Skinner`s Paper
... itself. The rat pressed the lever repeatedly until it got satisfied. Skinner called this effect positive reinforcement. On the other hand, he also studied negative reinforcement by placing rats into an electrified box that delivered unpleasant shocks. The box also had levers to cut the power. He obs ...
... itself. The rat pressed the lever repeatedly until it got satisfied. Skinner called this effect positive reinforcement. On the other hand, he also studied negative reinforcement by placing rats into an electrified box that delivered unpleasant shocks. The box also had levers to cut the power. He obs ...
Chapter 9 PowerPoint
... Depending on the effect of these behaviors, the learner will repeat or eliminate these behaviors (get rewards or avoid punishment) Differs from Classical condition in two ways 1. The learner must behave in a certain way that produces some consequence. The learner must take an active role. 2. Learnin ...
... Depending on the effect of these behaviors, the learner will repeat or eliminate these behaviors (get rewards or avoid punishment) Differs from Classical condition in two ways 1. The learner must behave in a certain way that produces some consequence. The learner must take an active role. 2. Learnin ...
Psych Ch. 9 Powerpoint
... Depending on the effect of these behaviors, the learner will repeat or eliminate these behaviors (get rewards or avoid punishment) Differs from Classical condition in two ways 1. The learner must behave in a certain way that produces some consequence. The learner must take an active role. 2. Learnin ...
... Depending on the effect of these behaviors, the learner will repeat or eliminate these behaviors (get rewards or avoid punishment) Differs from Classical condition in two ways 1. The learner must behave in a certain way that produces some consequence. The learner must take an active role. 2. Learnin ...
Operant Conditioning
... Edward Thorndike was the first to examine this process of conditioning in the 1890’s, by placing cats in “___________________________” ...
... Edward Thorndike was the first to examine this process of conditioning in the 1890’s, by placing cats in “___________________________” ...
What is Learning? - Okemos Public Schools
... show may result in the product itself generating excitement • Christmas music played in a story may trigger happy memories in a consumer’s mind persuading them to enter the store. Before we have heard of a product, it is Neutral. If we associate the product (N) with pleasant images (UCS), which prod ...
... show may result in the product itself generating excitement • Christmas music played in a story may trigger happy memories in a consumer’s mind persuading them to enter the store. Before we have heard of a product, it is Neutral. If we associate the product (N) with pleasant images (UCS), which prod ...
Operant Conditioning
... Edward Thorndike was the first to examine this process of conditioning in the 1890’s, by placing cats in “___________________________” ...
... Edward Thorndike was the first to examine this process of conditioning in the 1890’s, by placing cats in “___________________________” ...
Unit III: Learning
... – If a response is followed by a pleasurable consequence, it will be repeated – If followed by an unpleasant consequence, it will tend not to be repeated ...
... – If a response is followed by a pleasurable consequence, it will be repeated – If followed by an unpleasant consequence, it will tend not to be repeated ...
Ivan Pavlov
... Makes Causes Has no the aeffect behavior avoidance organism sifhabituation thethe of reward ofto less the avoid punishment, is previously greater punisher, likely, getting or ... the caught, or... than noted effects or... punishment is aversive, or... ...
... Makes Causes Has no the aeffect behavior avoidance organism sifhabituation thethe of reward ofto less the avoid punishment, is previously greater punisher, likely, getting or ... the caught, or... than noted effects or... punishment is aversive, or... ...
Chapter 6 No Media
... §Attached tube to dog’s salivary gland §Rang a bell, then presented food (repeated pairings) §Dogs soon began to salivate when bell rang – even when food wasn’t presented! ...
... §Attached tube to dog’s salivary gland §Rang a bell, then presented food (repeated pairings) §Dogs soon began to salivate when bell rang – even when food wasn’t presented! ...
Chapter 1
... • Learning—any process through which experience at one time can alter an individual’s behavior at a future time ...
... • Learning—any process through which experience at one time can alter an individual’s behavior at a future time ...
Tim`s Learning II
... superstitious behavior occurs in humans because the individual feels that, by continuing an action, reinforcement will happen; or that reinforcement has come at certain times in the past as a result of this action, although not all the time, but this may be one of those times ...
... superstitious behavior occurs in humans because the individual feels that, by continuing an action, reinforcement will happen; or that reinforcement has come at certain times in the past as a result of this action, although not all the time, but this may be one of those times ...
