Chapt13 Lecture 13ed Pt 1
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) sensory (afferent) nerves — carry sensory information into brain and spinal cord ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) sensory (afferent) nerves — carry sensory information into brain and spinal cord ...
Chapter 6: Summary and Discussion
... propose that the propagation of enhanced responses in early visual cortex (including V1) can explain the spread of attention the psychological level of description. In chapter 3 we investigated the relation between the coding of attention and reward in area V1 with a curve-tracing task where we vari ...
... propose that the propagation of enhanced responses in early visual cortex (including V1) can explain the spread of attention the psychological level of description. In chapter 3 we investigated the relation between the coding of attention and reward in area V1 with a curve-tracing task where we vari ...
31.1 The Neuron Functions of the Nervous System and external
... The sensory division transmits impulses from sense organs to the central nervous system. Sensory receptors are cells that transmit information about changes in the internal and external environment. Chemoreceptors respond to chemicals. Photoreceptors respond to light. Mechanoreceptors respond to tou ...
... The sensory division transmits impulses from sense organs to the central nervous system. Sensory receptors are cells that transmit information about changes in the internal and external environment. Chemoreceptors respond to chemicals. Photoreceptors respond to light. Mechanoreceptors respond to tou ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... • A synapse is the junction between: • The axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron (axodendritic) • The axon of one neuron and the soma of another neuron (axosomic) • The axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron (axoaxonic) • The axon of a neuron and a muscle ...
... • A synapse is the junction between: • The axon of one neuron and the dendrite of another neuron (axodendritic) • The axon of one neuron and the soma of another neuron (axosomic) • The axon of one neuron and the axon of another neuron (axoaxonic) • The axon of a neuron and a muscle ...
Objectives 53 - u.arizona.edu
... - if stroke diagnosed within 3 hours of onset of symptoms thrombolytic agents administered to enhance dissolution of clots and restore profusion of the brain; risk includes hemorrhage in brain (after 3 hours, risk is to great to administer thrombolytic agents) - new techniques involve infusing thr ...
... - if stroke diagnosed within 3 hours of onset of symptoms thrombolytic agents administered to enhance dissolution of clots and restore profusion of the brain; risk includes hemorrhage in brain (after 3 hours, risk is to great to administer thrombolytic agents) - new techniques involve infusing thr ...
pttx
... -The central nervous system (CNS) has two parts: The brain (enclosed in the cranium) and the spinal chord (enclosed within the foramen of ...
... -The central nervous system (CNS) has two parts: The brain (enclosed in the cranium) and the spinal chord (enclosed within the foramen of ...
Nervous System
... – Memories are stored in bits and pieces in association areas – Hippocampus pulls these all together to allow us to recall them all as a single event – Amygdala is responsible for emotions associated with some memories ...
... – Memories are stored in bits and pieces in association areas – Hippocampus pulls these all together to allow us to recall them all as a single event – Amygdala is responsible for emotions associated with some memories ...
Synaptic Neurotransmission and the Anatomically Addressed
... chemical signals, different from neurotransmitters, called adhesion molecules (Table 2-2). First, glial cells form a cellular matrix (Figures 2-2 and 2-11). Neurons can trace glial fibers like a trail through the brain to their destinations. Later, neurons can follow the axons of other neurons alrea ...
... chemical signals, different from neurotransmitters, called adhesion molecules (Table 2-2). First, glial cells form a cellular matrix (Figures 2-2 and 2-11). Neurons can trace glial fibers like a trail through the brain to their destinations. Later, neurons can follow the axons of other neurons alrea ...
Buzsaki and Draguhn (2004), Neuronal Oscillations in Cortical
... Input selection and plasticity. Single neuneuron “clocking” networks (19, 32). In many trace of an earlier event is retained, which then rons and networks respond with transient ossystems, electrical coupling by gap junctions alters the response to a subsequent event. In cillations to a strong input ...
