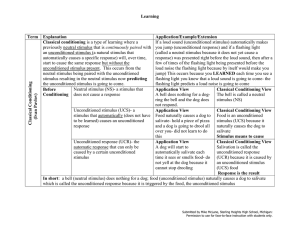
Learning
... eat the powder on your finger, and then dip your finger back into the cup to prepare for the next trial. You must eat some of the powder immediately after each tone, but not any other time. After several “learning” trials, you will be instructed to simply listen to the tone without eating the po ...
... eat the powder on your finger, and then dip your finger back into the cup to prepare for the next trial. You must eat some of the powder immediately after each tone, but not any other time. After several “learning” trials, you will be instructed to simply listen to the tone without eating the po ...
Learning Quiz - Rincon History Department
... 2. The last time you came home after your curfew, your parents grounded you for the next two ...
... 2. The last time you came home after your curfew, your parents grounded you for the next two ...
Photo Album
... or tone; the US here is a puff of air to the cornea. The eyelid closure response is indicated by upward movement of the tracing. The first marker is tone CS onset; the second is air puff US onset. In trial 1 the eyelid does not move to the CS but closes (blinks) following onset of the US. The condit ...
... or tone; the US here is a puff of air to the cornea. The eyelid closure response is indicated by upward movement of the tracing. The first marker is tone CS onset; the second is air puff US onset. In trial 1 the eyelid does not move to the CS but closes (blinks) following onset of the US. The condit ...
Essay #2: Relating Terms
... Double-blind research is an experimental method in which both the experimenters and the subjects are not aware of who belongs to the control group and tests are distributed randomly. This method was conceived in order to avoid experimental bias. Since neither the experimenters nor the subjects know ...
... Double-blind research is an experimental method in which both the experimenters and the subjects are not aware of who belongs to the control group and tests are distributed randomly. This method was conceived in order to avoid experimental bias. Since neither the experimenters nor the subjects know ...
Unit 6 Notes - Reading Community Schools
... paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also called second-order conditioning.) ...
... paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also called second-order conditioning.) ...
Learning and Memory
... •Can store vast amounts of information without removing old memories •You may think you’ve forgotten something, but a clue or hint can help you reconstruct it •Short-term memories must be consolidated into long-term ones •Meaningful and emotional events don’t require effort to consolidate (flashbulb ...
... •Can store vast amounts of information without removing old memories •You may think you’ve forgotten something, but a clue or hint can help you reconstruct it •Short-term memories must be consolidated into long-term ones •Meaningful and emotional events don’t require effort to consolidate (flashbulb ...
Operant Conditioning
... What would be occurring if you couldn’t sit in any chair while talking on the phone? What if you only refused to sit in beanbag chairs? What if you go away to college and your roommate has a chair that makes you chuckle as you sit in it and think about the story? And this can only occur after it’s g ...
... What would be occurring if you couldn’t sit in any chair while talking on the phone? What if you only refused to sit in beanbag chairs? What if you go away to college and your roommate has a chair that makes you chuckle as you sit in it and think about the story? And this can only occur after it’s g ...
Learning handout - Miami Beach Senior High School
... If you were to give a dog food and then ring a bell the dog would not the UCS associate the treat with the bell. Why? Because the dog already got what it wanted- food. It does not care about a bell. Extinction- extinguishing the learned The dog has learned that every time he or she hears the bell (C ...
... If you were to give a dog food and then ring a bell the dog would not the UCS associate the treat with the bell. Why? Because the dog already got what it wanted- food. It does not care about a bell. Extinction- extinguishing the learned The dog has learned that every time he or she hears the bell (C ...
9. BEHAVIORAL APPROACHES 9.1 PAVLOV: Ivan Petrovich Pavlov
... light just before the electric current came on. The rats soon learned to press the lever when the light came on because they knew that this would stop the electric current being switched on.These two learned responses are known as Escape Learning and Avoidance Learning. Punishment (weakens behavior) ...
... light just before the electric current came on. The rats soon learned to press the lever when the light came on because they knew that this would stop the electric current being switched on.These two learned responses are known as Escape Learning and Avoidance Learning. Punishment (weakens behavior) ...
ch03
... THEORIES OF LEARNING It was conducted by a Russian Physiologist Ivan Pavlov in the 1927. ...
... THEORIES OF LEARNING It was conducted by a Russian Physiologist Ivan Pavlov in the 1927. ...
Differential Psychology
... • At least, you would have quite different beliefs & views of the world and yourself • Because some cultures encourage & reward certain behaviours, whilst others value and emphasise certain other behaviours ...
... • At least, you would have quite different beliefs & views of the world and yourself • Because some cultures encourage & reward certain behaviours, whilst others value and emphasise certain other behaviours ...
Chapter 4 Learning - Western Washington University
... from a child who misbehaves. A number of cautions should be kept in mind when using punishment (see below for an example). ...
... from a child who misbehaves. A number of cautions should be kept in mind when using punishment (see below for an example). ...
Behaviourism - WordPress.com
... Skinner (OC) Operant Conditioning (OC) (Skinner): learning occurs through "consequences" of behaviours a positive or negative stimulus is associated with an event ...
