The Human Brain - Structure and Function
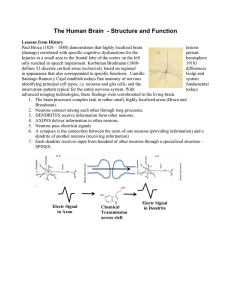
... system identifying principal cell types, i.e. neurons and glia cells, and the fundamental innervation pattern typical for the entire nervous system. With todays advanced imaging technologies, these findings were corroborated in the living brain. 1. The brain processes complex task in rather small, h ...
... system identifying principal cell types, i.e. neurons and glia cells, and the fundamental innervation pattern typical for the entire nervous system. With todays advanced imaging technologies, these findings were corroborated in the living brain. 1. The brain processes complex task in rather small, h ...
At the crossroads of metabolism and reproduction in the brain
... Animals: Our colony of DAT-Cre mice will either be crossed with reporter lines or injected stereotactically with viral (AAV) constructs to ensure anatomical specificity. The reporter lines and constructs will drive expression of fluorescent markers (e.g. tdTomato) for visualization, optogenetic prot ...
... Animals: Our colony of DAT-Cre mice will either be crossed with reporter lines or injected stereotactically with viral (AAV) constructs to ensure anatomical specificity. The reporter lines and constructs will drive expression of fluorescent markers (e.g. tdTomato) for visualization, optogenetic prot ...
The Nervous System - Kirchner-WHS
... system is the function of everything. ► It sends signals notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
... system is the function of everything. ► It sends signals notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
UNIT 2: Internal geological agents
... It consists of neurons which transmit It consists og endocrine glands which release information through electrical and chemical hormons signals. A -Nervous system: It follows the following pathway: Stimulus→Repectors→Effectors→Answer There are two types of stimuli: External stimuli: Chemical sustunc ...
... It consists of neurons which transmit It consists og endocrine glands which release information through electrical and chemical hormons signals. A -Nervous system: It follows the following pathway: Stimulus→Repectors→Effectors→Answer There are two types of stimuli: External stimuli: Chemical sustunc ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... Doi:10.1007/s11515-011-1146-2 compartments. En maintains Hh expression in the P compartment, which in turn activates En expression in cells immediately anterior to the AP compartment boundary. The expression of Ptc and Decapentaplegic Dpp is also induced in anterior cells near the compartment bounda ...
... Doi:10.1007/s11515-011-1146-2 compartments. En maintains Hh expression in the P compartment, which in turn activates En expression in cells immediately anterior to the AP compartment boundary. The expression of Ptc and Decapentaplegic Dpp is also induced in anterior cells near the compartment bounda ...
Slide 1
... Some local interneurons do not generate action potentials because their axons are short. Some neurons do not have a steady resting potential and are spontaneously active. Neurons differ in the types and combinations of ion channels in their cell membranes. Neurons differ in their neurotransmitters r ...
... Some local interneurons do not generate action potentials because their axons are short. Some neurons do not have a steady resting potential and are spontaneously active. Neurons differ in the types and combinations of ion channels in their cell membranes. Neurons differ in their neurotransmitters r ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and
... Action potentials, or nerve impulses, occur on axons and are the principle way neurons communicate. a. Generation of an action potential involves a transient increase in Na1 permeability, followed by restoration of Na1 impermeability, and then a short-lived increase in K1 permeability. b. Propagatio ...
... Action potentials, or nerve impulses, occur on axons and are the principle way neurons communicate. a. Generation of an action potential involves a transient increase in Na1 permeability, followed by restoration of Na1 impermeability, and then a short-lived increase in K1 permeability. b. Propagatio ...
solutions - Berkeley MCB
... a. Rods hyperpolarize to light, while cones depolarize to light b. Cones do not use the effector enzyme phosphodiesterase c. Cones and rods use different types of opsins d. Only cones contain retinal 2) The optic disk is a “blind spot” in the visual field because: This is where the retinal ganglion ...
... a. Rods hyperpolarize to light, while cones depolarize to light b. Cones do not use the effector enzyme phosphodiesterase c. Cones and rods use different types of opsins d. Only cones contain retinal 2) The optic disk is a “blind spot” in the visual field because: This is where the retinal ganglion ...
Chapter Eleven
... • Action potentials, or nerve impulses, are: – __________________________________ carried along the length of axons ...
... • Action potentials, or nerve impulses, are: – __________________________________ carried along the length of axons ...
PRACTICE QUIZ
... 28. At the posterior pole of the eye is an oval region called the ______________________________________. 29. The more numerous _____________________ are photoreceptors used for dim-light and peripheral vision. 30. The eye and olfactory epithelium possess specialized neurons that have only a single ...
... 28. At the posterior pole of the eye is an oval region called the ______________________________________. 29. The more numerous _____________________ are photoreceptors used for dim-light and peripheral vision. 30. The eye and olfactory epithelium possess specialized neurons that have only a single ...
Brain Anatomy
... friends of him. He died in 1861, thirtheen years after the accident, penniless and epileptic, and no autopsy was performed on his brain. ...
... friends of him. He died in 1861, thirtheen years after the accident, penniless and epileptic, and no autopsy was performed on his brain. ...
Chapter 3
... Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses? ...
... Are there parts of the brain that have specialized functions? What causes mental illnesses? ...
Peripheral Nerve Repair
... •crucial for human movement and function • Highway for information processing and response •Sensory Neurons- send stimulation information from senses to the brain. • Motor Neurons- send commands from the brain to muscles or other organs ...
... •crucial for human movement and function • Highway for information processing and response •Sensory Neurons- send stimulation information from senses to the brain. • Motor Neurons- send commands from the brain to muscles or other organs ...
1. Receptor cells
... The Biological Foundations of Behavior • The nervous system: the most complicated system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting ...
... The Biological Foundations of Behavior • The nervous system: the most complicated system in human body where billions of interconnected cells radiate all over the body. • Specialized Cells of nervous system include: 1. Receptor cells: Embedded in sense organs, (seeing – hearing – smelling – tasting ...
Document
... are your brain cells • These neurons each have connections to thousands of neighboring neurons • Average adult brain has between 100 – 500 trillion synapses • A child’s brain has about 1 quadrillion synapses! ...
... are your brain cells • These neurons each have connections to thousands of neighboring neurons • Average adult brain has between 100 – 500 trillion synapses • A child’s brain has about 1 quadrillion synapses! ...
Neuronal Anatomy - VCC Library
... grouped near each other or clustered together. These groups of clustered nerve cell bodies are called ganglia, and are usually only found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) (i.e. outside the brain and spinal cord), rather than the central nervous system (CNS). ...
... grouped near each other or clustered together. These groups of clustered nerve cell bodies are called ganglia, and are usually only found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) (i.e. outside the brain and spinal cord), rather than the central nervous system (CNS). ...
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling
... synapse in rapid succession- in this case the EPSP’s add together. Spatial Summation- two EPSP’s produced simultaneously at different synapses on the same postsynaptic neuronEPSP’s added together. ...
... synapse in rapid succession- in this case the EPSP’s add together. Spatial Summation- two EPSP’s produced simultaneously at different synapses on the same postsynaptic neuronEPSP’s added together. ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.