Approaches to Learning
... Billy has not suffered any physical damage from repeated volleyballs to the head). He now refuses to play volleyball after one disastrous game (needless to say he was not very good at it with all the blinking) What has happened to poor Billy? How would you try to fix his problem and what is the term ...
... Billy has not suffered any physical damage from repeated volleyballs to the head). He now refuses to play volleyball after one disastrous game (needless to say he was not very good at it with all the blinking) What has happened to poor Billy? How would you try to fix his problem and what is the term ...
Learning
... Punished behavior is not forgotten, it is suppressed Physical punishment increases aggression through modeling Can also create fear that will generalize Does not tell you “what to do”! Punishment if used swiftly, works best when accompanied with explanation and positive reinforcement for appro ...
... Punished behavior is not forgotten, it is suppressed Physical punishment increases aggression through modeling Can also create fear that will generalize Does not tell you “what to do”! Punishment if used swiftly, works best when accompanied with explanation and positive reinforcement for appro ...
Chapter 11: Behaviorism (18921956) Glossary New Directions in
... Behaviorism the psychological theory that conditioning can be used to explain the behavior of both animals and humans, with no reference to thoughts and feelings; this theory suggests that the altering of behavioral patterns should best treat psychological disorders Intervening Variables: Events ...
... Behaviorism the psychological theory that conditioning can be used to explain the behavior of both animals and humans, with no reference to thoughts and feelings; this theory suggests that the altering of behavioral patterns should best treat psychological disorders Intervening Variables: Events ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... Human Behavior • As we acknowledge that human behavior has both learned and genetic components, we also find examples of culture, once thought to be a uniquely human characteristic, in other animals. • Japanese macaques, for example, developed new methods of food preparation, and these methods were ...
... Human Behavior • As we acknowledge that human behavior has both learned and genetic components, we also find examples of culture, once thought to be a uniquely human characteristic, in other animals. • Japanese macaques, for example, developed new methods of food preparation, and these methods were ...
Module 19 Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning
... Punishment works best in natural settings when we encounter punishing consequences from actions such as reaching into a fire. In that case, operant conditioning helps us to avoid dangers. Punishment is less effective when we try to artificially create punishing consequences for other’s choices ...
... Punishment works best in natural settings when we encounter punishing consequences from actions such as reaching into a fire. In that case, operant conditioning helps us to avoid dangers. Punishment is less effective when we try to artificially create punishing consequences for other’s choices ...
02 Experimental Method and Statistical Reasoning in Psychology
... Experiments do have limitations, however. Because experiments are often conducted in highly controlled laboratory situations, they are frequently criticized for having little to do with actual behavior. That is, the artificial conditions of some experiments may produce results that do not generalize ...
... Experiments do have limitations, however. Because experiments are often conducted in highly controlled laboratory situations, they are frequently criticized for having little to do with actual behavior. That is, the artificial conditions of some experiments may produce results that do not generalize ...
An Overview to the Behavioral Perspective
... According to the behaviorists, learning can be defined as the relatively permanent change in behavior brought about as a result of experience or practice. [Note: an internal event displayed by overt behavior; contrasted with biological maturation or genetics as an explanation for relatively permanen ...
... According to the behaviorists, learning can be defined as the relatively permanent change in behavior brought about as a result of experience or practice. [Note: an internal event displayed by overt behavior; contrasted with biological maturation or genetics as an explanation for relatively permanen ...
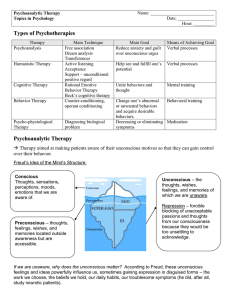
Psychoanalytic Therapy Notes
... which we are unaware. Repression – forcible blocking of unacceptable passions and thoughts from our consciousness because they would be too unsettling to acknowledge. ...
... which we are unaware. Repression – forcible blocking of unacceptable passions and thoughts from our consciousness because they would be too unsettling to acknowledge. ...
Operant Conditioning Notes File
... • Learning from reinforcement • Produces a response on whether or not the person will repeat the behavior ...
... • Learning from reinforcement • Produces a response on whether or not the person will repeat the behavior ...
The unexamined life is not worth living.
... behavior reflects innate ‘actualization’ focus on conscious forces and self perception More positive view of basic forces than Freud’s Individuals have freedom in directing his/her future and achieving personal growth ...
... behavior reflects innate ‘actualization’ focus on conscious forces and self perception More positive view of basic forces than Freud’s Individuals have freedom in directing his/her future and achieving personal growth ...
PMHS - Socpsychvita
... maintained a constant temperature at an appropriate level of warmth with monitoring to make any clothing other than a diaper unnecessary. The infant had room to move freely and there was no danger of smothering or choking. The device was not successful commercially but is clearly a prototype of toda ...
... maintained a constant temperature at an appropriate level of warmth with monitoring to make any clothing other than a diaper unnecessary. The infant had room to move freely and there was no danger of smothering or choking. The device was not successful commercially but is clearly a prototype of toda ...
