Pacifier Use May Decrease the Risk of SIDS Abstract Introduction
... largely comprised of pseudo-unipolar cells, but its caudal termination (Me5c) consists of small multipolar cells that are typically GABAergic. Since they are located just across from the Mo5, they are normally inhibited under rest conditions. When GABA released from the hypothalamus inhibits Me5c ce ...
... largely comprised of pseudo-unipolar cells, but its caudal termination (Me5c) consists of small multipolar cells that are typically GABAergic. Since they are located just across from the Mo5, they are normally inhibited under rest conditions. When GABA released from the hypothalamus inhibits Me5c ce ...
neurons
... The functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
... The functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
An Integrate-and-fire Model of Prefrontal Cortex Neuronal Activity during Performance of Goal-directed
... states and actions that are separately represented by the population of neurons of individual minicolumns. A state is indicated by the perception of specific sensory stimuli or the perception of reward received, while an action is indicated by proprioceptive input about motor activity. According to o ...
... states and actions that are separately represented by the population of neurons of individual minicolumns. A state is indicated by the perception of specific sensory stimuli or the perception of reward received, while an action is indicated by proprioceptive input about motor activity. According to o ...
12 - FacultyWeb
... • Dorsal horns—interneurons that receive somatic and visceral sensory input • Ventral horns—somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots • Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) – autonomic or sympathetic neurons • Dorsal root (spinal) ganglia—contain cell bodies of ...
... • Dorsal horns—interneurons that receive somatic and visceral sensory input • Ventral horns—somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots • Lateral horns (only in thoracic and lumbar regions) – autonomic or sympathetic neurons • Dorsal root (spinal) ganglia—contain cell bodies of ...
Test 1 Objectives
... Know about intra and extracellular ion concentrations as well as equilibrium. ...
... Know about intra and extracellular ion concentrations as well as equilibrium. ...
Jackson Rancheria Casino Shooting
... A brain tumor is found in a CT scan of Mr. Child’s head. The physician is assuming that it is not a secondary tumor (i.e. it did not spread from another part of the body) because an exhaustive workup has revealed no signs of cancer elsewhere in Mr. Child’s body. Is the brain tumor more likely to hav ...
... A brain tumor is found in a CT scan of Mr. Child’s head. The physician is assuming that it is not a secondary tumor (i.e. it did not spread from another part of the body) because an exhaustive workup has revealed no signs of cancer elsewhere in Mr. Child’s body. Is the brain tumor more likely to hav ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 11-30
... Auditory receptors lie within the Organ of Corti of the cochlea Organ of Corti o Hair cells = mechanoreceptors o The Organ of Corti rests on the basilar membrane o The auditory receptors, known as Hair cells, have cilia that are in contact with the tectorial membrane o Movement of the basilar me ...
... Auditory receptors lie within the Organ of Corti of the cochlea Organ of Corti o Hair cells = mechanoreceptors o The Organ of Corti rests on the basilar membrane o The auditory receptors, known as Hair cells, have cilia that are in contact with the tectorial membrane o Movement of the basilar me ...
Spontaneous firing patterns of identified spiny neurons in the rat
... for the occurrence of such phasic responses. These studies have not determined whether such bursts of action potentials represent a characteristic pattern of the neostriatal outflow, or rather the activity of interneurons involved in the local processing of afferent activity. A minority of neostriat ...
... for the occurrence of such phasic responses. These studies have not determined whether such bursts of action potentials represent a characteristic pattern of the neostriatal outflow, or rather the activity of interneurons involved in the local processing of afferent activity. A minority of neostriat ...
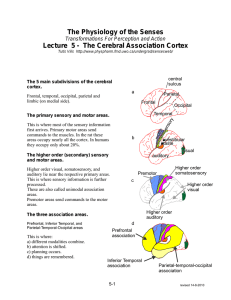
The Cerebral Association Cortex
... hyper-complex cells, and so on, until finally there is one unique cell that fires when you see your grandmother. If you loose that cell, you can no longer recognize your grandmother but have no problems with grandfather. Evidence for: Some lesions do impair the recognition of faces selectively. Some ...
... hyper-complex cells, and so on, until finally there is one unique cell that fires when you see your grandmother. If you loose that cell, you can no longer recognize your grandmother but have no problems with grandfather. Evidence for: Some lesions do impair the recognition of faces selectively. Some ...
No Slide Title
... backward from output nodes to input nodes and in fact can have arbitrary connections between any nodes. • While learning, the recurrent network feeds its inputs through the network including feeding data back from outputs to inputs and repeat this process until the values of the outputs do not chang ...
... backward from output nodes to input nodes and in fact can have arbitrary connections between any nodes. • While learning, the recurrent network feeds its inputs through the network including feeding data back from outputs to inputs and repeat this process until the values of the outputs do not chang ...
Materials - Web Adventures
... All of the words below are ones that students will encounter while playing Episode Four: Mystery of Morpheus. Their definitions are contained within the adventure in either the InfoArchives or the Glossary. Teachers should alert the students to the ability to click on the hot-linked words in the gam ...