... Input selection and plasticity. Single neuneuron “clocking” networks (19, 32). In many trace of an earlier event is retained, which then rons and networks respond with transient ossystems, electrical coupling by gap junctions alters the response to a subsequent event. In cillations to a strong input ...
Chapter 15 Anatomy & Physiology
... – Thermoreceptors – are essentially free nerve endings scattered immediately beneath the skin, skeletal muscles, the liver, and the hypothalamus. – There are several times more cold receptors than hot receptors and their structures are indistinguishable. – The pathways of pain receptors and those of ...
... – Thermoreceptors – are essentially free nerve endings scattered immediately beneath the skin, skeletal muscles, the liver, and the hypothalamus. – There are several times more cold receptors than hot receptors and their structures are indistinguishable. – The pathways of pain receptors and those of ...
CNS lecture
... Amygdala nucleus: part of the limbic system located deep within each hemisphere/ important part of emotional feelings linked to cognitive input (pleasure and fear emotions) Fear conditioning sends input to hypothalamus to signal the sympathetic NS to act Reticular Activating System: nuclei axons con ...
... Amygdala nucleus: part of the limbic system located deep within each hemisphere/ important part of emotional feelings linked to cognitive input (pleasure and fear emotions) Fear conditioning sends input to hypothalamus to signal the sympathetic NS to act Reticular Activating System: nuclei axons con ...
Inkwell @ SMUG - Indiana University
... • “Functional interactions with the environment.” • “Interdependence of parts.” • “Stability under perturbations.” • “The ability to evolve.” ...
... • “Functional interactions with the environment.” • “Interdependence of parts.” • “Stability under perturbations.” • “The ability to evolve.” ...
NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND RECEPTORS
... The Structure of the Neuron • Playing the piano, driving a car, or hitting a tennis ball depends, at one level, on exact muscle coordination. • But if we consider how the muscles can be activated so precisely, we see that more fundamental processes are involved. • For the muscles to produce the com ...
... The Structure of the Neuron • Playing the piano, driving a car, or hitting a tennis ball depends, at one level, on exact muscle coordination. • But if we consider how the muscles can be activated so precisely, we see that more fundamental processes are involved. • For the muscles to produce the com ...
RNI_Introduction - Cognitive and Linguistic Sciences
... An intermediate scale neural network based model we have worked on here at Brown is the Network of Networks. It assumes that the basic computational element in brain-like computation is not the neuron but a small network of neurons. These small (conjectured to be 103 -104 neurons) networks are nonli ...
... An intermediate scale neural network based model we have worked on here at Brown is the Network of Networks. It assumes that the basic computational element in brain-like computation is not the neuron but a small network of neurons. These small (conjectured to be 103 -104 neurons) networks are nonli ...
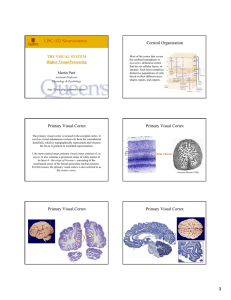
LISC-322 Neuroscience Cortical Organization Primary Visual Cortex
... show increase in cerebral flow in: A) area MT (V5) while they view a monochromatic scene in motion, and B) area V4 while they view a stationary colorful ...
... show increase in cerebral flow in: A) area MT (V5) while they view a monochromatic scene in motion, and B) area V4 while they view a stationary colorful ...
(Figure 4B) in 12 month old Cln5-/- mice. To survey effects on glial
... nature of the NCLs. Consistent with a mouse model of JNCL (Cln3 null mutant), Cln5-/- mice display a profound loss of sensory relay thalamic neurons, yet no loss of their target neurons in lamina IV of somatosensory cortex. Our preliminary data suggest that this vulnerability of thalamic neurons is ...
... nature of the NCLs. Consistent with a mouse model of JNCL (Cln3 null mutant), Cln5-/- mice display a profound loss of sensory relay thalamic neurons, yet no loss of their target neurons in lamina IV of somatosensory cortex. Our preliminary data suggest that this vulnerability of thalamic neurons is ...
