Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • Splicing that occurs in all eukaryotic species is called cis-splicing because it involves 2 or more exons that exist together in the same gene • Alternatively, trans-splicing has exons that are not part of the same gene at all, may not even be on the same chromosome ...
... • Splicing that occurs in all eukaryotic species is called cis-splicing because it involves 2 or more exons that exist together in the same gene • Alternatively, trans-splicing has exons that are not part of the same gene at all, may not even be on the same chromosome ...
3rd quarter Assessment
... • Dihybrid Crosses—Hetero for both traits X Hetero for both traits • 9:3:3:1 Ratio • Sex chromosomes are XX-female XY—male ...
... • Dihybrid Crosses—Hetero for both traits X Hetero for both traits • 9:3:3:1 Ratio • Sex chromosomes are XX-female XY—male ...
Protein Synthesis Study Sheet
... Draw the DNA base-pairing rule. Draw the RNA base-paring rule. Be able to transcribe and translate a DNA sequence using the amino acid decoding sheet. What is the difference between lytic and lysogenic viruses?* How does a virus reproduce if it does not have any ribosomes to make structural proteins ...
... Draw the DNA base-pairing rule. Draw the RNA base-paring rule. Be able to transcribe and translate a DNA sequence using the amino acid decoding sheet. What is the difference between lytic and lysogenic viruses?* How does a virus reproduce if it does not have any ribosomes to make structural proteins ...
10 DNA Vocabulary - Petal School District
... 1. DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid 2. RNA—ribonucleic acid 3. nucleotide—the monomer for nucleic acids; made of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base 4. hydrogen bonds—hold nitrogen base pairs together 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that ...
... 1. DNA—deoxyribonucleic acid 2. RNA—ribonucleic acid 3. nucleotide—the monomer for nucleic acids; made of a phosphate, sugar, and nitrogen base 4. hydrogen bonds—hold nitrogen base pairs together 5. genetic code—the sequence of the nitrogen bases (nucleotides) on DNA 6. DNA replication—process that ...
Name: Cell Biology Test #1: 50 points
... compartment/close proximity (no membranes between reactions) Another fine trick: Use allosteric regulation where the product of a reaction or reaction pathway is used to change enzyme function when you need more or less product by binding non-covalently at an allosteric site Other options: Change te ...
... compartment/close proximity (no membranes between reactions) Another fine trick: Use allosteric regulation where the product of a reaction or reaction pathway is used to change enzyme function when you need more or less product by binding non-covalently at an allosteric site Other options: Change te ...
Objectives • Describe the process of DNA transcription. • Explain
... In prokaryotic cells, the mRNA transcribed from a gene directly serves as the messenger molecule that is translated into a protein. But this is not the case in eukaryotic cells. In a eukaryotic cell, the RNA transcribed in the nucleus is modified or processed before it leaves the nucleus as mRNA to ...
... In prokaryotic cells, the mRNA transcribed from a gene directly serves as the messenger molecule that is translated into a protein. But this is not the case in eukaryotic cells. In a eukaryotic cell, the RNA transcribed in the nucleus is modified or processed before it leaves the nucleus as mRNA to ...
Tuesday5/10
... to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
... to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
MS Word file
... Hypothesis that each gene encoded a single, unique polypeptide Codon: a triplet RNA code that corresponds to an amino acid in a protein ...
... Hypothesis that each gene encoded a single, unique polypeptide Codon: a triplet RNA code that corresponds to an amino acid in a protein ...
IB Topics DNA HL no writing
... • nucleotides added to form new strands; • complementary base pairing; • A to T and G to C; • DNA polymerase forms the new complementary strands; • replication is semi-conservative; • each of the DNA molecules formed has one old and one new ...
... • nucleotides added to form new strands; • complementary base pairing; • A to T and G to C; • DNA polymerase forms the new complementary strands; • replication is semi-conservative; • each of the DNA molecules formed has one old and one new ...
Chapter 16 - HCC Learning Web
... A. Evidence from the Study of Metabolic Defects Archibald Garrod (1909) He was a physician who studied inborn errors in metabolism. He suggested that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions in cells. B. Nutritional Mutants in Neurospora. George Beadle and E ...
... A. Evidence from the Study of Metabolic Defects Archibald Garrod (1909) He was a physician who studied inborn errors in metabolism. He suggested that genes dictate phenotypes through enzymes that catalyze specific chemical reactions in cells. B. Nutritional Mutants in Neurospora. George Beadle and E ...
The DNA Connection - Conackamack Middle School
... 1. What forms the genetic code? 2. How does a cell produce proteins? 3. How can mutations effect an organism? ...
