Competitive Dynamics in Cortical Responses to Visual Stimuli
... suppress the other one. Although both pools of excitatory neurons were active, neither was as active as it would have been in the sole presence of its preferred stimulus, and thus the network operated in what we termed normalization mode. If the strength of the inhibition was increased, the network ...
... suppress the other one. Although both pools of excitatory neurons were active, neither was as active as it would have been in the sole presence of its preferred stimulus, and thus the network operated in what we termed normalization mode. If the strength of the inhibition was increased, the network ...
Applying Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation to the Study of Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity in Neural Networks
... physiologically accurate than the similar, but more complex, Hodgkin Huxley model, the FN model’s simplicity to implement and accurate mimicking of general neural spiking behavior make it an ideal first choice for the purposes of generating a neural micro-network. The specific FN model used here was ...
... physiologically accurate than the similar, but more complex, Hodgkin Huxley model, the FN model’s simplicity to implement and accurate mimicking of general neural spiking behavior make it an ideal first choice for the purposes of generating a neural micro-network. The specific FN model used here was ...
Artificial Intelligence (AI). Neural Networks
... Each neuron in the brain can take electrochemical signals as input via its dendrites and can process them before sending new signals along the axon and via the dendrites of the other connected neurons. The neuron sends signal if the collective influence of all its inputs reaches a threshold level (a ...
... Each neuron in the brain can take electrochemical signals as input via its dendrites and can process them before sending new signals along the axon and via the dendrites of the other connected neurons. The neuron sends signal if the collective influence of all its inputs reaches a threshold level (a ...
Sleep and Arousal
... • Entrainment by light, temperature, or arousing stimuli. • Photic entrainment in mammals due to retinohypothalamic path to SCN. • Rods and cones not needed for entrainment! • Search for new receptors in ganglion cell layer led to melanopsin. • Melanopsin ganglion cells directly activated by light, ...
... • Entrainment by light, temperature, or arousing stimuli. • Photic entrainment in mammals due to retinohypothalamic path to SCN. • Rods and cones not needed for entrainment! • Search for new receptors in ganglion cell layer led to melanopsin. • Melanopsin ganglion cells directly activated by light, ...
BIOLOGY II: CHAPTER 9: Neuromuscular Junction
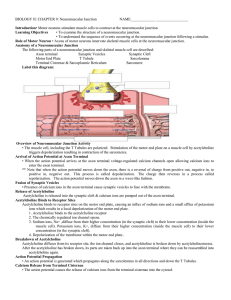
... muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of the membrane within the motor end plate.. Breakdown of Acetylcholine Acetylcholine diffuses from its receptor site, the ion ch ...
... muscle cell). Potassium ions, K+, diffuse from their higher concentration (inside the muscle cell) to their lower concentration (in the synaptic cleft). 4. Depolarization of the membrane within the motor end plate.. Breakdown of Acetylcholine Acetylcholine diffuses from its receptor site, the ion ch ...
Enteric Brain Technique - Evolutionary Healing Institute
... The brain sends signals to the gut by talking to a small number of “Command Neurons” or “Master Neurons” that in turn speak to “Interneurons” which are neurons spread through out the entire Enteric Brain complex. Command Neurons control the pattern of activity in the Enteric Brain. The Vagus Nerve a ...
... The brain sends signals to the gut by talking to a small number of “Command Neurons” or “Master Neurons” that in turn speak to “Interneurons” which are neurons spread through out the entire Enteric Brain complex. Command Neurons control the pattern of activity in the Enteric Brain. The Vagus Nerve a ...
4-CPG1
... Fictive Swimming: Spontaneous oscillations in isolated section of spinal cord, with phase lag of ~1% of a cycle per segment. The network that generates the oscillations is the CPG (Central Pattern Generator). ...
... Fictive Swimming: Spontaneous oscillations in isolated section of spinal cord, with phase lag of ~1% of a cycle per segment. The network that generates the oscillations is the CPG (Central Pattern Generator). ...
workbook - anglické gymnázium brno
... study the diagram. Then answer the questions. The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps b ...
... study the diagram. Then answer the questions. The nervous system is like a very complicated computer. As in a computer, electrical signals travel throughout the system. Instead of the wires you would see in a computer, the nervous system is made up of nerve cells, or neurons. The neurons have gaps b ...
felix may 2nd year neuroscience Investigation into the response to
... Glial cells constitute a major part of the central and peripheral nervous systems, there being about 30 times more glial cells than neurons. Glia are non-neuronal cells that support neuronal function by optimising the local environment and providing trophic factors and nutrients, having a homeostati ...
... Glial cells constitute a major part of the central and peripheral nervous systems, there being about 30 times more glial cells than neurons. Glia are non-neuronal cells that support neuronal function by optimising the local environment and providing trophic factors and nutrients, having a homeostati ...
Figure 2.25
... • Prevents harmful substances in the blood from entering the brain • The cells that make up the walls of the blood vessel walls are squeezed close together, so many molecules cannot pass through ...
... • Prevents harmful substances in the blood from entering the brain • The cells that make up the walls of the blood vessel walls are squeezed close together, so many molecules cannot pass through ...
