AP Biology - Pleasantville High School
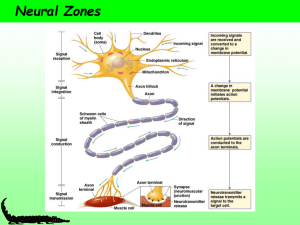
... membrane in a lock and key manner. (Inhibitor substances stop the impulse because they can fit into the receptor sites and block the normal neurotransmitter.) -this generates an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane and the nerve impulse continues on -after their release the neurotransmitter ...
... membrane in a lock and key manner. (Inhibitor substances stop the impulse because they can fit into the receptor sites and block the normal neurotransmitter.) -this generates an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane and the nerve impulse continues on -after their release the neurotransmitter ...
Test 1 Objectives
... What are the three kinds of gated channels? Understand what temporal summation and spatial summation. What are the variations between cells and what accounts for these variations? Know about the axon hillock. Know about saltatory conduction. What are the processes involved in the release of transmit ...
... What are the three kinds of gated channels? Understand what temporal summation and spatial summation. What are the variations between cells and what accounts for these variations? Know about the axon hillock. Know about saltatory conduction. What are the processes involved in the release of transmit ...
What do Babies See? By Dr. Lin Day, Baby Sensory. When a baby
... At birth, the baby’s image of the world is two dimensional or flat. As the eyes start to work together as a team, three-dimensional vision or depth perception develops. Depth perception allows the baby to estimate the distance of an object in the environment and to respond accurately. For example, i ...
... At birth, the baby’s image of the world is two dimensional or flat. As the eyes start to work together as a team, three-dimensional vision or depth perception develops. Depth perception allows the baby to estimate the distance of an object in the environment and to respond accurately. For example, i ...
Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural networks
... animals were young adult gerbils. A gerbil was deeply anaesthetized and its left cochlea was exposed. Tones from a loudspeaker were delivered to the ear via a tube ®tted to the left ear canal. The level of the tones was calibrated in the ear canal at the beginning of each experiment. Basal scala tym ...
... animals were young adult gerbils. A gerbil was deeply anaesthetized and its left cochlea was exposed. Tones from a loudspeaker were delivered to the ear via a tube ®tted to the left ear canal. The level of the tones was calibrated in the ear canal at the beginning of each experiment. Basal scala tym ...
Skeletal System
... If this depolarizing signal is strong enough when it reaches the initial segment of the axon, it acts as the trigger that initiates an action potential in the axon Signals from the receptive zone determine if the axon will fire an impulse ...
... If this depolarizing signal is strong enough when it reaches the initial segment of the axon, it acts as the trigger that initiates an action potential in the axon Signals from the receptive zone determine if the axon will fire an impulse ...
Introduction_to_the_Nervous_System1
... blood, pH, osmolarity, etc. Every one of these receptors is innervated by an afferent neuron at a neuroreceptor contact-place called a neuroreceptor synapse. When stimulated the receptor generates an excitatory state that is then transmitted at the synapse to the process of its innervating afferent ...
... blood, pH, osmolarity, etc. Every one of these receptors is innervated by an afferent neuron at a neuroreceptor contact-place called a neuroreceptor synapse. When stimulated the receptor generates an excitatory state that is then transmitted at the synapse to the process of its innervating afferent ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 3.3 Ultrastructure of dendritic spines and synapses in the human brain. A and B: Narrow spine necks (asterisks) emanate from the main dendritic shaft (D). The spine heads (S) contain filamentous material (A, B). Some large spines contain cisterns of a spine apparatus (sa, B). Asymmetric exci ...
... FIGURE 3.3 Ultrastructure of dendritic spines and synapses in the human brain. A and B: Narrow spine necks (asterisks) emanate from the main dendritic shaft (D). The spine heads (S) contain filamentous material (A, B). Some large spines contain cisterns of a spine apparatus (sa, B). Asymmetric exci ...
The Superior Olivary Nucleus and Its Influence on Nucleus
... because they constitute a feedback circuit for coincidence detection. In the present study, the chick SON was investigated. In vivo tracing studies show that the SON projects predominantly to the ipsilateral NM, NL, and NA. In vitro wholecell recording reveals single-cell morphology, firing properti ...
... because they constitute a feedback circuit for coincidence detection. In the present study, the chick SON was investigated. In vivo tracing studies show that the SON projects predominantly to the ipsilateral NM, NL, and NA. In vitro wholecell recording reveals single-cell morphology, firing properti ...
Steroids: The Brain`s Response
... STEROIDS The Brain’s Response to Drugs 800.232.4424 (Voice/TTY) 860.793.9813 (Fax) www.ctclearinghouse.org ...
... STEROIDS The Brain’s Response to Drugs 800.232.4424 (Voice/TTY) 860.793.9813 (Fax) www.ctclearinghouse.org ...
Lecture 6 - School of Computing | University of Leeds
... We introduced biological neural networks. We found complexity at every level, from the sub-cellular to the entire brain. We realised that even with a limited understanding, cartoon models can be derived for some functions of neurons (action potentials, synaptic transmission, neuronal computation and ...
... We introduced biological neural networks. We found complexity at every level, from the sub-cellular to the entire brain. We realised that even with a limited understanding, cartoon models can be derived for some functions of neurons (action potentials, synaptic transmission, neuronal computation and ...
