- In the second sentence, the author correctly uses the singular pronoun he or she to replace the singular noun recipient. But she then incorrectly uses the plural pronoun their to refer to the sa ...
... past tense belonged. To be consistent, that last verb needs to be changed to the present tense belong. 2- In the second sentence, the author correctly uses the singular pronoun he or she to replace the singular noun recipient. But she then incorrectly uses the plural pronoun their to refer to the sa ...
PARTNERSHIP FOR REVISING FLORIDA`S CONSTITUTION
... noun and after the verb. Thus, use “ a married couple” rather than “a couple who are married” or the verb (“a person may file only when” rather than “ a person may only file when”). C. P ...
... noun and after the verb. Thus, use “ a married couple” rather than “a couple who are married” or the verb (“a person may file only when” rather than “ a person may only file when”). C. P ...
Words and morphemes
... • many prepositions do have antonyms, and therefore could be thought of as having descriptive content (e.g. under/over, to/from, with/without, in/out, up/down) • but many prepositions do not have antonyms, and do not seem to pick out any particular spatial or temporal relationship; they perform a fu ...
... • many prepositions do have antonyms, and therefore could be thought of as having descriptive content (e.g. under/over, to/from, with/without, in/out, up/down) • but many prepositions do not have antonyms, and do not seem to pick out any particular spatial or temporal relationship; they perform a fu ...
Verb
... e.g. The circuit was closed (by the robber) . • There is also a kind of Middle voice. e.g. The circuit closed (by itself). ...
... e.g. The circuit was closed (by the robber) . • There is also a kind of Middle voice. e.g. The circuit closed (by itself). ...
The Study of Language Answers of page 37 1 Acoustic phonetics is
... cage (= noun), but (= conjunction), it (= pronoun), escaped (= verb), recently (= adverb) 2 Grammatical gender is based on the type of noun, such as masculine or feminine or neuter, and is not tied to sex. Natural gender is based on sex as a biological distinction between male, female or neither mal ...
... cage (= noun), but (= conjunction), it (= pronoun), escaped (= verb), recently (= adverb) 2 Grammatical gender is based on the type of noun, such as masculine or feminine or neuter, and is not tied to sex. Natural gender is based on sex as a biological distinction between male, female or neither mal ...
RUSTWOL: A Tool for Automatic Russian Word Form Recognition
... (1983). My description is based on a document written by me, when I was working as a linguist at Lingsoft (Vilkki 1997). This earlier version of RUSTWOL was later used at Lingsoft as a basis for a new format. The newer version of RUSTWOL, representing the new format, and its documentation, written b ...
... (1983). My description is based on a document written by me, when I was working as a linguist at Lingsoft (Vilkki 1997). This earlier version of RUSTWOL was later used at Lingsoft as a basis for a new format. The newer version of RUSTWOL, representing the new format, and its documentation, written b ...
Télécharger la source de la présentation
... The infinitive is a verbal which can function as a noun, an adjective or an adverb. The infinitive starts with the word ‘to’. Usage frequently defines whether to use a gerund or an infinitive. Use the chart on Page 180 as a guide. ...
... The infinitive is a verbal which can function as a noun, an adjective or an adverb. The infinitive starts with the word ‘to’. Usage frequently defines whether to use a gerund or an infinitive. Use the chart on Page 180 as a guide. ...
On Your Feet! - Amy Benjamin
... Punctuation: (WHITE) period, comma, semicolon S (for plural nouns and singular third person verb form ...
... Punctuation: (WHITE) period, comma, semicolon S (for plural nouns and singular third person verb form ...
Grammar Guide File - Wythe County Schools Moodle Site
... to-infinitive or preposition too-also two-number they’re-contraction of they are there-place their-possessive form of they its-possessive form of it it’s-contraction of it is sit-to place yourself in a seated position set-to place an object stationary-in a fixed position stationery-writing paper whe ...
... to-infinitive or preposition too-also two-number they’re-contraction of they are there-place their-possessive form of they its-possessive form of it it’s-contraction of it is sit-to place yourself in a seated position set-to place an object stationary-in a fixed position stationery-writing paper whe ...
Document
... 7. To find the Pr Nom, find the S and LV and find a noun or pronoun after the verb which is a “synonym” for the S. 8. To find the Pr Adj, find the S and LV and find an adjective after the LV which describes the S. ...
... 7. To find the Pr Nom, find the S and LV and find a noun or pronoun after the verb which is a “synonym” for the S. 8. To find the Pr Adj, find the S and LV and find an adjective after the LV which describes the S. ...
BasicGrammarReview
... The speaker will stand here. How? Kim carefully polished the car. To what extent? We were truly sorry. ...
... The speaker will stand here. How? Kim carefully polished the car. To what extent? We were truly sorry. ...
ing
... If something or someone is ... -ing, they will make you feel ... -ed Sometimes we doubt which adjective we have to use, -ed or -ing. * The -ed adjectives (bored, surprised, frightened, etc.) are used to express feelings, that is how people feel. e. g. Paco was exhausted after the flight from the Sta ...
... If something or someone is ... -ing, they will make you feel ... -ed Sometimes we doubt which adjective we have to use, -ed or -ing. * The -ed adjectives (bored, surprised, frightened, etc.) are used to express feelings, that is how people feel. e. g. Paco was exhausted after the flight from the Sta ...
3rd grade crct rdgradereadingandlanguageartscrctstudyguide1
... sentence and helps make the meaning clear. - 3 or more words listed together are called a series. In a series of 3 or more similar words, put a comma after each item except the last one. The last comma should be before and or or. Ex: Mountains, valleys, and islands are three natural landforms on Ear ...
