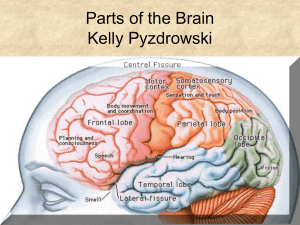
neurons
... hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task (ex: face recognition) and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
... hemispheric differences in mental abilities. A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task (ex: face recognition) and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. ...
Document
... b. The choline is then taken up by the axon terminal and used to make more ACh 2. What happens in postsynaptic cell? a. Binding to receptor initiates release of a “second messenger” into the cytoplasm of the postsynaptic cell. This is most often Ca ion, cyclic AMP (= cAMP), or cyclic GMP (= cGMP). b ...
... b. The choline is then taken up by the axon terminal and used to make more ACh 2. What happens in postsynaptic cell? a. Binding to receptor initiates release of a “second messenger” into the cytoplasm of the postsynaptic cell. This is most often Ca ion, cyclic AMP (= cAMP), or cyclic GMP (= cGMP). b ...
Neurobiology
... inside, the body. The processing within the brain can range from a knee-jerk reaction — which takes place entirely in the spinal cord — to the strategy adopted by a master chess player. In humans, we usually call this “thinking.” The output is most often a body movement, which results from the actio ...
... inside, the body. The processing within the brain can range from a knee-jerk reaction — which takes place entirely in the spinal cord — to the strategy adopted by a master chess player. In humans, we usually call this “thinking.” The output is most often a body movement, which results from the actio ...
Chapter_03_4E
... • Changes in membrane potential occur when ion gates in the membrane open, permitting ions to move from one side to the other - Depolarization (membrane potential becomes less negative) - Hyperpolarization (membrane potential becomes more negative) • If the membrane potential depolarizes by 15 mV to ...
... • Changes in membrane potential occur when ion gates in the membrane open, permitting ions to move from one side to the other - Depolarization (membrane potential becomes less negative) - Hyperpolarization (membrane potential becomes more negative) • If the membrane potential depolarizes by 15 mV to ...
Nervous System
... messages to other neurons Dendrites- extend from the cell body and pick up signals from the environment ...
... messages to other neurons Dendrites- extend from the cell body and pick up signals from the environment ...
Introduction to Machine Intelligence
... know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across neuronal membranes. Recording devices must intercept voltag ...
... know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across neuronal membranes. Recording devices must intercept voltag ...
Introduction to Machine Intelligence
... know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across neuronal membranes. Recording devices must intercept voltag ...
... know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across neuronal membranes. Recording devices must intercept voltag ...
Unit 3D Worksheet 1) In the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS
... 2) The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) has two branches, the ______________and the_________________. The Sympathetic NS which is referred to as the ______or _______ response called for during____________, excitement, ______________and embarrassment. It works with the ____________Nervous System (SNS) ...
... 2) The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) has two branches, the ______________and the_________________. The Sympathetic NS which is referred to as the ______or _______ response called for during____________, excitement, ______________and embarrassment. It works with the ____________Nervous System (SNS) ...
the brain - WordPress.com
... structure is rather old. This system contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus. The ...
... structure is rather old. This system contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, and hippocampus. The ...
Theory of Arachnid Prey Localization
... The key question is now: given the data from these eight sense organs, how does the sand scorpion—or for that matter any vibration-sensitive arachnid—determine the stimulus direction? To answer this question we must know the “hardware,” viz., the anatomy of the relevant part of the animal’s brain [9 ...
... The key question is now: given the data from these eight sense organs, how does the sand scorpion—or for that matter any vibration-sensitive arachnid—determine the stimulus direction? To answer this question we must know the “hardware,” viz., the anatomy of the relevant part of the animal’s brain [9 ...
File
... The proposed mechanism is rather simple. Each time an individual sees an action done by another individual, neurons that represent that action are activated in the observer’s premotor cortex. ...
... The proposed mechanism is rather simple. Each time an individual sees an action done by another individual, neurons that represent that action are activated in the observer’s premotor cortex. ...
Introduction to the Nervous System and Nerve Tissue
... Introduction to the Nervous System and Nerve Tissue Three Basic Functions 1. Sensory Functions: Sensory receptors detect both internal and external stimuli. Functional unit: Sensory or Afferent Neurons 2. Integrative Functions: CNS integrates sensory input and makes decisions regarding appropriate r ...
... Introduction to the Nervous System and Nerve Tissue Three Basic Functions 1. Sensory Functions: Sensory receptors detect both internal and external stimuli. Functional unit: Sensory or Afferent Neurons 2. Integrative Functions: CNS integrates sensory input and makes decisions regarding appropriate r ...
File
... information (except smell) goes here first 2. The Hypothalamus- monitors the internal systems to maintain the normal state of the body (homeostasis) by controlling the release of hormones it can moderate body functions (sleep, food intake, and liquid intake) WARNING- if out of balance difficult to c ...
... information (except smell) goes here first 2. The Hypothalamus- monitors the internal systems to maintain the normal state of the body (homeostasis) by controlling the release of hormones it can moderate body functions (sleep, food intake, and liquid intake) WARNING- if out of balance difficult to c ...
Brain growth, development and Autism
... disintegrative disorder and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. The term "spectrum" in ASD refers to the wide range of symptoms and severity. Although "Asperger's syndrome" is no longer a diagnosis, it is generally thought that this condition is a mild form of the disorder. Doc ...