... All of the words below are ones that students will encounter while playing Episode Four: Mystery of Morpheus. Their definitions are contained within the adventure in either the InfoArchives or the Glossary. Teachers should alert the students to the ability to click on the hot-linked words in the gam ...
Nerve activates contraction
... involuntary 2-Autonomic nervous system = involuntary, it controls smooth &cardiac muscles &glands This also is divided into sympathetic & parasympathetiuc ...
... involuntary 2-Autonomic nervous system = involuntary, it controls smooth &cardiac muscles &glands This also is divided into sympathetic & parasympathetiuc ...
Effect of exercise-induced fatigue on rat learning and memory ability... the brain
... This network constitutes an amplification cascade (negative feedback) that is triggered by increasing CaN activity and may lead to limited potentiation of synaptic transmission. The mechanisms by which the CaN-dependent negative signaling pathway participates in the fatigue-induced impairment of mem ...
... This network constitutes an amplification cascade (negative feedback) that is triggered by increasing CaN activity and may lead to limited potentiation of synaptic transmission. The mechanisms by which the CaN-dependent negative signaling pathway participates in the fatigue-induced impairment of mem ...
Fly MARCM and mouse MADM: Genetic methods of labeling and
... gene of interest, the daughter cell homozygous for the mutant gene (x) no longer contains GAL80. Therefore, the marker gene can be specifically turned on by GAL4 in homozygous mutant cells. Magenta rectangles and ovals indicate the GAL80 transgene and GAL80 protein respectively; orange rectangles an ...
... gene of interest, the daughter cell homozygous for the mutant gene (x) no longer contains GAL80. Therefore, the marker gene can be specifically turned on by GAL4 in homozygous mutant cells. Magenta rectangles and ovals indicate the GAL80 transgene and GAL80 protein respectively; orange rectangles an ...
UNC-55, an Orphan Nuclear Hormone Receptor, Orchestrates
... modifying the common genetic programs of neurons to create different synaptic specificities. The precisely defined sets of nerve and muscle cells responsible for locomotion in C. elegans allow genetic and cellular manipulations that provide a unique opportunity for investigating the generation of sp ...
... modifying the common genetic programs of neurons to create different synaptic specificities. The precisely defined sets of nerve and muscle cells responsible for locomotion in C. elegans allow genetic and cellular manipulations that provide a unique opportunity for investigating the generation of sp ...
Cell Assembly Sequences Arising from Spike
... New York, New York, 10032, 3Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, New York 10012, 4Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, Virginia 20147, and 5Center for Molecular and Behavioral Neuroscience, Rutgers University, Newark, New Jerse ...
... New York, New York, 10032, 3Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, New York 10012, 4Janelia Farm Research Campus, Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Ashburn, Virginia 20147, and 5Center for Molecular and Behavioral Neuroscience, Rutgers University, Newark, New Jerse ...
bio520_JANSEN_r4 - Cal State LA
... Values normalized to 6 hours. n=3 +/- SD Also found that BDNF and NGF are secreted constitutively (not shown). BDNF secretion linked to PKC pathway. Critique: graph of actual values in table 1 may have provided more information (relative amounts of release). ...
... Values normalized to 6 hours. n=3 +/- SD Also found that BDNF and NGF are secreted constitutively (not shown). BDNF secretion linked to PKC pathway. Critique: graph of actual values in table 1 may have provided more information (relative amounts of release). ...
Basal Ganglia and Associated Pathways
... is a source of input into the basal ganglia (striatum) and serves as a modulatory pathway of the direct and indirect basal ganglia pathways. Inputs into the pars compacta itself remain unclear, but at least some are from the striatum (striosome). Clinically, this pathway is most important for its ro ...
... is a source of input into the basal ganglia (striatum) and serves as a modulatory pathway of the direct and indirect basal ganglia pathways. Inputs into the pars compacta itself remain unclear, but at least some are from the striatum (striosome). Clinically, this pathway is most important for its ro ...
Chapter 12
... “Information” travels within the nervous system As propagated electrical signals (action potentials) The most important information (vision, balance, motor commands) Is carried by large-diameter, myelinated axons Synaptic Activity Action potentials (nerve impulses) Are transmitted from presynaptic n ...
... “Information” travels within the nervous system As propagated electrical signals (action potentials) The most important information (vision, balance, motor commands) Is carried by large-diameter, myelinated axons Synaptic Activity Action potentials (nerve impulses) Are transmitted from presynaptic n ...
THE SENSORIMOTOR SYSTEM (p.l) 1. Introduction Like the
... and are changed by the amount of prior practice/learning note: Ballistic movements (fast, brief, well-practiced) do not require sensory feedback (e.g. swatting a fly) note: much of sensory feedback in unconscious (e.g. proprioception) note: during initial phases of motor learning, performance is und ...
... and are changed by the amount of prior practice/learning note: Ballistic movements (fast, brief, well-practiced) do not require sensory feedback (e.g. swatting a fly) note: much of sensory feedback in unconscious (e.g. proprioception) note: during initial phases of motor learning, performance is und ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.