Mathematical model
... number of neurons for every hidden layer is different depending on the classification problem. Number of input layer and output layer usually come from number of attribute and class attribute. However there is no appropriate standard rule or theory to determine the optimal number of hidden nodes. In ...
... number of neurons for every hidden layer is different depending on the classification problem. Number of input layer and output layer usually come from number of attribute and class attribute. However there is no appropriate standard rule or theory to determine the optimal number of hidden nodes. In ...
Biopsychology The Nervous System
... tie brain structures to cognitive brain activities – SPECT : single proton emission computerized axial tomography, traces blood flow in the brain – SQUID : super conducting quantum interference device, senses tiny changes in the brain's magnetic fields and represents them in 3‐D, deals with elec ...
... tie brain structures to cognitive brain activities – SPECT : single proton emission computerized axial tomography, traces blood flow in the brain – SQUID : super conducting quantum interference device, senses tiny changes in the brain's magnetic fields and represents them in 3‐D, deals with elec ...
A General Purpose Architecture for Building Chris Eliasmith ()
... and controls a physically modelled arm. By presenting different visual inputs, the model can perform eight different tasks, including memorizing and writing a list of numbers, single-digit addition via counting, and flexible pattern completion in the Raven's Matrices task. This tutorial is meant to ...
... and controls a physically modelled arm. By presenting different visual inputs, the model can perform eight different tasks, including memorizing and writing a list of numbers, single-digit addition via counting, and flexible pattern completion in the Raven's Matrices task. This tutorial is meant to ...
week4am
... see depolarization (change from negative inside neuron to more positive) ◦ “threshold” – if a great enough depolarization occurs, an action potential will occur ◦ action potential – very quick – milliseconds Other terms – spike, firing, generating an AP ...
... see depolarization (change from negative inside neuron to more positive) ◦ “threshold” – if a great enough depolarization occurs, an action potential will occur ◦ action potential – very quick – milliseconds Other terms – spike, firing, generating an AP ...
Central nervous system (CNS)
... regulates the amount of water in your blood. About the size of a marble and found at the base of the cerebrum. It also releases HGH—controls how fast everything grows. Releases hormones that control all other glands. Referred to as the “master gland”. ...
... regulates the amount of water in your blood. About the size of a marble and found at the base of the cerebrum. It also releases HGH—controls how fast everything grows. Releases hormones that control all other glands. Referred to as the “master gland”. ...
A Neural Network Model for the Representation of Natural Language
... 1999), theories of linguistic analysis, and known variables drawn from the brain and cognitive sciences as well as previous neural network systems built for similar purposes. My basic hypothesis is that the association among concepts is primarily an expression of domain-general cognitive mechanisms ...
... 1999), theories of linguistic analysis, and known variables drawn from the brain and cognitive sciences as well as previous neural network systems built for similar purposes. My basic hypothesis is that the association among concepts is primarily an expression of domain-general cognitive mechanisms ...
The Nervous System (ppt).
... Master controlling and communicating system of the body Communicates by electrical impulses that cause rapid and specific responses ...
... Master controlling and communicating system of the body Communicates by electrical impulses that cause rapid and specific responses ...
Slide ()
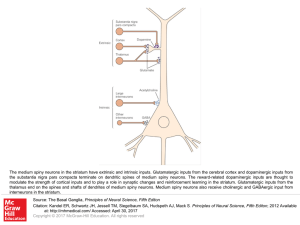
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
... The medium spiny neurons in the striatum have extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex and dopaminergic inputs from the substantia nigra pars compacta terminate on dendritic spines of medium spiny neurons. The reward-related dopaminergic inputs are thought to mod ...
1.nerve notes
... - They block the enzyme from destroying the neurotransmitter after the message has been sent, so they keep sending the message The receptors get worn out & stop working (this is addiction) Addiction is when the person physically needs the drug to function ...
... - They block the enzyme from destroying the neurotransmitter after the message has been sent, so they keep sending the message The receptors get worn out & stop working (this is addiction) Addiction is when the person physically needs the drug to function ...
BIOLOGY 12: U NIT M/N - C A. CHAPTER REVIEW 1. What are the
... 5. What is meant by the resting membrane potential? What is its value? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 5. What is meant by the resting membrane potential? What is its value? _____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Terms being described
... 11. It’s another name for motor neurons because of their direction of conduction. 13. It’s another name for sensory neurons because of their direction of conduction. 15. It’s the ability of a potential change to spread along the axon that is analogous to the conduction of electricity by a wire. 17. ...
... 11. It’s another name for motor neurons because of their direction of conduction. 13. It’s another name for sensory neurons because of their direction of conduction. 15. It’s the ability of a potential change to spread along the axon that is analogous to the conduction of electricity by a wire. 17. ...
