Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... ● rhodopsin absorbs light, and breaks apart, as its retinal component changes shape; opsin is now ACTIVE; ● this triggers a chain of metabolic events (signal-transduction pathway!) that makes the rod cell membrane less permeable to sodium and therefore hyperpolarizes the rod cell membrane; ● the rod ...
... ● rhodopsin absorbs light, and breaks apart, as its retinal component changes shape; opsin is now ACTIVE; ● this triggers a chain of metabolic events (signal-transduction pathway!) that makes the rod cell membrane less permeable to sodium and therefore hyperpolarizes the rod cell membrane; ● the rod ...
Development & Neuroplasticity - U
... • Parallels the course of human cognitive development • Linked to three main types of cognitive function: working memory, or the ability to keep information accessible for short periods of time; planning and completing sequences of actions; and inhibiting inappropriate responses • Damage leads to pe ...
... • Parallels the course of human cognitive development • Linked to three main types of cognitive function: working memory, or the ability to keep information accessible for short periods of time; planning and completing sequences of actions; and inhibiting inappropriate responses • Damage leads to pe ...
Dr. Carlos Paladini
... signal is encoded by the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons, which controls the release of dopamine at target regions. Specifically, transient, impulsedependent release of dopamine, driven by bursts of action potentials, is critical for natural processing in the brain. Disruptions of dopamine fu ...
... signal is encoded by the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons, which controls the release of dopamine at target regions. Specifically, transient, impulsedependent release of dopamine, driven by bursts of action potentials, is critical for natural processing in the brain. Disruptions of dopamine fu ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... Neurotransmitters = chemical messengers sent from the vesicle sacs of the axon through the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron, influencing its action potential. The sending neuron then reabsorbs excess NT molecules in a process called reuptake. NTs will ...
... Neurotransmitters = chemical messengers sent from the vesicle sacs of the axon through the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron, influencing its action potential. The sending neuron then reabsorbs excess NT molecules in a process called reuptake. NTs will ...
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.131: Introduction to Neuroscience
... exposure. Resting calcum is reduced, which disinhibits guanylyl cyclase and modestly increases cGMP concentration in the photoreceptor. b. The center-surround structure of horizontal cells tends to reduce signals in response to only extremely bright light, always resulting in an intermediate firing ...
... exposure. Resting calcum is reduced, which disinhibits guanylyl cyclase and modestly increases cGMP concentration in the photoreceptor. b. The center-surround structure of horizontal cells tends to reduce signals in response to only extremely bright light, always resulting in an intermediate firing ...
The NEURON
... 4.Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production However, neurons differ from other cells in the body because: 1.Neurons have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons 2.Neurons communicate with each other - electrochemical 3.Neurons contain some s ...
... 4.Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production However, neurons differ from other cells in the body because: 1.Neurons have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons 2.Neurons communicate with each other - electrochemical 3.Neurons contain some s ...
The NEURON
... 4.Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production However, neurons differ from other cells in the body because: 1.Neurons have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons 2.Neurons communicate with each other - electrochemical 3.Neurons contain some s ...
... 4.Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and energy production However, neurons differ from other cells in the body because: 1.Neurons have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons 2.Neurons communicate with each other - electrochemical 3.Neurons contain some s ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Chapter 33 Nervous System
... a. Carry impulse to motor neurons b. Located in spinal cord and brain 3. Motor neurons a. Carry impulses away from brain and spinal cord to a gland or muscle b. Causes a response vi. Reflex Arc 1. Nerve pathway that consists of a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron 2. Brain is NOT inv ...
... a. Carry impulse to motor neurons b. Located in spinal cord and brain 3. Motor neurons a. Carry impulses away from brain and spinal cord to a gland or muscle b. Causes a response vi. Reflex Arc 1. Nerve pathway that consists of a sensory neuron, an interneuron, and a motor neuron 2. Brain is NOT inv ...
28.1_Responses
... Review List three body systems that work together to create a response to a stimulus Sequence What is the correct sequence of the following in response to a stimuli: interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, muscle Review What are two general ways in which nervous systems differ among animal groups ...
... Review List three body systems that work together to create a response to a stimulus Sequence What is the correct sequence of the following in response to a stimuli: interneuron, motor neuron, sensory neuron, muscle Review What are two general ways in which nervous systems differ among animal groups ...
