Physiologically-Inspired Model for the Visual Tuning Properties of
... the positions of the object and the effector is extracted from the highest level of the form-hierarchy, which is not completely position-invariant and thus encodes these positions coarsely within a retinal frame of reference. In addition, the recognized effector view predicts a range of object posi ...
... the positions of the object and the effector is extracted from the highest level of the form-hierarchy, which is not completely position-invariant and thus encodes these positions coarsely within a retinal frame of reference. In addition, the recognized effector view predicts a range of object posi ...
NSOM: A Real-Time Network-Based Intrusion Detection System
... network traffic to or from our host, discarding packets that are intended for other hosts. Tcpdump is run as a background process, which dumps the information it collects into a file on a regular basis. Every time we collect 50 packets we store them in a file for further preprocessing and classifica ...
... network traffic to or from our host, discarding packets that are intended for other hosts. Tcpdump is run as a background process, which dumps the information it collects into a file on a regular basis. Every time we collect 50 packets we store them in a file for further preprocessing and classifica ...
Rubin, 2007
... it was initially concluded that peptides and amino acids could not be neurotransmitters, but we have since learned that this view was wrong. Bloom concluded his lecture by asking what the history of neuroscience will look like in 10 –15 years. Suppose we were able to map every pathway in the mammali ...
... it was initially concluded that peptides and amino acids could not be neurotransmitters, but we have since learned that this view was wrong. Bloom concluded his lecture by asking what the history of neuroscience will look like in 10 –15 years. Suppose we were able to map every pathway in the mammali ...
brain1
... At birth, the human brain weighs less than a pound (0.78-0.88 pounds or 350-400 g). As a child grows, the number of cell remains relatively stable, but the cells grow in size and the number of connections increases. The human brain reaches its full size at about 6 years of age. ...
... At birth, the human brain weighs less than a pound (0.78-0.88 pounds or 350-400 g). As a child grows, the number of cell remains relatively stable, but the cells grow in size and the number of connections increases. The human brain reaches its full size at about 6 years of age. ...
Congenital Malformation & Hydrocephalus
... Hydrocephalus developing after fusion of the sutures, in contrast, is associated with expansion of the ventricles and increased intracranial pressure, without a change in head circumference If there is an obstacle to the flow of CSF within the ventricular system, then a portion of the ventricles enl ...
... Hydrocephalus developing after fusion of the sutures, in contrast, is associated with expansion of the ventricles and increased intracranial pressure, without a change in head circumference If there is an obstacle to the flow of CSF within the ventricular system, then a portion of the ventricles enl ...
Cognitive Development - Oakland Schools Moodle
... Extremely important medical research area Research continues to show that a baby’s brain capacity is even greater than we ever imagined Our brains are stimulated through our senses Brain function is due to the brain’s capabilities as well as outside experiences ...
... Extremely important medical research area Research continues to show that a baby’s brain capacity is even greater than we ever imagined Our brains are stimulated through our senses Brain function is due to the brain’s capabilities as well as outside experiences ...
Nonmonotonic inferences in neural networks
... Thirdly, the next sections will be devoted to showing that schemata support default assumptions about the environ-ment. The neural network is thus capable of filling in missing information. There are some elementary operations on schemata that will be of interest when we consider nonmonotonic infere ...
... Thirdly, the next sections will be devoted to showing that schemata support default assumptions about the environ-ment. The neural network is thus capable of filling in missing information. There are some elementary operations on schemata that will be of interest when we consider nonmonotonic infere ...
Nervous System Overview
... • Motor (efferent) division (CNS to effectors) response to the environment through excitation of: – visceral motor division (ANS) Involuntary effectors: cardiac, smooth muscle, glands • sympathetic division (fight or flight) • parasympathetic division (rest and digestion) – somatic motor division (v ...
