Exam #2 Review Answers - Iowa State University
... a. Decreased extracellular sodium b. Increased intracellular calcium c. Increased intracellular sodium d. Decreased extracellular calcium e. Decreased intracellular potassium 23. In which type of potential is the magnitude directly proportional to the stimulus? a. Action potential b. Resting potenti ...
... a. Decreased extracellular sodium b. Increased intracellular calcium c. Increased intracellular sodium d. Decreased extracellular calcium e. Decreased intracellular potassium 23. In which type of potential is the magnitude directly proportional to the stimulus? a. Action potential b. Resting potenti ...
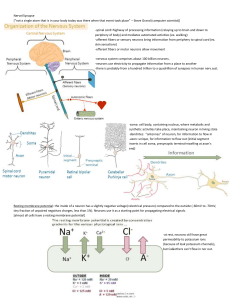
Nervous System
... The two major ions are sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+). Sodium diffuses out of the neuron, and Potassium diffuses into the neuron.The two ions cross the membrane through channel proteins (3). Some channel proteins never shut, so the ions diffuse through them all the time. Other channel proteins act ...
... The two major ions are sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+). Sodium diffuses out of the neuron, and Potassium diffuses into the neuron.The two ions cross the membrane through channel proteins (3). Some channel proteins never shut, so the ions diffuse through them all the time. Other channel proteins act ...
Study Guide for Chapter 7 - Neuron Function Be familiar with the
... action potential (“nerve impulse”), afferent, astrocyte, axon, axonal end bulbs (synaptic end bulbs, boutons, axon endings, synaptic knobs), bipolar neuron, blood-brain barrier, central nervous system (CNS), chemically-gated (ligand-gated) channel, dendrite, depolarization, efferent, electrochemical ...
... action potential (“nerve impulse”), afferent, astrocyte, axon, axonal end bulbs (synaptic end bulbs, boutons, axon endings, synaptic knobs), bipolar neuron, blood-brain barrier, central nervous system (CNS), chemically-gated (ligand-gated) channel, dendrite, depolarization, efferent, electrochemical ...
Supplementary Figure Legends (doc 40K)
... cells were transfected with M3C for 48 h. Then the cells were treated with 20 μM tanshinone1 for 4 h followed by Western blotting (e); the ectopic Stat3 (EC-Stat3) expressed by M3C contained green fluorescent protein and thus possessed bigger molecular weight than the endogenous Stat3 (EN-Stat3). ( ...
... cells were transfected with M3C for 48 h. Then the cells were treated with 20 μM tanshinone1 for 4 h followed by Western blotting (e); the ectopic Stat3 (EC-Stat3) expressed by M3C contained green fluorescent protein and thus possessed bigger molecular weight than the endogenous Stat3 (EN-Stat3). ( ...
Hypothalamus
... • Parvicellular hypophyseotropic neurons – Nuerons within Paraventricular hypothalamic nuclei and arcuate nuclei – Axons terminate in median eminence ...
... • Parvicellular hypophyseotropic neurons – Nuerons within Paraventricular hypothalamic nuclei and arcuate nuclei – Axons terminate in median eminence ...
PDF - The Journal of Cell Biology
... cell cycle, Dynlacht’s team looked for new binding partners. They fished out one especially strong candidate, which was associated with the ER, and named it SCAPER (S phase cyclin A–associated protein of the endoplasmic reticulum). Overexpression of SCAPER delayed progression of cells through M phase ...
... cell cycle, Dynlacht’s team looked for new binding partners. They fished out one especially strong candidate, which was associated with the ER, and named it SCAPER (S phase cyclin A–associated protein of the endoplasmic reticulum). Overexpression of SCAPER delayed progression of cells through M phase ...
Saladin, Human Anatomy 3e
... 5. The neural components of the eye are the retina and optic nerve. The retina absorbs light, partially processes the visual information, and encodes the stimulus in action potentials conducted via the optic nerve to the brain. The sharpest vision occurs in a region of retina called the fovea centra ...
... 5. The neural components of the eye are the retina and optic nerve. The retina absorbs light, partially processes the visual information, and encodes the stimulus in action potentials conducted via the optic nerve to the brain. The sharpest vision occurs in a region of retina called the fovea centra ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS
... • An action potential (nerve impulse) is a rapid, large change in membrane potential that reverses membrane polarity. • The membrane depolarizes from –65 mV at rest to about +40 mV (depolarization). • It is localized and brief but is propagated with no loss of size—an action potential at one locatio ...
... • An action potential (nerve impulse) is a rapid, large change in membrane potential that reverses membrane polarity. • The membrane depolarizes from –65 mV at rest to about +40 mV (depolarization). • It is localized and brief but is propagated with no loss of size—an action potential at one locatio ...
Unit 4 – Coordination Reflex Arc
... – Own immune system attacks and damages myelin – Scars form in white matter of CNS – Cause unknown, no cure • Cerebral Palsy – Damage to developing oligodendrocytes usually during infancy – Mutations, lack of oxygen, interruption of blood flow – Treatment of symptoms, no cure ...
... – Own immune system attacks and damages myelin – Scars form in white matter of CNS – Cause unknown, no cure • Cerebral Palsy – Damage to developing oligodendrocytes usually during infancy – Mutations, lack of oxygen, interruption of blood flow – Treatment of symptoms, no cure ...
Supplementary Information 1 (doc 48K)
... medium. EHT 1864 (50 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) were added 24 hours after cell plating. At the time indicated in the figure legends, cells were trypsinized and counted using a hemocytometer. On day 4, EHT 1864 was washed out by removing drug containing media, washing twice with PBS and adding media ...
