The Nervous System - Zen Shiatsu Chicago
... 2. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enters the axon terminal. 3. Ca2+ entry causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to release their contents by exocytosis. 4. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. 5. Binding of ...
... 2. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open and Ca2+ enters the axon terminal. 3. Ca2+ entry causes neurotransmitter-containing vesicles to release their contents by exocytosis. 4. Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. 5. Binding of ...
Nervous System Outline
... Nervous System Outline Nervous System Functions -100 billion nerve cells ...
... Nervous System Outline Nervous System Functions -100 billion nerve cells ...
Exam 5 Objectives Bio241
... 7. Describe the events at a synapse during neurotransmission including how a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell (calcium triggers exocytosis), what determines the effect that a neurotransmitter will have on the postsynaptic cell, and how the signal is terminated. What is the mech ...
... 7. Describe the events at a synapse during neurotransmission including how a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell (calcium triggers exocytosis), what determines the effect that a neurotransmitter will have on the postsynaptic cell, and how the signal is terminated. What is the mech ...
In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
Brain Anatomy PPT
... A diffuse network of neurons called the reticular formation is present in the core of the brainstem A ...
... A diffuse network of neurons called the reticular formation is present in the core of the brainstem A ...
The Nervous System
... 16. Within a neuron, what is the function of the axon? 17. What would happen to the resting potential of a neuron if it ran out of ATP? 18. When a neuron receives an excitatory stimulus, what causes the membrane to depolarize? 19. All stimuli cause neurons to depolarize. True or False 20. When thres ...
... 16. Within a neuron, what is the function of the axon? 17. What would happen to the resting potential of a neuron if it ran out of ATP? 18. When a neuron receives an excitatory stimulus, what causes the membrane to depolarize? 19. All stimuli cause neurons to depolarize. True or False 20. When thres ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I: Basic Structure and Function
... 4. The refractory period limits how many action potentials may be generated in a neuron in a given time. H. Impulse Conduction ...
... 4. The refractory period limits how many action potentials may be generated in a neuron in a given time. H. Impulse Conduction ...
X- and Y-Cells in the Dorsal Lateral Geniculate
... (Fig. 2A), poor activation by fast visual stimuli (Fig. 2B), and no activation by fast targets of appropriate contrast to excite the cell through the surround. The difference between X- and Y-cells based on the tonic-phasic distinction was particularly dramatic in the owl monkey. All ...
... (Fig. 2A), poor activation by fast visual stimuli (Fig. 2B), and no activation by fast targets of appropriate contrast to excite the cell through the surround. The difference between X- and Y-cells based on the tonic-phasic distinction was particularly dramatic in the owl monkey. All ...
Nervous System
... Also allows the action potential to move faster & easier. These are White in color, so heavily myelated cells appear as White Matter. ...
... Also allows the action potential to move faster & easier. These are White in color, so heavily myelated cells appear as White Matter. ...
NOB Ch 6 Answers - MCC Year 12 Biology
... The transmitter substance, such as acetylcholine, is released from the end of the axon and diffuses across the small gap between the axon and the muscle and binds to receptors on the muscle membrane. The muscle reacts to the message received, such as by contracting in response to the transmitter ...
... The transmitter substance, such as acetylcholine, is released from the end of the axon and diffuses across the small gap between the axon and the muscle and binds to receptors on the muscle membrane. The muscle reacts to the message received, such as by contracting in response to the transmitter ...
reverse engineering of the visual system using networks of spiking
... by an input until it reaches a threshold, at which point it generates an output pulse – the action potential or spike. Such neurons will naturally fire earliest when the input is strong, and will take progressively longer to fire when the input is weaker. In this way, the time at which a neuron fire ...
... by an input until it reaches a threshold, at which point it generates an output pulse – the action potential or spike. Such neurons will naturally fire earliest when the input is strong, and will take progressively longer to fire when the input is weaker. In this way, the time at which a neuron fire ...
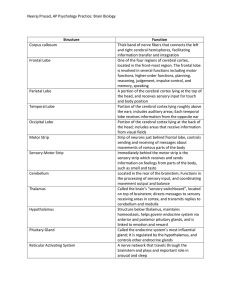
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
... information transfer and integration One of the four regions of cerebral cortex, located in the front-most region. The frontal lobe is involved in several functions including motor functions, higher-order functions, planning, reasoning, judgement, impulse control, and memory, speaking A portion of t ...
... information transfer and integration One of the four regions of cerebral cortex, located in the front-most region. The frontal lobe is involved in several functions including motor functions, higher-order functions, planning, reasoning, judgement, impulse control, and memory, speaking A portion of t ...
Development & Neuroplasticity - U
... young brain may contribute to its greater plasticity (capability for functions to be mediated by other neurons not originally involved) ...
... young brain may contribute to its greater plasticity (capability for functions to be mediated by other neurons not originally involved) ...
