Unit 13: Adjectives and Adverbs
... • The people’s mood turned angry. • In this sentence, “turned” can be replaced by “was”; therefore, “turned” is a linking verb. “The” adjective “angry” is used to modify the linking verb “turned”. • The students turned the pages quickly. • In this sentence, “turned” can not be replaced by “was”; th ...
... • The people’s mood turned angry. • In this sentence, “turned” can be replaced by “was”; therefore, “turned” is a linking verb. “The” adjective “angry” is used to modify the linking verb “turned”. • The students turned the pages quickly. • In this sentence, “turned” can not be replaced by “was”; th ...
Grammar Notes - Paulding County Schools
... demonstrative (dem pron): (demonstrate which one) this, that, these, those indefinite (ind pron): (don't refer to a definite person or thing) each, either, neither, few, some, all, most, several, few, many, none, one, someone, no one, everyone, anyone, somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, more, ...
... demonstrative (dem pron): (demonstrate which one) this, that, these, those indefinite (ind pron): (don't refer to a definite person or thing) each, either, neither, few, some, all, most, several, few, many, none, one, someone, no one, everyone, anyone, somebody, nobody, everybody, anybody, more, ...
Just Another Box of Games!
... Adverbs of place Too Early relative clauses Indirect object “There” as a noun That’s not… Isn’t/Aren’t Quantifiers An Became/Changed into Before/After Articulation ...
... Adverbs of place Too Early relative clauses Indirect object “There” as a noun That’s not… Isn’t/Aren’t Quantifiers An Became/Changed into Before/After Articulation ...
What is a participle?
... **to smile is an infinitive because it acts as the subject of the sentence** Infinitives are verbs that can be used as adjectives • That is the book to read. **to read is an infinitive because it uses a verb to modify or describe the object of the sentence** ...
... **to smile is an infinitive because it acts as the subject of the sentence** Infinitives are verbs that can be used as adjectives • That is the book to read. **to read is an infinitive because it uses a verb to modify or describe the object of the sentence** ...
QBS Continuum for Progression Grammar
... Indirect speech is another person’s report of what was said, e.g. Red Riding Hood told how the wolf said that he was going for a walk. Verbs and tenses The verb group must “agree” with the subject of the clause, i.e. a plural subject must have a plural verb, e.g. “the boys were going to school”, not ...
... Indirect speech is another person’s report of what was said, e.g. Red Riding Hood told how the wolf said that he was going for a walk. Verbs and tenses The verb group must “agree” with the subject of the clause, i.e. a plural subject must have a plural verb, e.g. “the boys were going to school”, not ...
The noun
... All English verbs fall into two groups: transitive verbs require an object followed by a noun or pronoun. The object completes the meaning of the verb and in most cases a transitive verb cannot be used without it, e.g. He raised prices on some goods. She laid a book on the table. intransitive verbs ...
... All English verbs fall into two groups: transitive verbs require an object followed by a noun or pronoun. The object completes the meaning of the verb and in most cases a transitive verb cannot be used without it, e.g. He raised prices on some goods. She laid a book on the table. intransitive verbs ...
Chapter 4: Verbs
... used to show that actions or conditions are, were, or will be in progress. To make the progressive form, add the present, past, or future form of “be” to the present participle. ...
... used to show that actions or conditions are, were, or will be in progress. To make the progressive form, add the present, past, or future form of “be” to the present participle. ...
Aspect cross-categorially: states in nominalizations DATA. In
... In (6a) the perfect form of the verb entails the state expressed by the participle and viceversa (Koontz-Garboden, 2009). We contend that this is due to the fact that both grammatical forms express the same D-state. In contrast, in (6b), the perfect form entails the state, but the state can be true ...
... In (6a) the perfect form of the verb entails the state expressed by the participle and viceversa (Koontz-Garboden, 2009). We contend that this is due to the fact that both grammatical forms express the same D-state. In contrast, in (6b), the perfect form entails the state, but the state can be true ...
W2 - 8 parts of speech 01
... For a number of nouns, the rule needs slight revision. Certain nouns in English belong to both classes: they have both a noncount and a count meaning. Normally the noncount meaning is abstract and general and the count meaning concrete and specific. (Count) • I've had some difficulties finding a job ...
... For a number of nouns, the rule needs slight revision. Certain nouns in English belong to both classes: they have both a noncount and a count meaning. Normally the noncount meaning is abstract and general and the count meaning concrete and specific. (Count) • I've had some difficulties finding a job ...
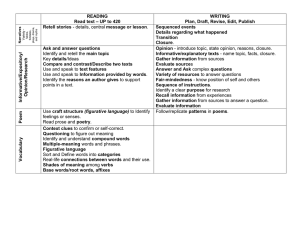
READING Read text – UP to 420 WRITING Plan, Draft, Revise, Edit
... Follow rules for discussions Responding to the comments of other Ask and answer questions with purpose. Explain major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information. Read silently and orally accurately and fluently with expression to comprehend ...