... • Motor (efferent) division (CNS to effectors) response to the environment through excitation of: – visceral motor division (ANS) Involuntary effectors: cardiac, smooth muscle, glands • sympathetic division (fight or flight) • parasympathetic division (rest and digestion) – somatic motor division (v ...
Wagner for the Womb
... short-term to long-term memory, and in spatial navigation. Damages to this area of the brain result in memory loss. Alzheimer’s disease is an example where the loss of memory is largely attributed to damages at the hippocampus. On the contrary, studies have found that increased neurogenesis at the h ...
... short-term to long-term memory, and in spatial navigation. Damages to this area of the brain result in memory loss. Alzheimer’s disease is an example where the loss of memory is largely attributed to damages at the hippocampus. On the contrary, studies have found that increased neurogenesis at the h ...
The Nervous System
... Smell – chemically sensitive neurons in the nose detect chemicals and transmit the information to the brain where smell information is processed & analyzed. ...
... Smell – chemically sensitive neurons in the nose detect chemicals and transmit the information to the brain where smell information is processed & analyzed. ...
Med Term Chapter 10
... from nerve cells. In multiple sclerosis, the immune system's T cells and B cells attack oligodendrocytes, ultimately damaging the myelin sheath to the point that the electrical signals transmitted by the axons beneath it are disrupted. (David Rowitch, et al. University of California - San Francisco. ...
... from nerve cells. In multiple sclerosis, the immune system's T cells and B cells attack oligodendrocytes, ultimately damaging the myelin sheath to the point that the electrical signals transmitted by the axons beneath it are disrupted. (David Rowitch, et al. University of California - San Francisco. ...
Optogenetics for Studying the Spinal Control of Movement
... “final common pathway” of the central nervous system, less is known about the complex network of spinal interneurons, populated by a mosaic of excitatory and inhibitory interneurons sub-types (e.g. serotonin, somatostatin, parvalbumin, glycine). Recently, the newly developed field of optogenetics ha ...
... “final common pathway” of the central nervous system, less is known about the complex network of spinal interneurons, populated by a mosaic of excitatory and inhibitory interneurons sub-types (e.g. serotonin, somatostatin, parvalbumin, glycine). Recently, the newly developed field of optogenetics ha ...
Optogenetics
... suppress firing of neurons in the subthalamic nucleus (STN). Optical neuromodulation could be used to shut down excitatory glutamatergic neurons in the STN that express halorhodopsin (NpHR) under the control of an excitatory neuron-specific promoter; this cell type specificity will result in a more ...
... suppress firing of neurons in the subthalamic nucleus (STN). Optical neuromodulation could be used to shut down excitatory glutamatergic neurons in the STN that express halorhodopsin (NpHR) under the control of an excitatory neuron-specific promoter; this cell type specificity will result in a more ...
Muscle
... -The autonomic nervous system responds to a variety of sensory inputs: most sensory information from visceral organs reaches the brain by way of the vagus nerve. Visceral sensory information from head and neck enter the brain through the glossopharyngeal and facial nerves. These inputs synapse in th ...
... -The autonomic nervous system responds to a variety of sensory inputs: most sensory information from visceral organs reaches the brain by way of the vagus nerve. Visceral sensory information from head and neck enter the brain through the glossopharyngeal and facial nerves. These inputs synapse in th ...
I. Nerve Organization
... sensory information from nose, eyes, and ears; in land-dwelling vertebrates, contains the highest integrating centers ...
... sensory information from nose, eyes, and ears; in land-dwelling vertebrates, contains the highest integrating centers ...
The Portable Neuromodulation Stimulator (PoNS™) FACT SHEET
... Non-Invasive Neuromodulation (CN-NINM). Therapy consists of targeted physical, occupational, relaxation and cognitive exercises, based on the patient's deficits. Clinical research shows that electrical stimulation of the tongue activates two major cranial nerves – the lingual nerve (part of the trig ...
