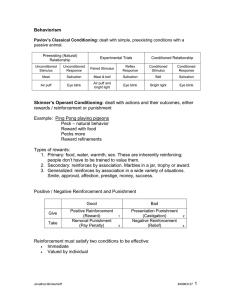
PSY100Learning
... CER is most commonly studied form of classical conditioning. First, a rat is trained to bar press in an operant chamber. Then, the rat is trained onto a medium-sized variableratio schedule to produce rapid, steady responding. Electric shock can be used a UCS that will temporarily suppress bar pressi ...
... CER is most commonly studied form of classical conditioning. First, a rat is trained to bar press in an operant chamber. Then, the rat is trained onto a medium-sized variableratio schedule to produce rapid, steady responding. Electric shock can be used a UCS that will temporarily suppress bar pressi ...
Notes: Classical Conditioning
... 1. Classical- The process by which a once neutral stimulus acquires the capacity to elicit a response due to becoming linked with something that automatically evokes a strong response. *Define this in your own words:_________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
... 1. Classical- The process by which a once neutral stimulus acquires the capacity to elicit a response due to becoming linked with something that automatically evokes a strong response. *Define this in your own words:_________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
Skinner`s Theory - BDoughertyAmSchool
... himself whether he could get more complex sorts of behaviors using this. He responded with the idea of shaping, or “the method of successive approximations.” Basically, it involved first reinforcing a behavior only vaguely similar to the one desired. Once that was established, you look out for varia ...
... himself whether he could get more complex sorts of behaviors using this. He responded with the idea of shaping, or “the method of successive approximations.” Basically, it involved first reinforcing a behavior only vaguely similar to the one desired. Once that was established, you look out for varia ...
PSYC550 Emotions and Memory
... • central nucleus (CE) – The region of the amygdala that receives information from the basal, lateral, and accessory basal nuclei and sends projections to a wide variety of regions in the brain; involved in emotional responses. ...
... • central nucleus (CE) – The region of the amygdala that receives information from the basal, lateral, and accessory basal nuclei and sends projections to a wide variety of regions in the brain; involved in emotional responses. ...
Learning
... presence of a particular stimulus is rewarded, the same response is more likely to occur when that stimulus is encountered again. • Operant conditioning – a process in which response are learned on the basis of their rewarding or punishing consequences. • Puzzle Box – learn to unlock door by pressin ...
... presence of a particular stimulus is rewarded, the same response is more likely to occur when that stimulus is encountered again. • Operant conditioning – a process in which response are learned on the basis of their rewarding or punishing consequences. • Puzzle Box – learn to unlock door by pressin ...
Read - Work
... monkey-do, learning), appeared to show flaws in the Iaw of effect and to require mental representations in their explanation. But in 1938 Burrhus Friederich Skinner powerfully defended and advanced behaviorism when he published The Behavior of Organisms,which was arguably the most influential work o ...
... monkey-do, learning), appeared to show flaws in the Iaw of effect and to require mental representations in their explanation. But in 1938 Burrhus Friederich Skinner powerfully defended and advanced behaviorism when he published The Behavior of Organisms,which was arguably the most influential work o ...
Behavior Modification
... personality – Personality is made up of 3 factors: 1. Values 2. Attitudes 3. Behavior ...
... personality – Personality is made up of 3 factors: 1. Values 2. Attitudes 3. Behavior ...
learning - Wofford
... Describe the basic elements of classical conditioning • Define the unconditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response Describe the basic elements of operant conditioning ...
... Describe the basic elements of classical conditioning • Define the unconditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response Describe the basic elements of operant conditioning ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 15. Based on what researchers have found about the effect of modeling on behavior, • A) we can decrease violence in our society if we decrease the amount of violence on TV. • B) we can increase pro-social behavior if we increase the amount of it on TV. • C) all of the above. • D) none of the above; ...
... 15. Based on what researchers have found about the effect of modeling on behavior, • A) we can decrease violence in our society if we decrease the amount of violence on TV. • B) we can increase pro-social behavior if we increase the amount of it on TV. • C) all of the above. • D) none of the above; ...
Jenkins “Defining Psychology” AP Psych Unit I: Thinking Critically
... based on unreliable personal beliefs, opinions, and emotions. In addition, scientists are characterized by skepticism. Skeptical people challenge whether a supposed fact is really true. Being skeptical can mean questioning what “everybody knows.” There was a time when “everybody knew” that women wer ...
... based on unreliable personal beliefs, opinions, and emotions. In addition, scientists are characterized by skepticism. Skeptical people challenge whether a supposed fact is really true. Being skeptical can mean questioning what “everybody knows.” There was a time when “everybody knew” that women wer ...
M_5_Glossary Learning - user.meduni
... Problem solving. The application of knowledge and skills to achieve certain goals (see Module 4). Procedural memory. A part of long-term memory that stores information about how to do things (Module 4) Qualia [Latin, plural of quale, neut. of qualis of what kind] 1: a property (as redness or softnes ...
... Problem solving. The application of knowledge and skills to achieve certain goals (see Module 4). Procedural memory. A part of long-term memory that stores information about how to do things (Module 4) Qualia [Latin, plural of quale, neut. of qualis of what kind] 1: a property (as redness or softnes ...
Lectures 8 & 9 - Operant Conditioning
... • Consciousness is a proper subject matter for psychology but it is not an explanation of behavior. It is what has to be explained (e.g., Tom hit Bill because Tom felt angry). – Why did Tom feel angry? – How did Tom know he was angry? • Consciousness vs. Awareness: –Animals are aware of objects (but ...