Histology of Nervous Tissue
... These neurons are present in some sense organs (e.g., the vestibular/cochlear mechanism). • c. Multipolar neurons possess a single axon and more than one dendrite. • These neurons are the most common type of neuron in vertebrates. • d. Pseudounipolar neurons possess a single process that extends • f ...
... These neurons are present in some sense organs (e.g., the vestibular/cochlear mechanism). • c. Multipolar neurons possess a single axon and more than one dendrite. • These neurons are the most common type of neuron in vertebrates. • d. Pseudounipolar neurons possess a single process that extends • f ...
Lecture 15
... Blynel, J. and Floreano, D. (2002) Levels of Dynamics and Adaptive Behavior in Evolutionary Neural Controllers. In B. Hallam, D. Floreano, J. Hallam, G. Hayes, and J.-A. Meyer, editors. From Animals to Animats 7: Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Simulation on Adaptive Behavior, ...
... Blynel, J. and Floreano, D. (2002) Levels of Dynamics and Adaptive Behavior in Evolutionary Neural Controllers. In B. Hallam, D. Floreano, J. Hallam, G. Hayes, and J.-A. Meyer, editors. From Animals to Animats 7: Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Simulation on Adaptive Behavior, ...
Slide 1
... Association areas - areas within each lobe of the cortex responsible for the coordination and interpretation of information, as well as higher mental processing. Broca’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Broca’s area (usually in left frontal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable ...
... Association areas - areas within each lobe of the cortex responsible for the coordination and interpretation of information, as well as higher mental processing. Broca’s aphasia - condition resulting from damage to Broca’s area (usually in left frontal lobe), causing the affected person to be unable ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
MOTILITY-FLOW AND GROWTH CONE NAVIGATION ANALYSIS
... • Experimental system that represents a simple and non- invasive approach to study neuronal growth • Special image processing algorithms were adapted • Detection of very small and slowly moving spatial changes, and to inspect low contrast image features characteristic of motion and dynamics of a liv ...
... • Experimental system that represents a simple and non- invasive approach to study neuronal growth • Special image processing algorithms were adapted • Detection of very small and slowly moving spatial changes, and to inspect low contrast image features characteristic of motion and dynamics of a liv ...
Aotearoa Neuroscience Postdoctoral Fellow Projects
... plasticity of inhibitory receptor synaptic complexes throughout the entire human brain. To delineate the postsynaptic complexity, we will adopt an ...
... plasticity of inhibitory receptor synaptic complexes throughout the entire human brain. To delineate the postsynaptic complexity, we will adopt an ...
Nervous System Notes
... • Sensory (afferent) Division – Sends impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors in body – Somatic sensory fibers: messages from skin, muscles and joints – Visceral sensory fibers: messages from internal organs ...
... • Sensory (afferent) Division – Sends impulses to the CNS from sensory receptors in body – Somatic sensory fibers: messages from skin, muscles and joints – Visceral sensory fibers: messages from internal organs ...
Nervous Tissue (Ch
... 2. dendrites - receive - short, highly branched - not usually myelinated 3. axon - sends - long, few branches (except for axon collaterals) - no Nissl bodies - originates at axon hillock - cytoplasm = axoplasm; plasma membrane = axolemma - terminal arborization: “tree” synapses with another neur ...
... 2. dendrites - receive - short, highly branched - not usually myelinated 3. axon - sends - long, few branches (except for axon collaterals) - no Nissl bodies - originates at axon hillock - cytoplasm = axoplasm; plasma membrane = axolemma - terminal arborization: “tree” synapses with another neur ...
AL4AI--Google2007
... Evolution found and stuck with nervous systems across all levels of complexity ...
... Evolution found and stuck with nervous systems across all levels of complexity ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • All parts of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) • All parts of the nervous system lying outside the brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
Central Nervous System
... Central Nervous System • Consist of the brain and vertebrates and the spinal cord. ...
... Central Nervous System • Consist of the brain and vertebrates and the spinal cord. ...
What is a neuron?
... Sensory (Afferent) Neurons. They are responsible for conveying information to the Central Nervous System. You can tell that these Neurons have huge cell bodies. These are some of the largest cells in the body. The larger the cell body, the further away the information is coming from.” Red arrows - C ...
... Sensory (Afferent) Neurons. They are responsible for conveying information to the Central Nervous System. You can tell that these Neurons have huge cell bodies. These are some of the largest cells in the body. The larger the cell body, the further away the information is coming from.” Red arrows - C ...
What is a neuron?
... Sensory (Afferent) Neurons. They are responsible for conveying information to the Central Nervous System. You can tell that these Neurons have huge cell bodies. These are some of the largest cells in the body. The larger the cell body, the further away the information is coming from.” Red arrows - C ...
... Sensory (Afferent) Neurons. They are responsible for conveying information to the Central Nervous System. You can tell that these Neurons have huge cell bodies. These are some of the largest cells in the body. The larger the cell body, the further away the information is coming from.” Red arrows - C ...