... Non-Invasive Neuromodulation (CN-NINM). Therapy consists of targeted physical, occupational, relaxation and cognitive exercises, based on the patient's deficits. Clinical research shows that electrical stimulation of the tongue activates two major cranial nerves – the lingual nerve (part of the trig ...
Alcohol on the nervous system
... • THC attacks certain receptors that control memory, thought, concentration, time and depth perception, and coordinated movement. THC also affects re-uptake of Marijuana. ...
... • THC attacks certain receptors that control memory, thought, concentration, time and depth perception, and coordinated movement. THC also affects re-uptake of Marijuana. ...
Grounded cognition Mirror neurons Mirror neurons Mirror neurons in
... system, facilitated by action-execution–actionobservation matching property of neurons in Broca's area paved the way to the evolution of the open vocalization system present in ...
... system, facilitated by action-execution–actionobservation matching property of neurons in Broca's area paved the way to the evolution of the open vocalization system present in ...
Intro to Remote Sensing
... The motivation for the development of neural network technology stemmed from the desire to develop an artificial system that could perform "intelligent" tasks similar to those performed by the human brain (thousands of different inputs-neurons, output to many other neurons), with ...
... The motivation for the development of neural network technology stemmed from the desire to develop an artificial system that could perform "intelligent" tasks similar to those performed by the human brain (thousands of different inputs-neurons, output to many other neurons), with ...
The Signal - WM Keck Center for Behavioral Biology
... people. Olivera went on to elaborate how he and his colleagues started getting interested in analyzing the venom of the magician’s cone. It turned out that there are many different components in it, including toxins that act similar to snake toxins that block acetylcholine receptors as well as toxin ...
... people. Olivera went on to elaborate how he and his colleagues started getting interested in analyzing the venom of the magician’s cone. It turned out that there are many different components in it, including toxins that act similar to snake toxins that block acetylcholine receptors as well as toxin ...
Small System of Neurons
... Ethologists (Lorenz, Tinbergen, and Frisch) demonstrated that there are commonalities in animal behavior. Thus, such commonality suggests that their may be some underlying common neuronal mechanisms (example: cellular and molecular similarities between our neurons and synapses). ...
... Ethologists (Lorenz, Tinbergen, and Frisch) demonstrated that there are commonalities in animal behavior. Thus, such commonality suggests that their may be some underlying common neuronal mechanisms (example: cellular and molecular similarities between our neurons and synapses). ...
Central Nervous System
... – Reticular formation in the brainstem receives impulses from the spinal cord – Relays signals to thalamus then to cerebral cortex – Continual excitement of the neurons in this system is necessary for a person to remain in a conscious state ...
... – Reticular formation in the brainstem receives impulses from the spinal cord – Relays signals to thalamus then to cerebral cortex – Continual excitement of the neurons in this system is necessary for a person to remain in a conscious state ...
Inside the Human Brain - Hale
... to get up before they have received enough sleep. As a result most adolescents are not able function properly in school as they are still in a sleep like ...
... to get up before they have received enough sleep. As a result most adolescents are not able function properly in school as they are still in a sleep like ...
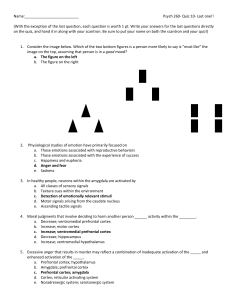
Quiz 10
... b. Recognition of emotion using tone of voice cues c. Grammar d. Facial expression of emotion e. Autonomic reactivity 8. The amygdala is most definitely involved in the recognition of _____ communicated via ____ a. Fear; facial expression b. Happiness; tone of voice c. Fear; tone of voice d. Happine ...
... b. Recognition of emotion using tone of voice cues c. Grammar d. Facial expression of emotion e. Autonomic reactivity 8. The amygdala is most definitely involved in the recognition of _____ communicated via ____ a. Fear; facial expression b. Happiness; tone of voice c. Fear; tone of voice d. Happine ...