Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 7: PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Olfactory neurons (first order neurons) to mitral cells (second order neurons) in olfactory bulb in forebrain to olfactory tubercle (in cerebrum, not in thalamus) to olfactory cortex and to limbic system (both in cerebral cortex) via third order neurons. This is an evolutionarily ancient pathway. A ...
... Olfactory neurons (first order neurons) to mitral cells (second order neurons) in olfactory bulb in forebrain to olfactory tubercle (in cerebrum, not in thalamus) to olfactory cortex and to limbic system (both in cerebral cortex) via third order neurons. This is an evolutionarily ancient pathway. A ...
Instrumental Conditioning Driven by Apparently Neutral Stimuli: A
... (a) phasic DA responses have been recorded following stimuli with no apparent rewarding value, if these stimuli have not been previously shown to the organism: novelty causes phasic DA independently of the appetitive value of the stimulus; (b) while the time required to establish an association vari ...
... (a) phasic DA responses have been recorded following stimuli with no apparent rewarding value, if these stimuli have not been previously shown to the organism: novelty causes phasic DA independently of the appetitive value of the stimulus; (b) while the time required to establish an association vari ...
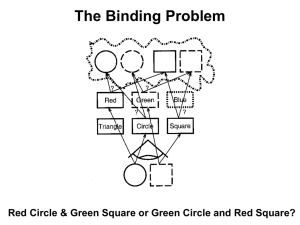
Optional extra slides on the Binding Problem
... Synchrony might also contribute to synaptic plasticity : Dynamic interplay between LTD and LTP could work to create new connections in response to a stimulus that are reset to near initial conditions when the stimulus is removed (e.g. Loebel and Tsyodyks, 2002). ...
... Synchrony might also contribute to synaptic plasticity : Dynamic interplay between LTD and LTP could work to create new connections in response to a stimulus that are reset to near initial conditions when the stimulus is removed (e.g. Loebel and Tsyodyks, 2002). ...
1. A unicellular protest may use a contractile vacuole to expel
... 8. What is the mechanism for the filtration of blood within the nephron? a. The active transport of Na+ and glucose, followed by osmosis. b. Both active and passive secretion of ions, toxins, and ammonia ...
... 8. What is the mechanism for the filtration of blood within the nephron? a. The active transport of Na+ and glucose, followed by osmosis. b. Both active and passive secretion of ions, toxins, and ammonia ...
Biopsychology – Paper 2
... What are neurons? Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue (the brain, spinal cord, PNS etc). They detect internal and external changes and form the communication link between the central nervous system, the brain and spinal cord and every part of the body. Neurons are microscopic in size a ...
... What are neurons? Neurons are the main components of nervous tissue (the brain, spinal cord, PNS etc). They detect internal and external changes and form the communication link between the central nervous system, the brain and spinal cord and every part of the body. Neurons are microscopic in size a ...
The BRAIN - davis.k12.ut.us
... Lead directly from the brain to various parts of the head, neck, and trunk Some involved in the special senses (such as seeing, hearing, and taste) Others control muscles in the face or regulate glands The nerves are named and numbered (according to their location, from the front of the brain to the ...
... Lead directly from the brain to various parts of the head, neck, and trunk Some involved in the special senses (such as seeing, hearing, and taste) Others control muscles in the face or regulate glands The nerves are named and numbered (according to their location, from the front of the brain to the ...
The CNS Efficiency Model of the Chiropractic Subluxation
... Immune System: The brain and the immune system are the two major adaptive systems of the body. During an immune response the brain and the immune system "talk to each other" and this process is essential for maintaining homeostasis. Two major pathway systems are involved in this cross-talk: the hypo ...
... Immune System: The brain and the immune system are the two major adaptive systems of the body. During an immune response the brain and the immune system "talk to each other" and this process is essential for maintaining homeostasis. Two major pathway systems are involved in this cross-talk: the hypo ...
Photo Album
... Figure 19.5 Neural tuning curves based on rate coding. (A) Orientation tuning curve from visual cortex. The firing rate of the neuron changes as a function of the orientation of the bar of light presented in the cell’s receptive field. The top shows peristimulus time histograms of the firing rate o ...
... Figure 19.5 Neural tuning curves based on rate coding. (A) Orientation tuning curve from visual cortex. The firing rate of the neuron changes as a function of the orientation of the bar of light presented in the cell’s receptive field. The top shows peristimulus time histograms of the firing rate o ...
NervousSystemPPT
... Chemical , Electrical In electrical synapses, ionic current spreads directly from one cell to another through tubular structures called connexons. A cluster of 100 or so connexons forms a pathway (connection) called a GAP JUNCTION between adjacent cells. Gap junctions are common between cardiac ...
... Chemical , Electrical In electrical synapses, ionic current spreads directly from one cell to another through tubular structures called connexons. A cluster of 100 or so connexons forms a pathway (connection) called a GAP JUNCTION between adjacent cells. Gap junctions are common between cardiac ...
Biology 232
... conscious sensations can also affect the ANS (eg. light, sound, taste) integrating centers – hypothalamus, brain stem, spinal cord, and limbic system; little conscious perception or voluntary control autonomic motor neurons – 2-neuron pathways from CNS; have excitatory or inhibitory effect on effect ...