... 1. What forms the genetic code? 2. How does a cell produce proteins? 3. How can mutations effect an organism? ...
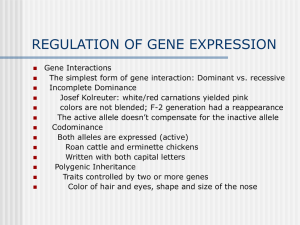
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
... a cluster of genes working together a region of the chromosome near the cluster: operator a region of the chromosome next to the operator: promotor products that initiates the production of enzymes are inducers ...
No Slide Title
... Eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes are larger and more complex than prokaryotic ribosomes. Mitochondrial and chloroplast ribosomes differ from both examples shown. ...
... Eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes are larger and more complex than prokaryotic ribosomes. Mitochondrial and chloroplast ribosomes differ from both examples shown. ...
protein synthesis and mutations
... The mRNA leaves the nucleus and binds to a ribosome in the cytoplasm. The ribosome reads that mRNA code in groups of 3 called codons, and tRNA hooks on the correct amino acids that is coded for. Once a stop codon is read, the polypeptide chain is released and a new protein is formed. ...
... The mRNA leaves the nucleus and binds to a ribosome in the cytoplasm. The ribosome reads that mRNA code in groups of 3 called codons, and tRNA hooks on the correct amino acids that is coded for. Once a stop codon is read, the polypeptide chain is released and a new protein is formed. ...
Chapter 8
... characteristics of a cell; use this information synthesize proteins. 2. What four functions are performed by nucleic acids? 1) store information that determines the characteristics of cells and organisms; 2) direct the synthesis of proteins essential to the operation of the cell or organism; 3) chem ...
... characteristics of a cell; use this information synthesize proteins. 2. What four functions are performed by nucleic acids? 1) store information that determines the characteristics of cells and organisms; 2) direct the synthesis of proteins essential to the operation of the cell or organism; 3) chem ...
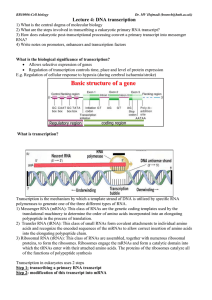
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Poly(A)polymerase and cleavage & polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) attach poly(A) generated from ATP ...
... Poly(A)polymerase and cleavage & polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) attach poly(A) generated from ATP ...
U - Helena High School
... Before making proteins, Your cell must first make RNA • Question: • How does RNA (ribonucleic acid) differ from DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? ...
... Before making proteins, Your cell must first make RNA • Question: • How does RNA (ribonucleic acid) differ from DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? ...
Chapter 15
... 3. Translocation- ribosomes move three more nucleotides along the mRNA. This relocates initial tRNA to the E site (exit) and ejects it from the ribosome, repositioning growing polypeptide chain to the P site and exposes the next codon at the A site. 4. Termination- nonsense codon is reached (UAA) an ...
... 3. Translocation- ribosomes move three more nucleotides along the mRNA. This relocates initial tRNA to the E site (exit) and ejects it from the ribosome, repositioning growing polypeptide chain to the P site and exposes the next codon at the A site. 4. Termination- nonsense codon is reached (UAA) an ...
Making Proteins - Foothill Technology High School
... Steps of DNA Transcription Making mRNA from DNA 1. Helicase unzips DNA at the gene of interest 2. RNA polymerase matches RNA nucleotide bases to DNA, using one side as a template. 3. The mRNA strand is created. It now compliments the original DNA strand (G-C and A-U). 4. Ligase helps the strand of ...
... Steps of DNA Transcription Making mRNA from DNA 1. Helicase unzips DNA at the gene of interest 2. RNA polymerase matches RNA nucleotide bases to DNA, using one side as a template. 3. The mRNA strand is created. It now compliments the original DNA strand (G-C and A-U). 4. Ligase helps the strand of ...
CH 11 Study Guide: DNA, RNA, and Proteins
... in a strand of mRNA? What tRNA sequence would pair up to this mRNA? mRNA: UUG AUC CCA tRNA: AAC UAG GGT 7. What will happen to a protein after a silent mutation? A missense mutation? A nonsense mutation? Silent: no change Missense: changes 1+ amino acid Nonsense: stop codon 8. What does the enzyme D ...
... in a strand of mRNA? What tRNA sequence would pair up to this mRNA? mRNA: UUG AUC CCA tRNA: AAC UAG GGT 7. What will happen to a protein after a silent mutation? A missense mutation? A nonsense mutation? Silent: no change Missense: changes 1+ amino acid Nonsense: stop codon 8. What does the enzyme D ...