ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... Delivers nutrients and removes wastes How do we tell one part from another? What does each part of the brain do? Cerebrum o Largest part of the brain o Controls higher mental functions Intellect, Reason, Learning and Memory, Planning and Emotion o Divided into left and right hemispheres by the ...
... Delivers nutrients and removes wastes How do we tell one part from another? What does each part of the brain do? Cerebrum o Largest part of the brain o Controls higher mental functions Intellect, Reason, Learning and Memory, Planning and Emotion o Divided into left and right hemispheres by the ...
Cognitive Neuroscience
... • RAS (reticular activating system) • Important in controlling consciousness (sleep, arousal), attention, cardiorespiratory function and movement • Extends into the hindbrain ...
... • RAS (reticular activating system) • Important in controlling consciousness (sleep, arousal), attention, cardiorespiratory function and movement • Extends into the hindbrain ...
B6 – Brain and mind - The Bicester School
... reflex response to a new stimulus can be learned by introducing the secondary (new) stimulus in association with the primary stimulus This is called conditioning. ...
... reflex response to a new stimulus can be learned by introducing the secondary (new) stimulus in association with the primary stimulus This is called conditioning. ...
Document
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. describe the structural and functional features of the inner ear. ...
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. describe the structural and functional features of the inner ear. ...
SAC 1 PRACTICE TEST 2017
... 13. Jacinta experienced a brain haemorrhage resulting in decreased blood supply and increased pressure on the brain tissue, which caused damage to her Wernicke’s area. Based on your knowledge of research of individuals who have sustained damage to their Wernicke’s area, Jacinta would most likely: A ...
... 13. Jacinta experienced a brain haemorrhage resulting in decreased blood supply and increased pressure on the brain tissue, which caused damage to her Wernicke’s area. Based on your knowledge of research of individuals who have sustained damage to their Wernicke’s area, Jacinta would most likely: A ...
Learning Skill
... This self-discovery of more efficient movements eventually leads to an array of somewhat efficient movements that are stored as motor memories and integrated with the sensory memories of those movements. ...
... This self-discovery of more efficient movements eventually leads to an array of somewhat efficient movements that are stored as motor memories and integrated with the sensory memories of those movements. ...
Vision I
... transduce is to convert energy from one form to another. – Sensory transduction is the process by which sensory stimuli are “translated” into changes in the cell membrane potential. ...
... transduce is to convert energy from one form to another. – Sensory transduction is the process by which sensory stimuli are “translated” into changes in the cell membrane potential. ...
Nervous - Anoka-Hennepin School District
... Action potentialA reversal in the polarity (depolarization) of the neuron. Sodium ions rush into the cell so the inside is now more positive than the outside of the cell. ...
... Action potentialA reversal in the polarity (depolarization) of the neuron. Sodium ions rush into the cell so the inside is now more positive than the outside of the cell. ...
November 2000 Volume 3 Number Supp pp 1184
... associations seem to evoke less activity in the PFC than relatively novel stimuli10, indicating that other mechanisms or brain regions might get involved after extensive training. Low spontaneous and selective high-activity states In contrast to the model in Fig. 2, PFC neurons in vivo are never si ...
... associations seem to evoke less activity in the PFC than relatively novel stimuli10, indicating that other mechanisms or brain regions might get involved after extensive training. Low spontaneous and selective high-activity states In contrast to the model in Fig. 2, PFC neurons in vivo are never si ...
Dissecting appetite
... laser made the mice hungry again.” When these neurons were repeatedly stimulated at 12-hour intervals for several days, the mice ate less and lost weight, indicating that stimulating CGRP neurons is sufficient to cause starvation7. To map neurons downstream of the CGRP neurons, Palmiter used a fluor ...
... laser made the mice hungry again.” When these neurons were repeatedly stimulated at 12-hour intervals for several days, the mice ate less and lost weight, indicating that stimulating CGRP neurons is sufficient to cause starvation7. To map neurons downstream of the CGRP neurons, Palmiter used a fluor ...
The combinatorics and dynamics of a discrete k winners take all
... We consider a modification of the classical perceptron model of neural networks inspired by neuroscience research on hippocampus. In this model, those k neurons fire whose weighted inputs are maximal. The model tries to mimic the dynamics of the neural activity in the hippocampus, where only a few p ...
... We consider a modification of the classical perceptron model of neural networks inspired by neuroscience research on hippocampus. In this model, those k neurons fire whose weighted inputs are maximal. The model tries to mimic the dynamics of the neural activity in the hippocampus, where only a few p ...
Lecture 6 Locomotion • Early 20th century experiments showed that
... Sensory afferent can modify stepping • Proprioceptors – in muscles and joints provides information to brain about limb position • Cutaneous receptors – spinal level reflex response to external obstacles (rocks ...
... Sensory afferent can modify stepping • Proprioceptors – in muscles and joints provides information to brain about limb position • Cutaneous receptors – spinal level reflex response to external obstacles (rocks ...