... sentence and helps make the meaning clear. - 3 or more words listed together are called a series. In a series of 3 or more similar words, put a comma after each item except the last one. The last comma should be before and or or. Ex: Mountains, valleys, and islands are three natural landforms on Ear ...
Grammar Notes: Subject / Verb Agreement
... Subjects and verbs must agree with one another in number. In the present tense, a singular subject takes a singular verb, and a plural subject takes a plural verb. Below is a list of common subject-verb agreement rules. Singular verbs end in –s or –es. ...
... Subjects and verbs must agree with one another in number. In the present tense, a singular subject takes a singular verb, and a plural subject takes a plural verb. Below is a list of common subject-verb agreement rules. Singular verbs end in –s or –es. ...
academic vocabulary exemplars 3/27
... Synonyms: distinguish, observe, distinguish, recognize, identify, grasp, behold Antonyms: ignore, disbelieve, disregard, misunderstand, neglect, Conjugations: present tense: perceive, perceives, perceiving past tense: perceived future tense: will perceive, shall perceive Other parts of speech and de ...
... Synonyms: distinguish, observe, distinguish, recognize, identify, grasp, behold Antonyms: ignore, disbelieve, disregard, misunderstand, neglect, Conjugations: present tense: perceive, perceives, perceiving past tense: perceived future tense: will perceive, shall perceive Other parts of speech and de ...
Spelling, Grammar and Punctuation Terminology Term Definition
... of a text fit together. In other words, they create cohesion. Some examples of cohesive devices are: determiners and pronouns, which can refer back to earlier words conjunctions and adverbs, which can make relations between words clear ellipsis of expected words. A common noun describes a clas ...
... of a text fit together. In other words, they create cohesion. Some examples of cohesive devices are: determiners and pronouns, which can refer back to earlier words conjunctions and adverbs, which can make relations between words clear ellipsis of expected words. A common noun describes a clas ...
Proper nouns
... Complete verbs change for person and tense and can form a sentence. eg She knew the answer. He thinks carefully. The participles need the help of auxiliary (extra) verbs to make ...
... Complete verbs change for person and tense and can form a sentence. eg She knew the answer. He thinks carefully. The participles need the help of auxiliary (extra) verbs to make ...
The Book of Grammar
... →Action verbs →Linking verbs • What a verb phrase is • The five basic verb forms: infinitive, ...
... →Action verbs →Linking verbs • What a verb phrase is • The five basic verb forms: infinitive, ...
ing. Past Participles usually end in
... Helping verbs help the main verb describe action that happened in the past, is happening in the present, or will happen in the future. am being do have must are can does is shall be could had may should been did has might was were will would ...
... Helping verbs help the main verb describe action that happened in the past, is happening in the present, or will happen in the future. am being do have must are can does is shall be could had may should been did has might was were will would ...
Verbs Reference
... Verbs A verb describes an action (perform, send, buy) or acts as a link between a subject and words that define or describe that subject (is, were, become, appear). An auxiliary verb is one that helps another verb and is used for showing tense, voice, and so on. A verb with its helpers is called a v ...
... Verbs A verb describes an action (perform, send, buy) or acts as a link between a subject and words that define or describe that subject (is, were, become, appear). An auxiliary verb is one that helps another verb and is used for showing tense, voice, and so on. A verb with its helpers is called a v ...
What are finite and non
... • A finite verb is a verb with a subject and tense. • A non-finite verb doesn’t have a subject or tense and cannot be the main verb in a sentence. • Non-finite verbs are either: - infinitives (basic verb, often preceded by to) - present participles (basic verb + ing ending) - past participles (basic ...
... • A finite verb is a verb with a subject and tense. • A non-finite verb doesn’t have a subject or tense and cannot be the main verb in a sentence. • Non-finite verbs are either: - infinitives (basic verb, often preceded by to) - present participles (basic verb + ing ending) - past participles (basic ...
Inflection

In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. The inflection of verbs is also called conjugation, and the inflection of nouns, adjectives and pronouns is also called declension.An inflection expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. For example, the Latin verb ducam, meaning ""I will lead"", includes the suffix -am, expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense (future). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause ""I will lead"", the word lead is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb.The inflected form of a word often contains both a free morpheme (a unit of meaning which can stand by itself as a word), and a bound morpheme (a unit of meaning which cannot stand alone as a word). For example, the English word cars is a noun that is inflected for number, specifically to express the plural; the content morpheme car is unbound because it could stand alone as a word, while the suffix -s is bound because it cannot stand alone as a word. These two morphemes together form the inflected word cars.Words that are never subject to inflection are said to be invariant; for example, the English verb must is an invariant item: it never takes a suffix or changes form to signify a different grammatical category. Its categories can be determined only from its context.Requiring the inflections of more than one word in a sentence to be compatible according to the rules of the language is known as concord or agreement. For example, in ""the choir sings"", ""choir"" is a singular noun, so ""sing"" is constrained in the present tense to use the third person singular suffix ""s"".Languages that have some degree of inflection are synthetic languages. These can be highly inflected, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, or weakly inflected, such as English. Languages that are so inflected that a sentence can consist of a single highly inflected word (such as many American Indian languages) are called polysynthetic languages. Languages in which each inflection conveys only a single grammatical category, such as Finnish, are known as agglutinative languages, while languages in which a single inflection can convey multiple grammatical roles (such as both nominative case and plural, as in Latin and German) are called fusional. Languages such as Mandarin Chinese that never use inflections are called analytic or isolating.