... Skinner (OC) Operant Conditioning (OC) (Skinner): learning occurs through "consequences" of behaviours a positive or negative stimulus is associated with an event ...
Lecture 18 evo wrap up Behaviorism and Learning
... The Essence of Behaviorism • "The consequences of behavior determine the probability that the behavior will occur again” – BF Skinner • Anyone’s personality can be formed or changed through patterns of reinforcement and punishment • If you are extraverted, that’s because extraverted behaviors were ...
... The Essence of Behaviorism • "The consequences of behavior determine the probability that the behavior will occur again” – BF Skinner • Anyone’s personality can be formed or changed through patterns of reinforcement and punishment • If you are extraverted, that’s because extraverted behaviors were ...
Unit 1: Motivation, Emotion and Stress - Ms. Anderson
... Unit 1: Motivation, Emotion and Stress ■ Essential Task 1-1: Identify and apply basic motivational concepts to understand behavior with specific attention to instincts for animals, biological factors like needs, drives, and homeostasis, and operant conditioning factors like incentives, and intrinsic ...
... Unit 1: Motivation, Emotion and Stress ■ Essential Task 1-1: Identify and apply basic motivational concepts to understand behavior with specific attention to instincts for animals, biological factors like needs, drives, and homeostasis, and operant conditioning factors like incentives, and intrinsic ...
Animal Behavior
... Submission leads to dominance Think of having a younger or older sibling? Who wins when you argue? Usually the older or stronger wins. With animals aggressive behavior may occur in groups. In these groups there may be different levels of dominant and submissive animals. A dominance hierarchy i ...
... Submission leads to dominance Think of having a younger or older sibling? Who wins when you argue? Usually the older or stronger wins. With animals aggressive behavior may occur in groups. In these groups there may be different levels of dominant and submissive animals. A dominance hierarchy i ...
Classical Conditioning
... Important Definitions spontaneous recovery: The reappearance of an extinguished response (in a weaker form) when an organism is exposed to the original conditioned stimulus following a rest period. generalization: In classical conditioning, the tendency to make a conditioned response to a stimu ...
... Important Definitions spontaneous recovery: The reappearance of an extinguished response (in a weaker form) when an organism is exposed to the original conditioned stimulus following a rest period. generalization: In classical conditioning, the tendency to make a conditioned response to a stimu ...
The Behaviorist Revolution: Pavlov and Watson
... Albert's fear of a seal skin coat - assuming that he comes to analysis at that age - will probably tease from him the recital of a dream which upon their analysis will show that Albert at three years of age attempted to play with the pubic hair of the mother and was scolded violently for it. (We are ...
... Albert's fear of a seal skin coat - assuming that he comes to analysis at that age - will probably tease from him the recital of a dream which upon their analysis will show that Albert at three years of age attempted to play with the pubic hair of the mother and was scolded violently for it. (We are ...
Chapter 7 Learning
... study the variables that influenced the strength and the persistence of conditioning. In some studies, after the conditioning had taken place, Pavlov presented the sound repeatedly but Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/books ...
... study the variables that influenced the strength and the persistence of conditioning. In some studies, after the conditioning had taken place, Pavlov presented the sound repeatedly but Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/books ...
The Behaviorist Revolution: Pavlov and Watson
... Albert's fear of a seal skin coat - assuming that he comes to analysis at that age - will probably tease from him the recital of a dream which upon their analysis will show that Albert at three years of age attempted to play with the pubic hair of the mother and was scolded violently for it. (We are ...
... Albert's fear of a seal skin coat - assuming that he comes to analysis at that age - will probably tease from him the recital of a dream which upon their analysis will show that Albert at three years of age attempted to play with the pubic hair of the mother and was scolded violently for it. (We are ...
avoidance behavior
... • A warning stimulus (e.g., a light) signals a forthcoming shock. • If the required response is made during the light (warning stimulus), before the shock occurs, the subject avoids the shock. • If a response is not made during the warning stimulus of the light, the shock occurs, and terminates when ...
... • A warning stimulus (e.g., a light) signals a forthcoming shock. • If the required response is made during the light (warning stimulus), before the shock occurs, the subject avoids the shock. • If a response is not made during the warning stimulus of the light, the shock occurs, and terminates when ...
Behavior Therapies
... and look to use well-established learning principles to eliminate the unwanted behavior. Usually used to treat anxiety disorders, drug addictions, bedwetting, sexual dysfunctions, and autism. ...
... and look to use well-established learning principles to eliminate the unwanted behavior. Usually used to treat anxiety disorders, drug addictions, bedwetting, sexual dysfunctions, and autism. ...
Chapter 6 Class Notes / Learning
... Variable Ratio Schedule (VR): Occurs when reinforcement is given on the average of a certain number of responses. Example: On the average of every 42 times a woman casts her lure out into the lake, she catches a fish (sometimes 31, sometimes 55, but averaging 42). Fixed Interval Schedule (FI): Occur ...
... Variable Ratio Schedule (VR): Occurs when reinforcement is given on the average of a certain number of responses. Example: On the average of every 42 times a woman casts her lure out into the lake, she catches a fish (sometimes 31, sometimes 55, but averaging 42). Fixed Interval Schedule (FI): Occur ...
Classical conditioning

Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.