Role of Basal Ganglia in the Regulation of Motor Activities by the
... The hyperdirect pathway functions to inhibit incorrect motor activities / movements. Lesions in this pathway (such as in case of stroke) results in the inability to inhibit incorrect / unwanted patterns of movements leading to hemiballismus which is marked by unilateral, voilent motor restlessness o ...
... The hyperdirect pathway functions to inhibit incorrect motor activities / movements. Lesions in this pathway (such as in case of stroke) results in the inability to inhibit incorrect / unwanted patterns of movements leading to hemiballismus which is marked by unilateral, voilent motor restlessness o ...
Notes Intro to Nervous System and Neurons
... Books says antagonistic, but they are more complimentary ...
... Books says antagonistic, but they are more complimentary ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... • Must depolarize to threshold (-55mV) before action potential begins – Voltage gated channels on excitable membrane open at threshold to propagate action potential ...
... • Must depolarize to threshold (-55mV) before action potential begins – Voltage gated channels on excitable membrane open at threshold to propagate action potential ...
Definition of the limbic system
... Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: .The limbic system and the autonomic nervous system One of its most important effects is causing the adrenal glands (which sit on top of the kidneys) to release epin ...
... Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: .The limbic system and the autonomic nervous system One of its most important effects is causing the adrenal glands (which sit on top of the kidneys) to release epin ...
Babylon university Medical physics exam
... negative than out side and this represent the resting potential . if stimulation heat, cold, light, sound cause change in action potential Fig a : resting potential of axon= - 80mV ...
... negative than out side and this represent the resting potential . if stimulation heat, cold, light, sound cause change in action potential Fig a : resting potential of axon= - 80mV ...
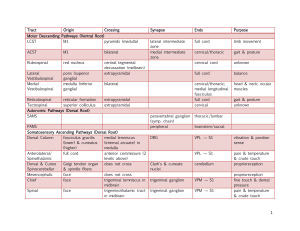
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... extremity ataxia: finger tapping test intermediate/paravermis: interposed nuclei (emboliform & globose) → same as above, except through magno red nucleus appendicular ataxia: dysrhythmia (abnormal timing) or dysmetria (abnormal trajectories in space) (excessive check/finger to nose test) medial: ver ...
... extremity ataxia: finger tapping test intermediate/paravermis: interposed nuclei (emboliform & globose) → same as above, except through magno red nucleus appendicular ataxia: dysrhythmia (abnormal timing) or dysmetria (abnormal trajectories in space) (excessive check/finger to nose test) medial: ver ...
Neural Networks
... Hoehl, Stefanie, Christine Michel, Vincent M Reid, Eugenio Parise, and Tricia Striano. 2014. “Eye Contact during Live Social Interaction Modulates Infants’ Oscillatory Brain Activity.” Social Neuroscience 00 (00) (February 7 ...
... Hoehl, Stefanie, Christine Michel, Vincent M Reid, Eugenio Parise, and Tricia Striano. 2014. “Eye Contact during Live Social Interaction Modulates Infants’ Oscillatory Brain Activity.” Social Neuroscience 00 (00) (February 7 ...
neural projections from nucleus accumbens to globus pallidus
... most obvious difference is that fibers from the caudoputamen travel to the substantia nigra through medial parts of the cerebral peduncle, while most of those from the nucleus accumbens descend through lateral parts of the medial forebrain bundle in the substantia innominata (SI), lateral preoptic a ...
... most obvious difference is that fibers from the caudoputamen travel to the substantia nigra through medial parts of the cerebral peduncle, while most of those from the nucleus accumbens descend through lateral parts of the medial forebrain bundle in the substantia innominata (SI), lateral preoptic a ...
1. Identify the functions of the nervous system and relate nervous
... Label the parts of the generalized neuron on this page. Indicate the function of each part of the neuron in your notebook. ...
... Label the parts of the generalized neuron on this page. Indicate the function of each part of the neuron in your notebook. ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.