... medium. EHT 1864 (50 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) were added 24 hours after cell plating. At the time indicated in the figure legends, cells were trypsinized and counted using a hemocytometer. On day 4, EHT 1864 was washed out by removing drug containing media, washing twice with PBS and adding media ...
The Nervous System and Senses
... • Muscles around the iris (the colored portion) control the size of the pupil (the black circle), controlling how much light enters the eye • From the pupil, light passes through a lens, which focuses light on the back of the eye (retina) • Rods and cones on the retina generate nerve impulses that t ...
... • Muscles around the iris (the colored portion) control the size of the pupil (the black circle), controlling how much light enters the eye • From the pupil, light passes through a lens, which focuses light on the back of the eye (retina) • Rods and cones on the retina generate nerve impulses that t ...
Identification of sleep-promoting neurons in vitro. Nature 6781:992-5
... cells may correspond to these sleep-active cells. To test this proposal we measured the effects of noradrenaline, an important transmitter of wakefulness3,7,8, and found that 18 out of 20 LTS cells (Fig. 2a, c) were hyperpolarized by noradrenaline (two were depolarized), whereas all (n = 8) non-LTS ...
... cells may correspond to these sleep-active cells. To test this proposal we measured the effects of noradrenaline, an important transmitter of wakefulness3,7,8, and found that 18 out of 20 LTS cells (Fig. 2a, c) were hyperpolarized by noradrenaline (two were depolarized), whereas all (n = 8) non-LTS ...
Reflex Arc - Cloudfront.net
... Talking Only… Which position on the soccer field do you THINK having a fast reaction time would be the greatest advantage? forward/striker, midfield, defense, goal keeper Reaction Time Drills for a Goal Keeper ...
... Talking Only… Which position on the soccer field do you THINK having a fast reaction time would be the greatest advantage? forward/striker, midfield, defense, goal keeper Reaction Time Drills for a Goal Keeper ...
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... Homeostasis is the process of maintaining a constant internal environment despite the changing external environment. Maintaining homeostasis is absolutely vital to an organisms survival Claude Bernard (1813-‐78): sta ...
... Homeostasis is the process of maintaining a constant internal environment despite the changing external environment. Maintaining homeostasis is absolutely vital to an organisms survival Claude Bernard (1813-‐78): sta ...
Multiarray silicon probes with integrated optical fibers
... cassette containing the mouse synapsin promoter, a woodchuck posttranscriptional regulatory element (WPRE), SV40 polyadenylation sequence and two inverted terminal repeats. rAAV-FLEX-rev-eNpHRGFP (Atasoy et al., 2008) was assembled using a modified helper-free system (Stratagene) as a serotype 2 ⁄ 7 ...
... cassette containing the mouse synapsin promoter, a woodchuck posttranscriptional regulatory element (WPRE), SV40 polyadenylation sequence and two inverted terminal repeats. rAAV-FLEX-rev-eNpHRGFP (Atasoy et al., 2008) was assembled using a modified helper-free system (Stratagene) as a serotype 2 ⁄ 7 ...
Neurotransmitter proteins
... 1) What is the function of the nervous system? 2) List the 3 main parts and describe the purpose of the 3 main parts of a neuron. 3) Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. 4) What is a synapse and why is it a problem for neurons? 5) What are the roles of the ...
... 1) What is the function of the nervous system? 2) List the 3 main parts and describe the purpose of the 3 main parts of a neuron. 3) Describe the internal and external environment of a neuron in resting potential. 4) What is a synapse and why is it a problem for neurons? 5) What are the roles of the ...
Chapter 12 - FacultyWeb Support Center
... B. Two cell types of nervous tissue are ________ and neuroglial cells. C. Neurons are specialized to react to _________ and chemical changes in their surroundings. D. ____________ are small cellular processes that receive input. E. Axons are long cellular processes that carry information away from _ ...
... B. Two cell types of nervous tissue are ________ and neuroglial cells. C. Neurons are specialized to react to _________ and chemical changes in their surroundings. D. ____________ are small cellular processes that receive input. E. Axons are long cellular processes that carry information away from _ ...
Neurons and how they communicate
... send a message to another neuron It does so through an electro-chemical process called action potential or neuronal firing ...
... send a message to another neuron It does so through an electro-chemical process called action potential or neuronal firing ...
The nervous system
... Depolarization must be completed and the nerve repolarized before the next action potential can be conducted as nerves conducting an impulse cannot be activated until the condition of the resting membrane is restored This time is called the refractory period (usually 1-10 ms) ...
... Depolarization must be completed and the nerve repolarized before the next action potential can be conducted as nerves conducting an impulse cannot be activated until the condition of the resting membrane is restored This time is called the refractory period (usually 1-10 ms) ...
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
... I. There are two different subtypes of ACh receptors: nicotinic and muscarinic. A. Nicotinic receptors enclose membrane channels and open when ACh bonds to the receptor. This causes a depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in skeletal muscle cells. B. The binding of ACh to ...
... I. There are two different subtypes of ACh receptors: nicotinic and muscarinic. A. Nicotinic receptors enclose membrane channels and open when ACh bonds to the receptor. This causes a depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in skeletal muscle cells. B. The binding of ACh to ...
Vestibular senses
... Opponent process theory (Hering) = Opponent colors “linked” together. Red-green opponents Blue-yellow opponents Black-white opponents Color perception due to relative activity of these 3 types of opponent systems True at the level of ganglion cells and in the rest of the visual system after (i.e., g ...
... Opponent process theory (Hering) = Opponent colors “linked” together. Red-green opponents Blue-yellow opponents Black-white opponents Color perception due to relative activity of these 3 types of opponent systems True at the level of ganglion cells and in the rest of the visual system after (i.e., g ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.