... • Consciousness is a proper subject matter for psychology but it is not an explanation of behavior. It is what has to be explained (e.g., Tom hit Bill because Tom felt angry). – Why did Tom feel angry? – How did Tom know he was angry? • Consciousness vs. Awareness: –Animals are aware of objects (but ...
Module 9: Learning
... All four of these phenomena occur in both operant & classical conditioning. Three Kinds of Learning cont. 3. _______________learning: learning that involves mental processes (attention & memory), may be learned through observation or imitation & may not involve _______________ rewards or require the ...
... All four of these phenomena occur in both operant & classical conditioning. Three Kinds of Learning cont. 3. _______________learning: learning that involves mental processes (attention & memory), may be learned through observation or imitation & may not involve _______________ rewards or require the ...
Powerpoint – Learning – Operant Conditioning
... consequences will occur more frequently; behaviors with unfavorable consequences will occur less frequently ...
... consequences will occur more frequently; behaviors with unfavorable consequences will occur less frequently ...
Psychology of Language
... If I form a hypothesis about language understanding/production, how would I test it? What would count as data? Let’s give it a shot… ...
... If I form a hypothesis about language understanding/production, how would I test it? What would count as data? Let’s give it a shot… ...
Operant Conditioning
... Form of learning based on the consequences of actions People and animals learn to do things (and not to do others) because of the results of what they do. Learning from the consequences. In operant conditioning, behaviors that people and animals have control over are conditioned. ...
... Form of learning based on the consequences of actions People and animals learn to do things (and not to do others) because of the results of what they do. Learning from the consequences. In operant conditioning, behaviors that people and animals have control over are conditioned. ...
quantity or quality of the reinforcer
... • Just like all CSs are not equally associable with all USs, not all responses are equally conditioned with all reinforcers • Breland & Breland: “The Misbehavior of Organisms” – animal training for entertainment such as drop a coin in a bank – Instinctive drift • gradual movement away from the opera ...
... • Just like all CSs are not equally associable with all USs, not all responses are equally conditioned with all reinforcers • Breland & Breland: “The Misbehavior of Organisms” – animal training for entertainment such as drop a coin in a bank – Instinctive drift • gradual movement away from the opera ...
Chapter Seven Part Two - K-Dub
... aversion was actually caused by an illness. Higher-order conditioning involves some cognition; the name of a food may trigger salivation. ...
... aversion was actually caused by an illness. Higher-order conditioning involves some cognition; the name of a food may trigger salivation. ...
High School Psychology
... guide for instruction. It is not intended to be a state-mandated curriculum for how and when content is taught. The outline is not a list of required items, and so, was developed with the understanding that content often overlaps. Because of this overlap, it may seem as if important ideas, people, p ...
... guide for instruction. It is not intended to be a state-mandated curriculum for how and when content is taught. The outline is not a list of required items, and so, was developed with the understanding that content often overlaps. Because of this overlap, it may seem as if important ideas, people, p ...
Behaviorism
... School connection: students in a classroom where they rarely experience reinforcement – only punishment. Over time they come to believe they can’t learn well. Kids might see school as a place where they can’t escape or avoid punishment. Can’t win so don’t try or withdraw. When they move to a new cla ...
... School connection: students in a classroom where they rarely experience reinforcement – only punishment. Over time they come to believe they can’t learn well. Kids might see school as a place where they can’t escape or avoid punishment. Can’t win so don’t try or withdraw. When they move to a new cla ...
Toward optimal learning dynamics
... A second, quite different application of this approach is to the study of spacing effects. Spacing of study and testing are well known to influence the duration and effectiveness of learning. We extended the understanding of spacing effects to educationally-relevant time scales, and found that spaci ...
... A second, quite different application of this approach is to the study of spacing effects. Spacing of study and testing are well known to influence the duration and effectiveness of learning. We extended the understanding of spacing effects to educationally-relevant time scales, and found that spaci ...
Another “Stage” Theory: Freud`s Stages of Psychosexual Development
... • Measures personality traits and emotional characteristics – including many associated with psychological disorders ...
... • Measures personality traits and emotional characteristics – including many associated with psychological disorders ...
The History of Psychology
... – Behavior - observable actions of a person or animal – Mental Processes - feelings, sensations, perceptions, memories, dreams, motives and other subjective experiences – Science - an objective way to answer questions based on observable facts/data and well-described methods ...
... – Behavior - observable actions of a person or animal – Mental Processes - feelings, sensations, perceptions, memories, dreams, motives and other subjective experiences – Science - an objective way to answer questions based on observable facts/data and well-described methods ...
Psychological behaviorism

Psychological behaviorism is a form of behaviorism - a major theory within psychology which holds that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcements. The theory recommends that psychological concepts (such as personality, learning and emotion) are to be explained in terms of observable behaviors that respond to stimulus. Behaviorism was first developed by John B. Watson (1912), who coined the term ""behaviorism,"" and then B.F. Skinner who developed what is known as ""radical behaviorism."" Watson and Skinner rejected the idea that psychological data could be obtained through introspection or by an attempt to describe consciousness; all psychological data, in their view, was to be derived from the observation of outward behavior. Recently, Arthur W. Staats has proposed a psychological behaviorism - a ""paradigmatic behaviorist theory"" which argues that personality consists of a set of learned behavioral patterns, acquired through the interaction between an individual's biology, environment, cognition, and emotion. Holth also critically reviews psychological behaviorism as a ""path to the grand reunification of psychology and behavior analysis"".Psychological behaviorism’s theory of personality represents one of psychological behaviorism’s central differences from the preceding behaviorism’s; the other parts of the broader approach as they relate to each other will be summarized in the paradigm sections