sensory1
... lips, palm, fingertip, calf). For touch discrimination, small receptive fields allow greater accuracy in “two point discrimination” test (upcoming lab!) ...
... lips, palm, fingertip, calf). For touch discrimination, small receptive fields allow greater accuracy in “two point discrimination” test (upcoming lab!) ...
Large-scale spatiotemporal spike patterning consistent with
... cortex of mammals including monkeys15–18 and humans19,20. In particular, we have previously demonstrated that across the precentral gyrus of the upper-limb area of primary motor cortex (MI), these oscillations are not perfectly synchronized but rather exhibit phase gradients that indicate planar pro ...
... cortex of mammals including monkeys15–18 and humans19,20. In particular, we have previously demonstrated that across the precentral gyrus of the upper-limb area of primary motor cortex (MI), these oscillations are not perfectly synchronized but rather exhibit phase gradients that indicate planar pro ...
DNA, Human Memory, and the Storage
... eventually assembles the mass-produced components of the SFV, and sends them out at the rate of several thousand per hour to infect other cells within the host organism.8 This paper reviews some of the fundamental aspects of cellular processes and neuronal behavior in biological systems, with an eye ...
... eventually assembles the mass-produced components of the SFV, and sends them out at the rate of several thousand per hour to infect other cells within the host organism.8 This paper reviews some of the fundamental aspects of cellular processes and neuronal behavior in biological systems, with an eye ...
Chapter 17-Pathways and Integrative Functions
... Functional anatomy of sensory pathways two or three neurons • primary neuron: dendrites are part of receptor that detects a specific stimulus (pain, texture, vibration, temperature, proprioception) • secondary neuron: interneuron; cell body resides in posterior horn of spinal cord or brainstem nucl ...
... Functional anatomy of sensory pathways two or three neurons • primary neuron: dendrites are part of receptor that detects a specific stimulus (pain, texture, vibration, temperature, proprioception) • secondary neuron: interneuron; cell body resides in posterior horn of spinal cord or brainstem nucl ...
PSE4U1 - 10.Unit 4
... – Good insulator covering the axon between nodes, allowing transmission to be fast – Formed by Schwann Cells that wrap around some axons outside the central nervous system – Neurilemma is the outer cell membrane of a Schwann Cell – Nodes of Ranvier are indentations that exist between adjancent Schwa ...
... – Good insulator covering the axon between nodes, allowing transmission to be fast – Formed by Schwann Cells that wrap around some axons outside the central nervous system – Neurilemma is the outer cell membrane of a Schwann Cell – Nodes of Ranvier are indentations that exist between adjancent Schwa ...
Article Link - Cortical Systems and Behavior Laboratory
... (Chaplin et al. 2013; Kaas 2006). These shared neural processes likely underlie the many aspects of social behavior and cognition characteristic of all primate species (Seyfarth and Cheney 2014). Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) have been the dominant model for studies of neural function in primates ...
... (Chaplin et al. 2013; Kaas 2006). These shared neural processes likely underlie the many aspects of social behavior and cognition characteristic of all primate species (Seyfarth and Cheney 2014). Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) have been the dominant model for studies of neural function in primates ...
presentation source
... SOMATOTOPIC ORGANIZATION MORE AREA TAKEN BY SENSITIVE REGIONS (GREATER RECEPTOR DENSITYSMALLER RECEPTIVE FIELDS) CELLS RESPONDING TO ONE TYPE OF SENSATION IN VERTICLE COLUMNS(FOR EXAMPLE..PACINIAN CORPUSCLES IN A FINGERTIP) ...
... SOMATOTOPIC ORGANIZATION MORE AREA TAKEN BY SENSITIVE REGIONS (GREATER RECEPTOR DENSITYSMALLER RECEPTIVE FIELDS) CELLS RESPONDING TO ONE TYPE OF SENSATION IN VERTICLE COLUMNS(FOR EXAMPLE..PACINIAN CORPUSCLES IN A FINGERTIP) ...
Nervous System Lect/96
... Neurons and their processes are extremely variable in size and shape. According to the size and shape of their processes, most neurons can be classified as either: a). multipolar neurons, which have more than two cell processes, one process being the axon and the others dendrites; b). bipolar neuron ...
... Neurons and their processes are extremely variable in size and shape. According to the size and shape of their processes, most neurons can be classified as either: a). multipolar neurons, which have more than two cell processes, one process being the axon and the others dendrites; b). bipolar neuron ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... fewer dendritic spines. Despite the role of MeCP2 in transcriptional regulation, however, brain-wide gene expression is relatively normal in MeCP2-deficient mice, suggesting that gene expression changes are subtle or restricted to a small subset of cells. MeCP2ishighlyexpressedinneurons,and neuron-s ...
... fewer dendritic spines. Despite the role of MeCP2 in transcriptional regulation, however, brain-wide gene expression is relatively normal in MeCP2-deficient mice, suggesting that gene expression changes are subtle or restricted to a small subset of cells. MeCP2ishighlyexpressedinneurons,and neuron-s ...
Folie 1 - uni-tuebingen.de
... • Descending projections to: LC, SNpc/VTA, Raphe N., whole arousal system widely into the brain stem ...
... • Descending projections to: LC, SNpc/VTA, Raphe N., whole arousal system widely into the brain stem ...
Poster
... According to the National Institutes of Health, 5.1 million Americans have Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which affects memory and the ability to learn. In long-term potentiation (LTP), a correlate of learning and memory, the number of receptors at the synapse between neurons, increases. Calcium/calmodul ...
... According to the National Institutes of Health, 5.1 million Americans have Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which affects memory and the ability to learn. In long-term potentiation (LTP), a correlate of learning and memory, the number of receptors at the synapse between neurons, increases. Calcium/calmodul ...