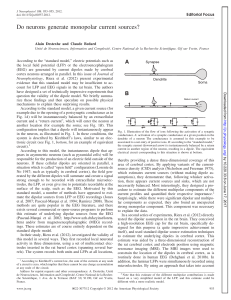
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... evidence that this standard model may be insufficient to account for LFP and EEG signals in the rat brain. The authors have designed a set of technically impressive experiments that question the validity of the dipole model. We briefly summarize these findings and then speculate on possible physical ...
... evidence that this standard model may be insufficient to account for LFP and EEG signals in the rat brain. The authors have designed a set of technically impressive experiments that question the validity of the dipole model. We briefly summarize these findings and then speculate on possible physical ...
Tail Region of the Primary Somatosensory Cortex and Its Relation to
... In the present study, electrophysiological mapping methods were used to estimate the size of the tail representation area of the primary somatosensory cortex (SI) of the rat. Using a half-maximal evoked potential method and multiunit recording method, we estimated that the SI tail area was 0.51 and ...
... In the present study, electrophysiological mapping methods were used to estimate the size of the tail representation area of the primary somatosensory cortex (SI) of the rat. Using a half-maximal evoked potential method and multiunit recording method, we estimated that the SI tail area was 0.51 and ...
fluctuations in somatosensory responsiveness and baseline firing
... were presented 5–10 s apart. Instantaneously on contact of the bipolar probe with the animal, a DC pulse was delivered to the computer to generate a time-stamp, or node, of the approximate onset of each stimulus. Neurons were selected if they exhibited cutaneous responsiveness and little or no corre ...
... were presented 5–10 s apart. Instantaneously on contact of the bipolar probe with the animal, a DC pulse was delivered to the computer to generate a time-stamp, or node, of the approximate onset of each stimulus. Neurons were selected if they exhibited cutaneous responsiveness and little or no corre ...
Chapter 12 The Nervous System
... The gated K+ channels close and the gates of the Na+ channels open Na+ ions move into the axon, making the interior more positive than the outside of the neuron. This causes a depolarization in this area of the neuron, causing the polarity to be reversed area of the axon. The sodium rushes in displ ...
... The gated K+ channels close and the gates of the Na+ channels open Na+ ions move into the axon, making the interior more positive than the outside of the neuron. This causes a depolarization in this area of the neuron, causing the polarity to be reversed area of the axon. The sodium rushes in displ ...
Session 4
... If move perpendicular to the surface of the cortex, cells will respond primarily to input from one eye (ocular dominance). The pattern of responses forms columns of ocular dominance. ...
... If move perpendicular to the surface of the cortex, cells will respond primarily to input from one eye (ocular dominance). The pattern of responses forms columns of ocular dominance. ...
Chapter 49 and 50 Presentations-Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
... Ion channels in the membranes of the dendrites open and close in response to the stimuli. The flow of ions across the membranes of these receptors results in a change in the membrane potential. ...
... Ion channels in the membranes of the dendrites open and close in response to the stimuli. The flow of ions across the membranes of these receptors results in a change in the membrane potential. ...
Purkinje cells
... The indirect pathway takes a detour from the striatum, (GABA) first to the external segment of the globus pallidus (GABA) and then to the subthalamic nucleus (Glu), before finally reaching the internal segment of the globus pallidus or the substantia nigra pars reticulata. The isgp and the snpr pr ...
... The indirect pathway takes a detour from the striatum, (GABA) first to the external segment of the globus pallidus (GABA) and then to the subthalamic nucleus (Glu), before finally reaching the internal segment of the globus pallidus or the substantia nigra pars reticulata. The isgp and the snpr pr ...
Seminars of Interest
... Remember that experiment in class where the pyramid tract was lesioned unilaterally (on one side, in this case we’ll say the right) in a monkey? The monkey lost fine control of his left hand. Why the left hand? The lesion occurred above the pyramidal decussation, where the corticospinal fibers cros ...
... Remember that experiment in class where the pyramid tract was lesioned unilaterally (on one side, in this case we’ll say the right) in a monkey? The monkey lost fine control of his left hand. Why the left hand? The lesion occurred above the pyramidal decussation, where the corticospinal fibers cros ...
Motor system - Brain Facts
... parietal cortex (area 5, 7). One kind of neuron is active before goal-directed, reaching movements, such as when a monkey stretches its hand toward a banana. Such neurons do not become active, however, in relation to movement in the same direction but without a specific aim, or in relation to a pass ...
... parietal cortex (area 5, 7). One kind of neuron is active before goal-directed, reaching movements, such as when a monkey stretches its hand toward a banana. Such neurons do not become active, however, in relation to movement in the same direction but without a specific aim, or in relation to a pass ...
ppt
... Synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse to reach the postsynaptic neuron or the cell membrane of an effector. ...
... Synaptic vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse to reach the postsynaptic neuron or the cell membrane of an effector. ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.