Nervous tissue
... • slow signals supply the stomach and dilate pupil • fast signals supply skeletal muscles and transport sensory signals for vision and balance ...
... • slow signals supply the stomach and dilate pupil • fast signals supply skeletal muscles and transport sensory signals for vision and balance ...
Powerpoint slides
... About -70 mV Selectively allowing certain ions in With stimulation Na+ is allowed in ...
... About -70 mV Selectively allowing certain ions in With stimulation Na+ is allowed in ...
I. Functions and Divisions of the Nervous System A. The nervous
... 1. Neurons use changes in membrane potential as communication signals and can be brought on by changes in membrane permeability to any ion, or alteration of ion concentrations on the two sides of the membrane. 2. Changes in membrane potential can produce either graded potentials, usually incoming si ...
... 1. Neurons use changes in membrane potential as communication signals and can be brought on by changes in membrane permeability to any ion, or alteration of ion concentrations on the two sides of the membrane. 2. Changes in membrane potential can produce either graded potentials, usually incoming si ...
nervous system
... serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
... serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions, hallucinations, delusions, and rapid mood swings. ...
nervous system
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
... sheath which provides the electrical insulation for certain neurons in the CNS ...
Biological Psychology
... Learning Objectives Chapters 1 and 3 Spring 2013 Chapter 1: Biopsychology as a Neuroscience Define biopsychology Describe the different disciplines that contribute to the field of neuroscience Key Terms: o Neurons o Neuroanatomy o Neuropathology o Neuropharmacology o Neuropsychology o Cognitiv ...
... Learning Objectives Chapters 1 and 3 Spring 2013 Chapter 1: Biopsychology as a Neuroscience Define biopsychology Describe the different disciplines that contribute to the field of neuroscience Key Terms: o Neurons o Neuroanatomy o Neuropathology o Neuropharmacology o Neuropsychology o Cognitiv ...
Slide 1
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
... Advantages: Spikes of biological neurons are well localized in time and not very frequent. Thus low number of events (sparse coding). Disadvantages: We need a mathematical expression (or method) to calculate the value of each state variable after an arbitrary time (the time of the next event). ...
Slide 1
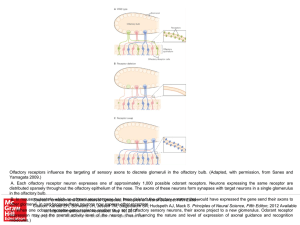
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Slide ()
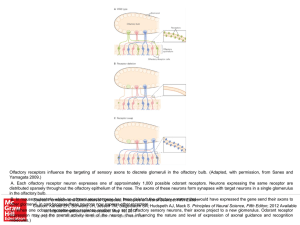
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Simulation of Stroke-related Damage in Cultured Human Nerve Cells
... treatment with the morphogen retinoic acid, the NT-2 line can be induced to differentiate into postmitotic neurons (Pleasure et al., 1992). This protocol involves a 5-7 weeks exposure with the morphogen, followed by two replates, a 7-10 days lasting treatment with mitotic inhibtors, and selective tr ...
... treatment with the morphogen retinoic acid, the NT-2 line can be induced to differentiate into postmitotic neurons (Pleasure et al., 1992). This protocol involves a 5-7 weeks exposure with the morphogen, followed by two replates, a 7-10 days lasting treatment with mitotic inhibtors, and selective tr ...
Physiology of hearing. Vestibular analyzer
... gelatinous mass known as cupula. Hair cells have two kinds of cilia – kinocilium and stereocilia. • Kinocilium is large cilium located at one end of hair cell. Stereocilia are small. When stereocilia are bent towards kinocilium, hair cell is depolarized, i.e. stimulated. ...
... gelatinous mass known as cupula. Hair cells have two kinds of cilia – kinocilium and stereocilia. • Kinocilium is large cilium located at one end of hair cell. Stereocilia are small. When stereocilia are bent towards kinocilium, hair cell is depolarized, i.e. stimulated. ...
Nervous System Function
... dendrites + one axon; found in CNS and motor neurons Bipolar = one dendrite and one axon; found in eye and nose ...
... dendrites + one axon; found in CNS and motor neurons Bipolar = one dendrite and one axon; found in eye and nose ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.