Visuomotor neurons: ambiguity of the discharge or `motor` perception?
... towards the stimulus ŽB2.. This last condition is the critical one that allows to determine whether F4 visual receptive fields are coded in a non-retinotopic coordinate system: In the case of a retinotopically coded visual receptive field, the gaze deviation towards the visual stimulus should be acc ...
... towards the stimulus ŽB2.. This last condition is the critical one that allows to determine whether F4 visual receptive fields are coded in a non-retinotopic coordinate system: In the case of a retinotopically coded visual receptive field, the gaze deviation towards the visual stimulus should be acc ...
The Nervous System
... simultaneous (at the same time) stimuli at different location have accumulative effect on transmembrane potential (involves multiple synapses). • More than one synapse is active at the same time → all will "pour" Na+ ions across postsynaptic membrane → as an effect on the initial segment is accumula ...
... simultaneous (at the same time) stimuli at different location have accumulative effect on transmembrane potential (involves multiple synapses). • More than one synapse is active at the same time → all will "pour" Na+ ions across postsynaptic membrane → as an effect on the initial segment is accumula ...
Vision - Florida Atlantic University
... Each pigment consists of an opsin (a protein) and retinal (a lipid) ...
... Each pigment consists of an opsin (a protein) and retinal (a lipid) ...
Neural Conduction
... • Robinson and Berridge (1993) have suggested that the expectation of the pleasurable effects of drugs may become sensitized in addicts; a key point of this theory is that addicts don’t receive more pleasure from the drug, it is the anticipated pleasure that motivates their behavior; thus in drug ad ...
... • Robinson and Berridge (1993) have suggested that the expectation of the pleasurable effects of drugs may become sensitized in addicts; a key point of this theory is that addicts don’t receive more pleasure from the drug, it is the anticipated pleasure that motivates their behavior; thus in drug ad ...
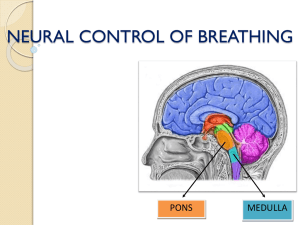
Neural Control of Breathing (By Mohit Chhabra)
... neurons extends along most of the length of the medulla. Most of its neurons are located within the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. ...
... neurons extends along most of the length of the medulla. Most of its neurons are located within the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. ...
The Implications of Neurological Models of Memory for Learning and
... (Eriksson et al., 1998). The DG is located inside the medial temporal lobe, beneath the cortical surface (Figure 3B), where new nerves are functionally integrated into pre-existing neuronal circuits and conduct learning and memory functions (Zhao, Deng and Gage, 2008). The survival of new neurons is ...
... (Eriksson et al., 1998). The DG is located inside the medial temporal lobe, beneath the cortical surface (Figure 3B), where new nerves are functionally integrated into pre-existing neuronal circuits and conduct learning and memory functions (Zhao, Deng and Gage, 2008). The survival of new neurons is ...
Document
... Source: ‘Chronic neural recordings using silicon microelectrode arrays electrochemically deposited with a poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) film’, K. Ludwig, J. Neural Eng. 3. 2006, 59-70. ...
... Source: ‘Chronic neural recordings using silicon microelectrode arrays electrochemically deposited with a poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) film’, K. Ludwig, J. Neural Eng. 3. 2006, 59-70. ...
Done by : Noor Bjant.hala Dr: loai zghol
... This graded potential can indicate the intensity of the stimulus, while at the hillock and at nodes of ranvier the potential is action potential because there're voltage gated ion channels. Note : When the receptor potential rises above the threshold, action potentials appear and the receptor is act ...
... This graded potential can indicate the intensity of the stimulus, while at the hillock and at nodes of ranvier the potential is action potential because there're voltage gated ion channels. Note : When the receptor potential rises above the threshold, action potentials appear and the receptor is act ...
Rules relating connections to cortical structure in primate prefrontal cortex H. Barbas
... sensory areas always originate in areas with higher laminar de4nition in comparison with the site of termination, while the opposite is true for projections proceeding in the reverse direction. We recently tested the structural model in the connections between prefrontal areas with medial temporal a ...
... sensory areas always originate in areas with higher laminar de4nition in comparison with the site of termination, while the opposite is true for projections proceeding in the reverse direction. We recently tested the structural model in the connections between prefrontal areas with medial temporal a ...
Chapter 1 A Perspective on Human Genetics
... Spinal Cord • Extends from brain stem through vertebral canal • 31 pairs of spinal nerves emerge from spinal cord through spaces formed between arches of ...
... Spinal Cord • Extends from brain stem through vertebral canal • 31 pairs of spinal nerves emerge from spinal cord through spaces formed between arches of ...
Cerebellum_seminar
... Cerebellum (Latin, little brain): only 10 % total volume of the brain but more than half of all its neurons. arranged in a highly regular manner as repeating units but with input and outputs from different parts similar computational operations but on different inputs. the cerebellum is provid ...
... Cerebellum (Latin, little brain): only 10 % total volume of the brain but more than half of all its neurons. arranged in a highly regular manner as repeating units but with input and outputs from different parts similar computational operations but on different inputs. the cerebellum is provid ...
Compete to Compute
... Competitive interactions between neurons and neural circuits have long played an important role in biological models of brain processes. This is largely due to early studies showing that many cortical [3] and sub-cortical (e.g., hippocampus [1] and cerebellum [2]) regions of the brain exhibit a recu ...
... Competitive interactions between neurons and neural circuits have long played an important role in biological models of brain processes. This is largely due to early studies showing that many cortical [3] and sub-cortical (e.g., hippocampus [1] and cerebellum [2]) regions of the brain exhibit a recu ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.