... disintegrative disorder and pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified. The term "spectrum" in ASD refers to the wide range of symptoms and severity. Although "Asperger's syndrome" is no longer a diagnosis, it is generally thought that this condition is a mild form of the disorder. Doc ...
What Our Brains Can Teach Us
... lead to a much deeper understanding of how the brain works. The ultimate aim, probably not reachable for decades, is to answer such fundamental questions as how the brain generates thoughts, dreams, memories, perception and consciousness — and to find ways to intervene and influence such brain activ ...
... lead to a much deeper understanding of how the brain works. The ultimate aim, probably not reachable for decades, is to answer such fundamental questions as how the brain generates thoughts, dreams, memories, perception and consciousness — and to find ways to intervene and influence such brain activ ...
Chapters 11: Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous
... 3. Neurotransmitters bind to ____________ on postsynaptic neuron 4. Ion channels open, leading to a local potential and possibly an AP if threshold is reached Postsynaptic potentials – can be Excitatory or Inhibitory: a. Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) = Membrane potential moves ___________ ...
... 3. Neurotransmitters bind to ____________ on postsynaptic neuron 4. Ion channels open, leading to a local potential and possibly an AP if threshold is reached Postsynaptic potentials – can be Excitatory or Inhibitory: a. Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) = Membrane potential moves ___________ ...
Ch12 notes Martini 9e
... • The sodium–potassium exchange pump ejects 3 Na+ ions for every 2 K+ ions that it brings into the cell • It serves to stabilize the resting potential when the ratio of Na+ entry to K+ loss through passive channels is 3:2 • At the normal resting potential, these passive and active mechanisms are in ...
... • The sodium–potassium exchange pump ejects 3 Na+ ions for every 2 K+ ions that it brings into the cell • It serves to stabilize the resting potential when the ratio of Na+ entry to K+ loss through passive channels is 3:2 • At the normal resting potential, these passive and active mechanisms are in ...
Document
... Idealized neurons are used in artificial neural nets to model brain function Neurons typically form two-way pathways, providing the basis for reentrant connectivity The nervous system is formed into arrays or maps of neurons Hebbian cell assemblies underlie the change from transient to stable, ...
... Idealized neurons are used in artificial neural nets to model brain function Neurons typically form two-way pathways, providing the basis for reentrant connectivity The nervous system is formed into arrays or maps of neurons Hebbian cell assemblies underlie the change from transient to stable, ...
weiten6_PPT03
... such as pain, drug use, and some diseases—can be explained in terms of how they alter one or more of these processes (usually at synapses releasing a specific Table of Contents neurotransmitter). ...
... such as pain, drug use, and some diseases—can be explained in terms of how they alter one or more of these processes (usually at synapses releasing a specific Table of Contents neurotransmitter). ...
SPHS 4050, Neurological bases, PP 03a
... gyrus) is part of the LIMBIC SYSTEM which includes the hippocampus and amygdala, interconneted with parts of the diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus) and olfactory (smell) system. The limbic system is strongly associated with memory and emotion ...
... gyrus) is part of the LIMBIC SYSTEM which includes the hippocampus and amygdala, interconneted with parts of the diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus) and olfactory (smell) system. The limbic system is strongly associated with memory and emotion ...
NERVOUS SYSTEMS – FUNCTION AT THE CELLULAR LEVEL
... - ion channels are selective and dynamic – only one type of ion can pass; can be open or closed (gated) At rest, some K+ channels are always open free movement of K+ in or out ...
... - ion channels are selective and dynamic – only one type of ion can pass; can be open or closed (gated) At rest, some K+ channels are always open free movement of K+ in or out ...
Structures and Learning Simulations
... Recurrence: secondary, repeated activation; from this come networks with recurrence (bidirectional). Bottom-up and vice versa, or recognition and imagination. Recurrence makes possible the completion of images, formation of resonances between associated representations, strengthening of weak activat ...
... Recurrence: secondary, repeated activation; from this come networks with recurrence (bidirectional). Bottom-up and vice versa, or recognition and imagination. Recurrence makes possible the completion of images, formation of resonances between associated representations, strengthening of weak activat ...
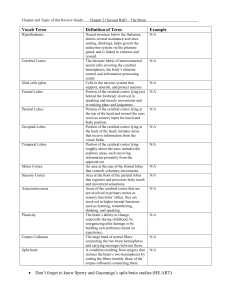
Chapter 2 - The Brain (Part II)
... Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body t ...
... Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements. Area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body t ...
There are about 3 million miles of axons in the human brain. The
... important for the rapid-eye movements of REM sleep (one of the 5 stages of sleep and usually makes up 90-120 minutes of an adult’s sleep) and may be important for turning REM sleep on and off. • Functions of the MIDBRAIN include controlling responses to sight, eye Movement, pupil dilation, hearing a ...
... important for the rapid-eye movements of REM sleep (one of the 5 stages of sleep and usually makes up 90-120 minutes of an adult’s sleep) and may be important for turning REM sleep on and off. • Functions of the MIDBRAIN include controlling responses to sight, eye Movement, pupil dilation, hearing a ...
Autonomic nervous system
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...
... • Receptors for _______________ come in 2 forms: __________ = excitatory (Na+ channels) __________ = excitatory/inhibitory (G proteins) • ______________________ comes from neurons and/or adrenal medulla • Effects… near sympathetic usually excitatory otherwise variable responses (see table 16.3) ...