Linking or Action Verb? (Sense words) Definition: Linking verb: A
... Linking verb: A linking verb is a verb that links a word in the predicate to the subject. That word will either be a noun (predicate noun), which will rename the subject or an adjective (predicate adjective), which will describe the subject. Action verb: A verb that shows action. It may or may not h ...
... Linking verb: A linking verb is a verb that links a word in the predicate to the subject. That word will either be a noun (predicate noun), which will rename the subject or an adjective (predicate adjective), which will describe the subject. Action verb: A verb that shows action. It may or may not h ...
... There is one exception with the 3rd conjugation on how it is handled in the present tense for some regular verbs. That is, there are some verbs that you have to insert the letters "ISC" after the infinitive root and before the present indicative ending for Io, Tu, Lui/Lei and Loro. Therefore, we con ...
Latin I Test Ch.1-7 Study Guide READING SECTION (30 Multiple
... ** Look back over homework sentences from worksheets and passages. ...
... ** Look back over homework sentences from worksheets and passages. ...
LECTURE 10
... the most sophisticated type of sentence we can use; is comprised of at least two independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses; as it is normally longer than other sentences, it is very important to punctuate it correctly. The team captain jumped for joy, and the fans cheered because we won ...
... the most sophisticated type of sentence we can use; is comprised of at least two independent clauses and one or more dependent clauses; as it is normally longer than other sentences, it is very important to punctuate it correctly. The team captain jumped for joy, and the fans cheered because we won ...
Week 21
... • A verb should agree in number with its subject. • The number of a subject is not changed by a phrase following the subject • Example: These shades of blue are my favorite ...
... • A verb should agree in number with its subject. • The number of a subject is not changed by a phrase following the subject • Example: These shades of blue are my favorite ...
Grammar wrap-up — Verbs, Adverbs, and Prepositions I realized
... In our western dialect we only have a few personal pronoun endings to worry about when conjugating verbs. Most of the time the verb doesn't change for person. Unlike other European languages, you can either use the personal pronoun endings or the separated stand-alone pronouns, but not both. cheanna ...
... In our western dialect we only have a few personal pronoun endings to worry about when conjugating verbs. Most of the time the verb doesn't change for person. Unlike other European languages, you can either use the personal pronoun endings or the separated stand-alone pronouns, but not both. cheanna ...
Verbs in Hittite
... desired actions). Both moods can be expressed in all grammatical persons, singular and plural. There is no specific grammatical form for modus irrealis, which is expressed instead by the particle -man- appearing in the beginning of a clause (-man- can also express a real wish for the future). ...
... desired actions). Both moods can be expressed in all grammatical persons, singular and plural. There is no specific grammatical form for modus irrealis, which is expressed instead by the particle -man- appearing in the beginning of a clause (-man- can also express a real wish for the future). ...
Year 2 Test 10 answers
... 5-6. (W2:6,22,24. Sp 2:27,28) The suffix ‘ness’ does not change the meaning of the root word. It turns an adjective into a noun (sadsadness). The prefixes ‘un’ and ‘dis’ mean ‘not’ or ‘opposite’. When added to a word, they give it the opposite meaning (Sp 1:30) ...
... 5-6. (W2:6,22,24. Sp 2:27,28) The suffix ‘ness’ does not change the meaning of the root word. It turns an adjective into a noun (sadsadness). The prefixes ‘un’ and ‘dis’ mean ‘not’ or ‘opposite’. When added to a word, they give it the opposite meaning (Sp 1:30) ...
Parts of speech
... heavy. But: The two boxes of books have to be moved. 4 Expressions of amounts require singular verbs: Ten dollars is not much these days. 5 There are some nouns which are singular although the form seems plural - the USA and the news are such examples: The USA is a diverse country. 6 Plural nou ...
... heavy. But: The two boxes of books have to be moved. 4 Expressions of amounts require singular verbs: Ten dollars is not much these days. 5 There are some nouns which are singular although the form seems plural - the USA and the news are such examples: The USA is a diverse country. 6 Plural nou ...
Verbs in Hittite
... desired actions). Both moods can be expressed in all grammatical persons, singular and plural. There is no specific grammatical form for modus irrealis, which is expressed instead by the particle -man- appearing in the beginning of a clause (-man- can also express a real wish for the future). ...
... desired actions). Both moods can be expressed in all grammatical persons, singular and plural. There is no specific grammatical form for modus irrealis, which is expressed instead by the particle -man- appearing in the beginning of a clause (-man- can also express a real wish for the future). ...
File
... Prepositions: above, across, after, against, along, around at, before, behind, below, beside, between, by, down, for, from, in, inside, into, like near, of, off, on, out, outside, over, through, to, under, underneath, up, with, without A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with a ...
... Prepositions: above, across, after, against, along, around at, before, behind, below, beside, between, by, down, for, from, in, inside, into, like near, of, off, on, out, outside, over, through, to, under, underneath, up, with, without A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with a ...