... Follow rules for discussions Responding to the comments of other Ask and answer questions with purpose. Explain major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information. Read silently and orally accurately and fluently with expression to comprehend ...
Grammar Made Easier by Harriett Stoker and Tammy Crouch
... this, that, these, those • Interrogative Pronouns o An interrogative pronoun introduces a question what, which, who, whom, whose • Relative Pronouns o A relative pronoun introduces a subordinate clause that, which, who, whom, whose ...
... this, that, these, those • Interrogative Pronouns o An interrogative pronoun introduces a question what, which, who, whom, whose • Relative Pronouns o A relative pronoun introduces a subordinate clause that, which, who, whom, whose ...
verb forms for TeachLing
... past tense and past participial forms. Compare with others and discuss. Activity – present vs. present participle/progressive. Find examples of the present tense in a book or other text. Write them down and discuss your findings. Is the present ever used to describe something not happening right now ...
... past tense and past participial forms. Compare with others and discuss. Activity – present vs. present participle/progressive. Find examples of the present tense in a book or other text. Write them down and discuss your findings. Is the present ever used to describe something not happening right now ...
L2 Summer Review Packet
... INDIRECT STATEMENT and ABLATIVE ABSOLUTE This year you learned how to translate infinitives in an indirect statement and participles in an ablative absolute. Below are the rules for each of these and translation examples. Read carefully and refer to these examples when you translate the sentences. I ...
... INDIRECT STATEMENT and ABLATIVE ABSOLUTE This year you learned how to translate infinitives in an indirect statement and participles in an ablative absolute. Below are the rules for each of these and translation examples. Read carefully and refer to these examples when you translate the sentences. I ...
The Most Common Language Problems in Technical Papers
... happened and is or may be continuing to happen. Modal auxiliary forms are suitable when there is some degree of speculation involved Adjectives and adverbs are used more sparsely in scientific writing than in general literature and quantitative measures are more common than qualitative descriptions. ...
... happened and is or may be continuing to happen. Modal auxiliary forms are suitable when there is some degree of speculation involved Adjectives and adverbs are used more sparsely in scientific writing than in general literature and quantitative measures are more common than qualitative descriptions. ...
Parts of Speech Review
... downstairs, knowing that Chauncey had jumped against a switch, but the fire department had gotten there first. She went outside calling his name; he was gone. She then walked toward the house she had once seen Ashley go into. Ashley was outside with all the other neighbors and looked pleased to see ...
... downstairs, knowing that Chauncey had jumped against a switch, but the fire department had gotten there first. She went outside calling his name; he was gone. She then walked toward the house she had once seen Ashley go into. Ashley was outside with all the other neighbors and looked pleased to see ...
LIFEPAC® 5th Grade Language Arts Unit 8 Worktext
... structure of language so they can communicate in a meaningful way. Words are divided into classes known as parts of speech. This division gives every word in a sentence a special task. As a result, when the words are arranged in meaningful thought patterns, the words become complete sentences. In th ...
... structure of language so they can communicate in a meaningful way. Words are divided into classes known as parts of speech. This division gives every word in a sentence a special task. As a result, when the words are arranged in meaningful thought patterns, the words become complete sentences. In th ...
verbal phrases - Montville.net
... • It is part verb and part noun. • We form GERUNDS by adding -ing to the verb and using it as a subject or an object. ...
... • It is part verb and part noun. • We form GERUNDS by adding -ing to the verb and using it as a subject or an object. ...
Year 5 Glossary
... words’ because they name people, places and ‘things’; this is often true, but it doesn’t help to distinguish nouns from other word classes. The surest way to identify nouns is by the ways they can be used after determiners such as the: for example, most nouns will fit into the frame “The __ matters/ ...
... words’ because they name people, places and ‘things’; this is often true, but it doesn’t help to distinguish nouns from other word classes. The surest way to identify nouns is by the ways they can be used after determiners such as the: for example, most nouns will fit into the frame “The __ matters/ ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... each other in terms of number. In other words, they both must be singular or they ...
... each other in terms of number. In other words, they both must be singular or they ...
Bedford marking key
... 42c – Underline or italicize foreign words 42e – Avoid excessive use for emphasis 43 – Spelling 43a – Refer to a dictionary 43b – Words that sound alike but have different meanings 44 – The hyphen 44a – Consult dictionary for compound words 44b – Connecting 2 or more words functioning as an adjectiv ...
... 42c – Underline or italicize foreign words 42e – Avoid excessive use for emphasis 43 – Spelling 43a – Refer to a dictionary 43b – Words that sound alike but have different meanings 44 – The hyphen 44a – Consult dictionary for compound words 44b – Connecting 2 or more words functioning as an adjectiv ...