File - teacherver.com
... occur. C. Verbal Learning This is only true for humans. It involves activities that need the use of language like speaking, writing, reading, reciting. Memory plays an important role in learning because, like Operant Conditioning, it should be an active process. Memorization, like operant conditioni ...
... occur. C. Verbal Learning This is only true for humans. It involves activities that need the use of language like speaking, writing, reading, reciting. Memory plays an important role in learning because, like Operant Conditioning, it should be an active process. Memorization, like operant conditioni ...
Chapter 4 Learning (II)
... — A form of learning in which a behavior becomes more or less probable, depending on its consequences Respondent behavior Operant behavior — behavior that operates on the environment, producing consequences. ...
... — A form of learning in which a behavior becomes more or less probable, depending on its consequences Respondent behavior Operant behavior — behavior that operates on the environment, producing consequences. ...
Chapter 1: The Science of Psychology Module 1: Psychology`s
... Adaptive behaviors become habits: the “flywheel of society.” Like physical traits, useful behavioral traits could be passed to future generations. ...
... Adaptive behaviors become habits: the “flywheel of society.” Like physical traits, useful behavioral traits could be passed to future generations. ...
CPEM Lecture 2
... • Learning a conditioned response involves building up an association between the unconditioned stimuli and the conditioned stimuli. • When unconditioned and conditioned stimuli are paired, the conditioned stimuli takes on the properties of the unconditioned stimuli and generates a conditioned respo ...
... • Learning a conditioned response involves building up an association between the unconditioned stimuli and the conditioned stimuli. • When unconditioned and conditioned stimuli are paired, the conditioned stimuli takes on the properties of the unconditioned stimuli and generates a conditioned respo ...
Chapter 4 Learning - Western Washington University
... Fixed Ratio Behavior (FR) • Reinforcement based on the number of response accomplished. For humans, piece work – payment for the number of ...
... Fixed Ratio Behavior (FR) • Reinforcement based on the number of response accomplished. For humans, piece work – payment for the number of ...
AP Psychology Quiz – pages 326
... 4. A response that leads to the removal of an unpleasant stimulus is one being: A) positively reinforced. B) negatively reinforced. C) punished. D) extinguished. ...
... 4. A response that leads to the removal of an unpleasant stimulus is one being: A) positively reinforced. B) negatively reinforced. C) punished. D) extinguished. ...
Chapter 6: Learning (Operant Conditioning)
... response in the presence of one stimulus but not another. When this occurs, the response is under stimulus control. e.g., Although you are repeatedly rewarded for telling jokes during lunch, you are not likely to do so at a funeral. e.g., ______________________________ STIMULUS GENERALIZATION occurs ...
... response in the presence of one stimulus but not another. When this occurs, the response is under stimulus control. e.g., Although you are repeatedly rewarded for telling jokes during lunch, you are not likely to do so at a funeral. e.g., ______________________________ STIMULUS GENERALIZATION occurs ...
Behaviorism - Michael Johnson's Homepage
... Ravenscroft says this is a plus for behaviorism: supposedly states of the world cause MSs. E.g. standing on a tack causes pain. But is this true? Does standing on a tack cause me to have the disposition that when I stand on a tack, I say “ouch”? Usually I have that disposition prior to standing on t ...
... Ravenscroft says this is a plus for behaviorism: supposedly states of the world cause MSs. E.g. standing on a tack causes pain. But is this true? Does standing on a tack cause me to have the disposition that when I stand on a tack, I say “ouch”? Usually I have that disposition prior to standing on t ...
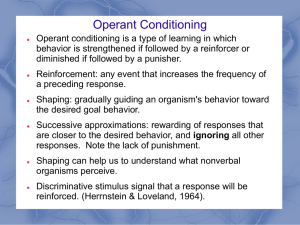
Module 21 Operant Conditioning
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
... Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher. Reinforcement: any event that increases the frequency of a preceding response. ...
Verbal Behavior

Verbal Behavior is a 1957 book by psychologist B. F. Skinner that inspects human behavior, describing what is traditionally called linguistics. The book Verbal Behavior is almost entirely theoretical, involving little experimental research in the work itself. It was an outgrowth of a series of lectures first presented at the University of Minnesota in the early 1940s and developed further in his summer lectures at Columbia and William James lectures at Harvard in the decade before the book's publication. A growing body of research and applications based on Verbal Behavior has occurred since its original publication, particularly in the past decade.In addition, a growing body of research has developed on structural topics in verbal behavior such as grammar.