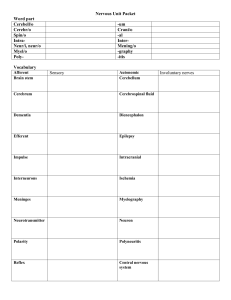
Nervous System Guided Notes
... 1) _______________________________or sensory neurons - bring stimuli to CNS -- affect the body by internal or external information 2) _______________________________or motor neurons -- cause muscles or glands to respond -- effect a change / response ...
... 1) _______________________________or sensory neurons - bring stimuli to CNS -- affect the body by internal or external information 2) _______________________________or motor neurons -- cause muscles or glands to respond -- effect a change / response ...
Memory Systems
... • Lesioned amygdala, hippocampus and perirhinal cortex in temporal lobe of monkeys and found that they could no longer perform in recognition memory tests • Later showed that perirhinal cortex is most important for new memory; temporary storage? Memory consolidation? ...
... • Lesioned amygdala, hippocampus and perirhinal cortex in temporal lobe of monkeys and found that they could no longer perform in recognition memory tests • Later showed that perirhinal cortex is most important for new memory; temporary storage? Memory consolidation? ...
Neurons and Functional Neuroanatomy
... length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
... length of the axon in one direction The action potential moves in one direction because the membrane is refractory (unable to respond) once the action potential has been initiated at any particular place on the membrane ...
UNIT 3
... A cell that is not being stimulated to send an impulse is in a resting state. Factors that contribute to resting membrane potential include unequal distribution of ions across the plasma membrane (high concentration of sodium ions outside the cell and a high concentration of potassium inside), or a ...
... A cell that is not being stimulated to send an impulse is in a resting state. Factors that contribute to resting membrane potential include unequal distribution of ions across the plasma membrane (high concentration of sodium ions outside the cell and a high concentration of potassium inside), or a ...
Reflex Arc - TangHua2012-2013
... Each axon branches off and ends with a swelled tip or __________________that lies close to but not touching the dendrite of another neuron. (or an organ). The entire region is called a ____________. Transmission of nerve impulses across a ______________________ is carried out by chemicals called ___ ...
... Each axon branches off and ends with a swelled tip or __________________that lies close to but not touching the dendrite of another neuron. (or an organ). The entire region is called a ____________. Transmission of nerve impulses across a ______________________ is carried out by chemicals called ___ ...
Slide ()
... The olfactory epithelium. A. The olfactory epithelium contains sensory neurons interspersed with supporting cells as well as a basal layer of stem cells. Cilia extend from the dendrite of each neuron into the mucus lining the nasal cavity. An axon extends from the basal end of each neuron to the olf ...
... The olfactory epithelium. A. The olfactory epithelium contains sensory neurons interspersed with supporting cells as well as a basal layer of stem cells. Cilia extend from the dendrite of each neuron into the mucus lining the nasal cavity. An axon extends from the basal end of each neuron to the olf ...
document
... was greatest when the monkey used its wrist flexor muscles against a load. Modified from Evarts (1968). Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... was greatest when the monkey used its wrist flexor muscles against a load. Modified from Evarts (1968). Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
NeuralNets273ASpring09
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
LIMBIC SYSTEM
... panicky, fearful sensation. During the following week, she had repeated stereotyped episodes of this kind followed by decreased ...
... panicky, fearful sensation. During the following week, she had repeated stereotyped episodes of this kind followed by decreased ...
Chapter 10
... 26. Explain the relationship between an action potential and a nerve impulse. (Outcome 10.16) An action potential occurs at a specific site. When an action potential occurs at the trigger zone of a nerve cell, it sends an electrical impulse to the adjacent membrane. This causes an action potential a ...
... 26. Explain the relationship between an action potential and a nerve impulse. (Outcome 10.16) An action potential occurs at a specific site. When an action potential occurs at the trigger zone of a nerve cell, it sends an electrical impulse to the adjacent membrane. This causes an action potential a ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... 1. The synapse between a postganglionic neuron and its target cell is called the _______________ junction a. Autonomic neuron axon terminals form bead-like strands called ________________, which lie across the target tissue b. Neurotransmitter released from the varicosities diffuses to ____________ ...
... 1. The synapse between a postganglionic neuron and its target cell is called the _______________ junction a. Autonomic neuron axon terminals form bead-like strands called ________________, which lie across the target tissue b. Neurotransmitter released from the varicosities diffuses to ____________ ...
Course Introduction: The Brain, chemistry, neural signaling
... IPSPs will counteract the effect of EPSPs at the same neuron. Summation means the effect of many coincident IPSPs and EPSPs at one neuron. If there is sufficient depolarization at the axon hillock, an action potential will be triggered. ...
... IPSPs will counteract the effect of EPSPs at the same neuron. Summation means the effect of many coincident IPSPs and EPSPs at one neuron. If there is sufficient depolarization at the axon hillock, an action potential will be triggered. ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.