Neuroscience 5a – Touch and Proprioception
... Slow adapting receptors: these are generally receptors that are associated with pressure. They constantly fire action potentials and change in frequency depending on the strength of the stimulus. These include: Merkle’s Corpuscle – touch Ruffini Corpuscle – pressure Receptor – Modified terminals ...
... Slow adapting receptors: these are generally receptors that are associated with pressure. They constantly fire action potentials and change in frequency depending on the strength of the stimulus. These include: Merkle’s Corpuscle – touch Ruffini Corpuscle – pressure Receptor – Modified terminals ...
Chapter 13
... C.fat accumulates in the liver; also, liver cells die D.immune system functioning declines E.All of the choices are correct. 24. Reflex centers for visual, auditory, and tactile responses are located in which part of the brain? A.midbrain B.corpus callosum C.cerebrum D.medulla oblongata E.cerebellum ...
... C.fat accumulates in the liver; also, liver cells die D.immune system functioning declines E.All of the choices are correct. 24. Reflex centers for visual, auditory, and tactile responses are located in which part of the brain? A.midbrain B.corpus callosum C.cerebrum D.medulla oblongata E.cerebellum ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... The neuronal membrane – embedded with multiple ion channels and receptors connected to scaffolding and effector proteins – represents a key information processing system in the neuron. In addition to receptors that mediate electrophysiological responses, there exist distinct membrane receptor populati ...
... The neuronal membrane – embedded with multiple ion channels and receptors connected to scaffolding and effector proteins – represents a key information processing system in the neuron. In addition to receptors that mediate electrophysiological responses, there exist distinct membrane receptor populati ...
03/14 PPT
... Glomerular structure is a general feature of olfactory systems • Fruit flies have 60 different receptors • Neurons with the same receptor project to one glomerulus ...
... Glomerular structure is a general feature of olfactory systems • Fruit flies have 60 different receptors • Neurons with the same receptor project to one glomerulus ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... their axons extend to the skeletal muscles they innervate. 3. The ANS consists of a two-neuron chain in which the cell body of the first neuron, the preganglionic neuron, resides in the spinal cord, and synapses with a second neuron, the postganglionic neuron, reside within an autonomic ganglion out ...
... their axons extend to the skeletal muscles they innervate. 3. The ANS consists of a two-neuron chain in which the cell body of the first neuron, the preganglionic neuron, resides in the spinal cord, and synapses with a second neuron, the postganglionic neuron, reside within an autonomic ganglion out ...
Synaptic receptors, neurotransmitters and brain modulators
... Many regions of the brain control hypothalamus: the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, the entorhinal cortex, parts of the thalamus, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and the reticular formation. ...
... Many regions of the brain control hypothalamus: the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, the entorhinal cortex, parts of the thalamus, basal ganglia, cerebellum, and the reticular formation. ...
The neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses: the same, but different?
... of mutations in these disease-causing genes may have radically different consequences. A key consideration is whether these phenotypes observed in mice are also present in a more complex CNS (central nervous system), most importantly in the human disease. In this respect, large animal models of NCL ...
... of mutations in these disease-causing genes may have radically different consequences. A key consideration is whether these phenotypes observed in mice are also present in a more complex CNS (central nervous system), most importantly in the human disease. In this respect, large animal models of NCL ...
Unit III: Biological Basis of Behavior
... • Modules & Connections - The brain is modular – different parts do different things. These parts; however, are densely interconnected. Thus, many parts only work w/ the support of other parts. • Individuality – All brains share basic anatomy, but each individual brain is unique based on genetics an ...
... • Modules & Connections - The brain is modular – different parts do different things. These parts; however, are densely interconnected. Thus, many parts only work w/ the support of other parts. • Individuality – All brains share basic anatomy, but each individual brain is unique based on genetics an ...
P312 Ch05_PerceivingObjectsII
... Connecting Neural Activity and Perception Something to Consider: Models of Brain Activity That Can Predict What a Person is Looking At Topic 10: Perception of Objects- 1 ...
... Connecting Neural Activity and Perception Something to Consider: Models of Brain Activity That Can Predict What a Person is Looking At Topic 10: Perception of Objects- 1 ...
Endocrine and Nervous Systems
... When you are hot or exercise strenuously, you lose water through sweat. If you lose too much water, your pituitary gland releases a hormone called ADH. Your blood carries the ADH to your kidneys, where it signals the kidneys to slow the removal of water from the blood. You also feel thirsty and tak ...
... When you are hot or exercise strenuously, you lose water through sweat. If you lose too much water, your pituitary gland releases a hormone called ADH. Your blood carries the ADH to your kidneys, where it signals the kidneys to slow the removal of water from the blood. You also feel thirsty and tak ...
Neuroplasticity
... – Voltage attenuation of EPSPs, EPSP to AP – Voltage attenuation and filtering of backpropagating AP • STDP (spike-timing dependent plasticity) ...
... – Voltage attenuation of EPSPs, EPSP to AP – Voltage attenuation and filtering of backpropagating AP • STDP (spike-timing dependent plasticity) ...