... conscious sensations can also affect the ANS (eg. light, sound, taste) integrating centers – hypothalamus, brain stem, spinal cord, and limbic system; little conscious perception or voluntary control autonomic motor neurons – 2-neuron pathways from CNS; have excitatory or inhibitory effect on effect ...
temporal visual event recognition
... in the ventral visual pathway [2]. How the brain creates prediction signals in general relates to the fundamental question of how the brain represents time. Buonomano [4] discussed the two prevalent views of how this may be – “labeled lines”, in which each neuron’s firing can represent events on dif ...
... in the ventral visual pathway [2]. How the brain creates prediction signals in general relates to the fundamental question of how the brain represents time. Buonomano [4] discussed the two prevalent views of how this may be – “labeled lines”, in which each neuron’s firing can represent events on dif ...
research statement
... With raising awareness and deepening neurobiological knowledge of neural processes that take place in living creatures and the development of computational techniques, it is possible to build complex dynamic, reactive neural automatically reconfigurable associative systems for modeling real machine ...
... With raising awareness and deepening neurobiological knowledge of neural processes that take place in living creatures and the development of computational techniques, it is possible to build complex dynamic, reactive neural automatically reconfigurable associative systems for modeling real machine ...
Understanding the brain by controlling neural activity
... changes because neurons with similar response properties can be found in close proximity to one other, like for instance in cortical columns [18,19], and therefore can be stimulated together. Thus, electrical microstimulation methods have primarily been applied in brain structures exhibiting an anat ...
... changes because neurons with similar response properties can be found in close proximity to one other, like for instance in cortical columns [18,19], and therefore can be stimulated together. Thus, electrical microstimulation methods have primarily been applied in brain structures exhibiting an anat ...
Blue-Brain Technology
... • Traveling into the spine and brain, they will be able to monitor the activity and structure of our central nervous system. • They will be able to provide an interface with computer that is as close as our mind can be while we still reside in our biological form . ...
... • Traveling into the spine and brain, they will be able to monitor the activity and structure of our central nervous system. • They will be able to provide an interface with computer that is as close as our mind can be while we still reside in our biological form . ...
Reticular Activating System
... All sensory input that enters brain via the medulla is also sent to neurons of the reticular formation. These neurons may monitor sensory input for importance. May alert higher brain centers when critical input is detected. ...
... All sensory input that enters brain via the medulla is also sent to neurons of the reticular formation. These neurons may monitor sensory input for importance. May alert higher brain centers when critical input is detected. ...
48_Lectures_PPT
... • The vast majority of synapses are chemical synapses • In a chemical synapse, a presynaptic neuron releases chemical neurotransmitters stored in the synaptic terminal ...
... • The vast majority of synapses are chemical synapses • In a chemical synapse, a presynaptic neuron releases chemical neurotransmitters stored in the synaptic terminal ...
test - Scioly.org
... c. breakdown of the membrane structure d. all of the above 23.The action potential is measured in millivolts [mVO and is ranged from: a. -90mV to +20mV b. -70mVto +30mV c. -65mV to +40mV d. -30mV to +60mV 24. With an action potential, depolarization of the axomembrane is recorded as the gates open, ...
... c. breakdown of the membrane structure d. all of the above 23.The action potential is measured in millivolts [mVO and is ranged from: a. -90mV to +20mV b. -70mVto +30mV c. -65mV to +40mV d. -30mV to +60mV 24. With an action potential, depolarization of the axomembrane is recorded as the gates open, ...
File - Wk 1-2
... trabeculae are the subarachnoid space (communicates with ventricles of the brain) which is filled with CSF and completely separated from subdural space. It functions to protect CNS from trauma. Composed of CT devoid of BV’s. - Pia mater: loose CT containing BV’s. Close to nerve tissue but not indire ...
... trabeculae are the subarachnoid space (communicates with ventricles of the brain) which is filled with CSF and completely separated from subdural space. It functions to protect CNS from trauma. Composed of CT devoid of BV’s. - Pia mater: loose CT containing BV’s. Close to nerve tissue but not indire ...
Thalamus & Hypothalamus
... • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
... • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
Atomic computing-a different perspective on massively parallel
... delays are present in both the entities and their interconnect, we may, without loss of modelling accuracy, roll the interconnect delay into the entity model and treat the interconnect as zero-delay. The physical system under simulation - neural aggregates - consist of an interconnect topology (whi ...
... delays are present in both the entities and their interconnect, we may, without loss of modelling accuracy, roll the interconnect delay into the entity model and treat the interconnect as zero-delay. The physical system under simulation - neural aggregates - consist of an interconnect topology (whi ...
PID *****2515 1.Why is it difficult to understand olfactory neural
... is hard to know their exact function. ...
... is hard to know their exact function. ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM GENERALITY – INTRODUCTION
... neurons that innervate skeletal muscles. 2. the autonomic nervous system (ANS), including the visceral motor neurons that innervate all other peripheral effectors (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands and adipose tissue). - signals from CNS motor neurons to visceral effectors pass through synapses ...
... neurons that innervate skeletal muscles. 2. the autonomic nervous system (ANS), including the visceral motor neurons that innervate all other peripheral effectors (smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands and adipose tissue). - signals from CNS motor neurons to visceral effectors pass through synapses ...