Person Class Notes Behaviorism:
... - said he "listened" to his clients; they were talking about their own experiences as parent, child, and adult. Ego States: - born as child, parents tell us the "shoulds" - Parent: the shoulds, what is right and wrong; how something should be done. (the 2nd part to develop) - The Critical P: the sel ...
... - said he "listened" to his clients; they were talking about their own experiences as parent, child, and adult. Ego States: - born as child, parents tell us the "shoulds" - Parent: the shoulds, what is right and wrong; how something should be done. (the 2nd part to develop) - The Critical P: the sel ...
Classical Conditioning, continued
... Immediate Reinforcer: A reinforcer that occurs instantly after a behavior. A rat gets a food pellet for a bar press. Delayed Reinforcer: A reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. A paycheck that comes at the end of a week. We may be inclined to engage in small immediate reinforcer ...
... Immediate Reinforcer: A reinforcer that occurs instantly after a behavior. A rat gets a food pellet for a bar press. Delayed Reinforcer: A reinforcer that is delayed in time for a certain behavior. A paycheck that comes at the end of a week. We may be inclined to engage in small immediate reinforcer ...
Social Learning Theory
... between two points of view (that of the actor and the observer). 3. Self-Serving Bias – The tendency we have to attribute positive outcomes to our own dispositions and negative outcomes to ...
... between two points of view (that of the actor and the observer). 3. Self-Serving Bias – The tendency we have to attribute positive outcomes to our own dispositions and negative outcomes to ...
Chapter 17:1 Pages 454-459
... 4. Learning can modify instincts…grouse and quail chicks leave their nest the day they hatch…They can run and find food, but they can’t fly…when something moves above them, they crouch down and keep perfectly still until the danger is past…They will crouch without moving even if it is a falling lea ...
... 4. Learning can modify instincts…grouse and quail chicks leave their nest the day they hatch…They can run and find food, but they can’t fly…when something moves above them, they crouch down and keep perfectly still until the danger is past…They will crouch without moving even if it is a falling lea ...
Unit 1: Motivation, Emotion and Stress - Ms. Anderson
... concepts to understand behavior with specific attention to instincts for animals, biological factors like needs, drives, and homeostasis, and operant conditioning factors like incentives, and intrinsic versus extrinsic motivators. ...
... concepts to understand behavior with specific attention to instincts for animals, biological factors like needs, drives, and homeostasis, and operant conditioning factors like incentives, and intrinsic versus extrinsic motivators. ...
Chapter 1
... Id (pleasure principle; illogical, emotional, irrational) Ego (reality principle; logical and rational) Superego (moral principles; keeps Id and Ego in balance) Defense Mechanisms: When the Ego Loses the Battle with the Id and Superego Displacement: transferring a feeling onto a less threate ...
... Id (pleasure principle; illogical, emotional, irrational) Ego (reality principle; logical and rational) Superego (moral principles; keeps Id and Ego in balance) Defense Mechanisms: When the Ego Loses the Battle with the Id and Superego Displacement: transferring a feeling onto a less threate ...
Social Development - University of Alberta
... dependant on our expectancies expectancies: what a person thinks will result from behaving in a certain way under certain circumstances self-efficacy - expectation that one will be successful in his/her efforts ...
... dependant on our expectancies expectancies: what a person thinks will result from behaving in a certain way under certain circumstances self-efficacy - expectation that one will be successful in his/her efforts ...
... herself considers false. Each term of this definition is discussed in detail and, in doing so, it becomes apparent that several deception theories and a variety of social psychology and communication contributions have been integrated to build it. In addition, some specific implications of the defin ...
Behaviorism Fall 2014
... resembles the desired behavior, then one that is closer etc. Think of animal training or the hyper kid who can’t sit in his chair in class – do things in small steps ...
... resembles the desired behavior, then one that is closer etc. Think of animal training or the hyper kid who can’t sit in his chair in class – do things in small steps ...
Positive Reinforcement, Negative Reinforcement and Discipline
... have a list of possible incentives to choose from on a daily basis Make sure the child understands what is expected of them Break the steps toward the end result into smaller, achievable steps Reprioritize your expectations and put your focus on one or two top issues, if you focus on too many things ...
... have a list of possible incentives to choose from on a daily basis Make sure the child understands what is expected of them Break the steps toward the end result into smaller, achievable steps Reprioritize your expectations and put your focus on one or two top issues, if you focus on too many things ...
Chapter 14, Modules 32
... 8. Outline the conditions under which conformity is likely to occur. 9. Define obedience and describe Milgram’s classic study on obedience (include results). 10. What factors tended to increase or decrease obedience in Milgram’s study? 11. Define the following terms: a) social facilitation; b) socia ...
... 8. Outline the conditions under which conformity is likely to occur. 9. Define obedience and describe Milgram’s classic study on obedience (include results). 10. What factors tended to increase or decrease obedience in Milgram’s study? 11. Define the following terms: a) social facilitation; b) socia ...