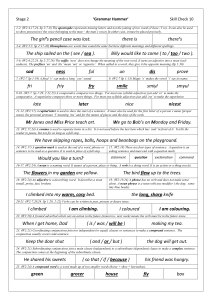
p28 Ir + A + Infinitive.ppsx
... Verbs that do not follow certain patterns are called IRREGULAR verbs. ...
... Verbs that do not follow certain patterns are called IRREGULAR verbs. ...
Future
... Used to tell what will happen in the future; “will” in English. Hablaré a su maestro. I will speak to his teacher. Conjecture probability, or speculation in the present tense. Juan tendrá cuarenta años. Juan must be forty years old. ...
... Used to tell what will happen in the future; “will” in English. Hablaré a su maestro. I will speak to his teacher. Conjecture probability, or speculation in the present tense. Juan tendrá cuarenta años. Juan must be forty years old. ...
Grammar Cheat Sheet 3 - Bowling Green City Schools
... Subject, Direct Object, Object of the Prepositional Phrase, Predicate Nominative, Object Complement Most commonly used linking verb- is Connects the subject to another noun( which usually follows the verb) in the sentence or connects to another adjective( which usually follows the verb) in the sente ...
... Subject, Direct Object, Object of the Prepositional Phrase, Predicate Nominative, Object Complement Most commonly used linking verb- is Connects the subject to another noun( which usually follows the verb) in the sentence or connects to another adjective( which usually follows the verb) in the sente ...
Underline the prepositional phrase in each of the following sentences
... Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. a) Use relative pronouns (who, whose, whom, which, that) and relative adverbs (where, when, and why). b) Form and use the progressive (e.g., I was walking; I am walking; I will be walking) verb ten ...
... Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. a) Use relative pronouns (who, whose, whom, which, that) and relative adverbs (where, when, and why). b) Form and use the progressive (e.g., I was walking; I am walking; I will be walking) verb ten ...
Grammar
... around, as, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, but, by, despite, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, onto, opposite, out, outside, over, past, since, through, toward, under, underneath, until, upon, with, within, without. ...
... around, as, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, but, by, despite, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, onto, opposite, out, outside, over, past, since, through, toward, under, underneath, until, upon, with, within, without. ...
Grammar for Better Writing Simple Modifiers
... These are not true adjectives in that they can not be compared (we can say clearer water but not chemistrier teacher. Most of them do not lend themselves to use in the predicate (verb) position (the chair is clear but not the teacher is chemistry). Although these words in their FORM are nouns, they ...
... These are not true adjectives in that they can not be compared (we can say clearer water but not chemistrier teacher. Most of them do not lend themselves to use in the predicate (verb) position (the chair is clear but not the teacher is chemistry). Although these words in their FORM are nouns, they ...
introduction to latin 2010
... 5. Adverbs: modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. 6. Prepositions: joins a noun or pronoun to some other word. 7. Conjunctions: connect words or groups of words (i.e. clauses). 8. Interjections: used to express strong or sudden feelings. ...
... 5. Adverbs: modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. 6. Prepositions: joins a noun or pronoun to some other word. 7. Conjunctions: connect words or groups of words (i.e. clauses). 8. Interjections: used to express strong or sudden feelings. ...
common english grammar errors
... Regular verbs in English end in –ed in both the past tense and past participle (work – worked – has worked), while irregular verbs often change form (take/ took, has taken). Their usage is particularly tricky in the past tense. The best way to learn irregular verb forms is to memorize them. Incorrec ...
... Regular verbs in English end in –ed in both the past tense and past participle (work – worked – has worked), while irregular verbs often change form (take/ took, has taken). Their usage is particularly tricky in the past tense. The best way to learn irregular verb forms is to memorize them. Incorrec ...
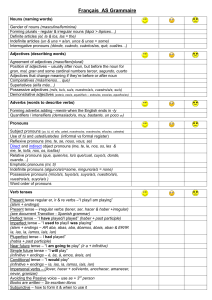
Français AS Grammaire
... Français AS Grammaire Nouns (naming words) Gender of nouns (masculine/feminine) Forming plurals - regular & irregular nouns (lápiz > lápices…) Definite articles (el, la & los, las = the) Indefinite articles (un & una = a/an, unos & unas = some) Interrogative pronouns (dónde, cuándo, cuántos/as, qué, ...
... Français AS Grammaire Nouns (naming words) Gender of nouns (masculine/feminine) Forming plurals - regular & irregular nouns (lápiz > lápices…) Definite articles (el, la & los, las = the) Indefinite articles (un & una = a/an, unos & unas = some) Interrogative pronouns (dónde, cuándo, cuántos/as, qué, ...
Types of Sentences - Mr Spencer`s Guide to English Language Arts
... - EXAMPLE: Neither Mark nor Judith will be allowed to go on the field trip. ...
... - EXAMPLE: Neither Mark nor Judith will be allowed to go on the field trip. ...
Film Strip
... • A action verb tells what the subject does, did, or will do. • What does the dog do? • The dog barks. ...
... • A action verb tells what the subject does, did, or will do. • What does the dog do? • The dog barks. ...