Neurons
... Neurotransmitters chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
... Neurotransmitters chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
WangCellTableHW_JW
... Their job is to transport oxygen all throughout the body. Iron conjugate Phagocytosis—process of engulfing. Signaling for inflammatory response. Contracts by action potentials, have vesicles of ions/signal Electrical conduction has to be FAST. Have lots of voltage gated channels to transmit AP. ...
... Their job is to transport oxygen all throughout the body. Iron conjugate Phagocytosis—process of engulfing. Signaling for inflammatory response. Contracts by action potentials, have vesicles of ions/signal Electrical conduction has to be FAST. Have lots of voltage gated channels to transmit AP. ...
A- A- A- K+ A - How Your Brain Works
... can have a large variety of gated ion channels which will open transiently in the presence of certain stimuli or chemical signals. These gated channels may be permeable to Na+, Cl- or Ca++. • When these gated channels open, the voltage across the membrane will change to reflect the new permeabilitie ...
... can have a large variety of gated ion channels which will open transiently in the presence of certain stimuli or chemical signals. These gated channels may be permeable to Na+, Cl- or Ca++. • When these gated channels open, the voltage across the membrane will change to reflect the new permeabilitie ...
E.2 - Perception of Stimuli
... Suppose that you are driving on the freeway and notice that the car in front of you has stopped. You react by slamming on the breaks. But, this “reaction time” process has taken up a certain amount of time. What nervous system processes needed to happen? ...
... Suppose that you are driving on the freeway and notice that the car in front of you has stopped. You react by slamming on the breaks. But, this “reaction time” process has taken up a certain amount of time. What nervous system processes needed to happen? ...
Structure of a Neuron
... Basis of the Resting Membrane Potential • Since Na+ ion are more concentrated in the ECF when a specific voltage gated Na+ channel opens Na+ will always rush into the cell by diffusion. • Since K+ ion channels are more concentrated in the ICF when a specific voltage gated K+ channel opens K+ will a ...
... Basis of the Resting Membrane Potential • Since Na+ ion are more concentrated in the ECF when a specific voltage gated Na+ channel opens Na+ will always rush into the cell by diffusion. • Since K+ ion channels are more concentrated in the ICF when a specific voltage gated K+ channel opens K+ will a ...
Organs-on-a-chip
... - Most important cell types for central nervous system (CNS): neurons and glial cells (non neuron support cells of CNS). - In vitro studies: brain slices or primary neurons and glial cells are commonly used. - Immortal cell lines with neuron like properties also exist. - In future, patient derived i ...
... - Most important cell types for central nervous system (CNS): neurons and glial cells (non neuron support cells of CNS). - In vitro studies: brain slices or primary neurons and glial cells are commonly used. - Immortal cell lines with neuron like properties also exist. - In future, patient derived i ...
An adult is experiencing inferior alternating hemiplegia. Which
... B) Muscles of the lower face are weak on the right side. C) The protruded tongue deviates to the right side. D) Brisk DTRs are present in the right arm. E) Stroking the left foot produces a Babinski response. DTRs = deep tendon reflexes = muscle stretch reflexes ...
... B) Muscles of the lower face are weak on the right side. C) The protruded tongue deviates to the right side. D) Brisk DTRs are present in the right arm. E) Stroking the left foot produces a Babinski response. DTRs = deep tendon reflexes = muscle stretch reflexes ...
The Nervous System : communication
... ●Zoloft is part of a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or ● SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
... ●Zoloft is part of a class of drugs called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or ● SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
Chapter 7 Part 1 Nervous Tissue
... • Are gaps in the myelin sheath formed by spaces between successive oligodendrocytes (in CNS) or Schwann cells (in PNS) along the length of the axon. • Nodes of Ranvier contain Na+ ion channels, and are sites where action potentials are generated by membrane depolarizations. • They are the sites whe ...
... • Are gaps in the myelin sheath formed by spaces between successive oligodendrocytes (in CNS) or Schwann cells (in PNS) along the length of the axon. • Nodes of Ranvier contain Na+ ion channels, and are sites where action potentials are generated by membrane depolarizations. • They are the sites whe ...
action potentials - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... neurotransmitter ACh when voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enters the axon terminal. Vesicles release ACh into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis, ACh diffuses across the cleft and binds to receptors on the motor end plate. ...
... neurotransmitter ACh when voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enters the axon terminal. Vesicles release ACh into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis, ACh diffuses across the cleft and binds to receptors on the motor end plate. ...
The Nervous System
... that uses pigments in structures called rods and cones to absorb photons of light. ...
... that uses pigments in structures called rods and cones to absorb photons of light. ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... Neurons are the building-blocks of the body’s nervous system. They are specialized nerve cells that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an arti ...
... Neurons are the building-blocks of the body’s nervous system. They are specialized nerve cells that communicate electrical and chemical messages between the brain, through the spinal cord, and to other parts of the body. Expanded Definition: History: The term “neuron” was first introduced in an arti ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... – Neurotransmitters cross synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
... – Neurotransmitters cross synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
Linköping University Post Print Neuroscience: Light moulds plastic brains
... In tadpoles, the number of neurons expressing the neurotransmitter dopamine increases on exposure to light. Such plasticity might allow animals to physically match their brains’ activity to environmental stimuli. The nervous systems are known to adapt to environmental inputs. But such plasticity has ...
... In tadpoles, the number of neurons expressing the neurotransmitter dopamine increases on exposure to light. Such plasticity might allow animals to physically match their brains’ activity to environmental stimuli. The nervous systems are known to adapt to environmental inputs. But such plasticity has ...
Biology of Humans 2/e
... The signal passes across the synaptic cleft as a chemical called neurotransmitter which is released from vesicles by exocytosis. Neurotransmitter is a chemical that is secreted into a synaptic cleft by a neuron that affects another neuron or an effector by binding with receptors on it. The sending c ...
... The signal passes across the synaptic cleft as a chemical called neurotransmitter which is released from vesicles by exocytosis. Neurotransmitter is a chemical that is secreted into a synaptic cleft by a neuron that affects another neuron or an effector by binding with receptors on it. The sending c ...
Inhibitory Control of Hippocampal Inhibitory Neurons
... CA3 and CA1 regions. These cells are organized into a recurrent network and also inhibitory cells helps to refine output. However, these cells fire in a random manner, so they need synchronization because long term potentiation requires accurate timing (action potentials must occur within 2-3 ms to ...
... CA3 and CA1 regions. These cells are organized into a recurrent network and also inhibitory cells helps to refine output. However, these cells fire in a random manner, so they need synchronization because long term potentiation requires accurate timing (action potentials must occur within 2-3 ms to ...
Slide ()
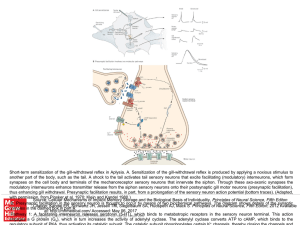
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.