Ingestive Behaviour Chapter 12
... When we eat (and digest) we incorporate molecules that were once part of other plants and animals into our bodies. These molecules are ingested to provide molecular building blocks and fuel. Cells need fuel and O2 to stay alive; fuel comes from digestive tract (and is there because of eating). ...
... When we eat (and digest) we incorporate molecules that were once part of other plants and animals into our bodies. These molecules are ingested to provide molecular building blocks and fuel. Cells need fuel and O2 to stay alive; fuel comes from digestive tract (and is there because of eating). ...
Impact of Correlated inputs on Simple Neural Models
... c = Correlation coefficient Th = Threshold ...
... c = Correlation coefficient Th = Threshold ...
Sensation_and_Perception
... Ganglion Cells – they sum up the signals from the rods and cones and send action potentials through the optic nerve and to the brain. The axons from the network of Ganglion Cells converge like the strands of a rope to form an Optic Nerve= passage way to the visual cortex through the thalamus ...
... Ganglion Cells – they sum up the signals from the rods and cones and send action potentials through the optic nerve and to the brain. The axons from the network of Ganglion Cells converge like the strands of a rope to form an Optic Nerve= passage way to the visual cortex through the thalamus ...
Auditory Nerve - Neurobiology of Hearing
... And now, we can complete the near 80-year old diagram by Lorente de Nó on the axons in the inner ear that are not attached to cell bodies of the spiral ganglion. These turn out to be the efferent axons, that arise in the brainstem—one set called the lateral efferents that terminate on ANFs under th ...
... And now, we can complete the near 80-year old diagram by Lorente de Nó on the axons in the inner ear that are not attached to cell bodies of the spiral ganglion. These turn out to be the efferent axons, that arise in the brainstem—one set called the lateral efferents that terminate on ANFs under th ...
Cellular Senescence
... - p53 and pRB: important tumor suppressor pathways - Both pathways are crucial for establishing and maintaining the senescent phenotype - the senescence response is, very likely, a failsafe mechanism to prevent the growth of potentially oncogenic cells, rendering them incapable of tumorigenesis - a ...
... - p53 and pRB: important tumor suppressor pathways - Both pathways are crucial for establishing and maintaining the senescent phenotype - the senescence response is, very likely, a failsafe mechanism to prevent the growth of potentially oncogenic cells, rendering them incapable of tumorigenesis - a ...
BioTech - University of Illinois at Chicago
... electrical stimulation of the retina at the cellular level, in vivo, in a clinically-relevant animal model • Using pharmacological dissection, we have begun to identify the types of retinal neurons targeted by electrical stimulation • Ultimate Goal: To communicate the visual scene to the diseased re ...
... electrical stimulation of the retina at the cellular level, in vivo, in a clinically-relevant animal model • Using pharmacological dissection, we have begun to identify the types of retinal neurons targeted by electrical stimulation • Ultimate Goal: To communicate the visual scene to the diseased re ...
15. Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System
... This section of the text reinforces the concept of thoracolumbar control. Although you do not need to memorize specific pathways, you should understand the general point illustrated by Fig. 15.6. Notice that all preganglionic axons of the sympathetic enter the sympathetic trunk. Many of these axons ...
... This section of the text reinforces the concept of thoracolumbar control. Although you do not need to memorize specific pathways, you should understand the general point illustrated by Fig. 15.6. Notice that all preganglionic axons of the sympathetic enter the sympathetic trunk. Many of these axons ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
... adaptations that increase the speed of propagation. Describe saltatory conduction. 14) Compare an electrical synapse and a chemical synapse. 15) Describe the structures of a chemical synapse and explain how they transmit an action potential from one cell to another. 16) Explain how excitatory postsy ...
Synapses - UBC Zoology
... - membranes are separated by 2 nm - gap junctions link the cytosol of two cells - provide a passageway for movement of very small molecules and ions between the cells - gap junction channels have a large conductance - NO synaptic delay (current spread from cell to cell is instantaneous) - important ...
... - membranes are separated by 2 nm - gap junctions link the cytosol of two cells - provide a passageway for movement of very small molecules and ions between the cells - gap junction channels have a large conductance - NO synaptic delay (current spread from cell to cell is instantaneous) - important ...
Trigeminal system
... Self-assessment: When you think you have mastered the pathways, select 2 colors in both a dark and light shade. Use the dark color for the body and the lighter color for the face pathways. ...
... Self-assessment: When you think you have mastered the pathways, select 2 colors in both a dark and light shade. Use the dark color for the body and the lighter color for the face pathways. ...
Strategies for the Generation of Neuronal Diversity in the
... Under the second mechanismthat contributes to the determination of specific neuronal fates, neuronal precursorsor their progeny are multipotent-that is, the cells may develop along a variety of possiblepathways, and the particular pathway chosen resultsfrom interactions between cells and their local ...
... Under the second mechanismthat contributes to the determination of specific neuronal fates, neuronal precursorsor their progeny are multipotent-that is, the cells may develop along a variety of possiblepathways, and the particular pathway chosen resultsfrom interactions between cells and their local ...
File
... • Chemicals in the body are ions (electrically charged) • Two important ions in the nervous system – sodium (Na) and potassium (K) ...
... • Chemicals in the body are ions (electrically charged) • Two important ions in the nervous system – sodium (Na) and potassium (K) ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.