Chapter 7 Class Slides…
... Payoff Different ways to schedule payoff Choice Choice is everywhere Impulsiveness and self-control Behavioral economics: Are reinforcers all alike? Theories of Reinforcement Drive reduction The Premack principle Problems with the Premack principle ...
... Payoff Different ways to schedule payoff Choice Choice is everywhere Impulsiveness and self-control Behavioral economics: Are reinforcers all alike? Theories of Reinforcement Drive reduction The Premack principle Problems with the Premack principle ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 19. It is easier to train a dog to bark for food than to train it to stand on its hind legs for food. This best illustrates the importance of ______ in learning. ...
... 19. It is easier to train a dog to bark for food than to train it to stand on its hind legs for food. This best illustrates the importance of ______ in learning. ...
Intro to Psychological Disorders
... There is no one absolute definition of psychological disorders; moreover, a continuum exists between mental health on the one hand and pathology on the other. Some proposed definitions include: ...
... There is no one absolute definition of psychological disorders; moreover, a continuum exists between mental health on the one hand and pathology on the other. Some proposed definitions include: ...
Psychology`s Three Big Debates
... started to ignore how you feel inside. • All that mattered was how you acted. • If they could change your behavior, who cares how you feel. • Very popular during the conservative 1950’s when social appearance mattered more than self expression. ...
... started to ignore how you feel inside. • All that mattered was how you acted. • If they could change your behavior, who cares how you feel. • Very popular during the conservative 1950’s when social appearance mattered more than self expression. ...
Personality and Its Assessment
... Traits are used to DESCRIBE different personality types. Traits can be innate (born with) or acquired; but stay fairly constant across situations ...
... Traits are used to DESCRIBE different personality types. Traits can be innate (born with) or acquired; but stay fairly constant across situations ...
Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or
... 40. Placing a child in time-out removes the child from playtime, television, and other positive situations. Therefore, time-out would be considered a. positive punishment. b. response cost. c. negative reinforcement. d. discriminative stimuli. 41. Each time he steps up to the plate, a baseball playe ...
... 40. Placing a child in time-out removes the child from playtime, television, and other positive situations. Therefore, time-out would be considered a. positive punishment. b. response cost. c. negative reinforcement. d. discriminative stimuli. 41. Each time he steps up to the plate, a baseball playe ...
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
... Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychological treatment that has been demonstrated to be effective for a range of problems including depression, anxiety disorders, alcohol and drug use problems, marital problems, eating disorders, and severe mental illness. Numerous research studies ...
... Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of psychological treatment that has been demonstrated to be effective for a range of problems including depression, anxiety disorders, alcohol and drug use problems, marital problems, eating disorders, and severe mental illness. Numerous research studies ...
What is Psychology?
... • pursue goals that are challenging, yet attainable through hard work, ability, determination, and persistence • see their success as a result of their own talents, abilities, persistence, and hard work ...
... • pursue goals that are challenging, yet attainable through hard work, ability, determination, and persistence • see their success as a result of their own talents, abilities, persistence, and hard work ...
Okami Study Guide
... 4. Associative learning is more complex than habituation and sensitization. Associative learning occurs when an organism comes to associate two or more stimuli or events that occur close together in space and time. Classical conditioning is the most basic form of associative learning. The capacity t ...
... 4. Associative learning is more complex than habituation and sensitization. Associative learning occurs when an organism comes to associate two or more stimuli or events that occur close together in space and time. Classical conditioning is the most basic form of associative learning. The capacity t ...
Learning - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... importance to the survival of the species. • Animals seem to be biologically prepared to fear certain types of stimuli that represent natural threats to survival. – We are predisposed to avoid threats our ancestors faced-food that made us sick, storms, heights, snakes, etc. – But not modern-day thre ...
... importance to the survival of the species. • Animals seem to be biologically prepared to fear certain types of stimuli that represent natural threats to survival. – We are predisposed to avoid threats our ancestors faced-food that made us sick, storms, heights, snakes, etc. – But not modern-day thre ...
What is Psychology?
... • pursue goals that are challenging, yet attainable through hard work, ability, determination, and persistence • see their success as a result of their own talents, abilities, persistence, and hard work ...
... • pursue goals that are challenging, yet attainable through hard work, ability, determination, and persistence • see their success as a result of their own talents, abilities, persistence, and hard work ...
PSY402 Theories of Learning
... The person may not recognize the contingency between the behavior and the punishment. ...
... The person may not recognize the contingency between the behavior and the punishment. ...
Chapter Outline - Cengage Learning
... 25. The partial reinforcement extinction effect occurs when a partial reinforcement schedule has been used in the operant conditioning process. The more difficult it is for the organism to predict the occurrence of reinforcement (meaning the behavior isn’t rewarded every time), the harder the respon ...
... 25. The partial reinforcement extinction effect occurs when a partial reinforcement schedule has been used in the operant conditioning process. The more difficult it is for the organism to predict the occurrence of reinforcement (meaning the behavior isn’t rewarded every time), the harder the respon ...
chapter 6 review with answers
... - environmental stimuli serve as signals and that some stimuli are better, or more dependable signals than others 4. Response-outcome relations - Response will be strengthened if you liked the outcome 5. Latent learning - Learning that is not apparent from behavior when it first occurs 6. Instinct - ...
... - environmental stimuli serve as signals and that some stimuli are better, or more dependable signals than others 4. Response-outcome relations - Response will be strengthened if you liked the outcome 5. Latent learning - Learning that is not apparent from behavior when it first occurs 6. Instinct - ...
Module 10: Operant & Cognitive Approaches
... 20. Todd feels happy whenever he smells chocolate-chip cookies baking because, when he was a child, his grandmother, whom he loved very much, used to bake chocolate-chip cookies for him whenever he visited her. In this example, the CS is A. the smell of chocolate-chip cookies baking. B. the happines ...
... 20. Todd feels happy whenever he smells chocolate-chip cookies baking because, when he was a child, his grandmother, whom he loved very much, used to bake chocolate-chip cookies for him whenever he visited her. In this example, the CS is A. the smell of chocolate-chip cookies baking. B. the happines ...
Programmed Learning Review Answers
... of practice or other past experience. Since all behavior does not fit into this definition of __LEARNING__ we must narrow the definition 2. Learning refers to a relatively __PERMANENT__ change in behavior. 3. __REFLEXES___ are simple automatic behaviors which are not included within the definition o ...
... of practice or other past experience. Since all behavior does not fit into this definition of __LEARNING__ we must narrow the definition 2. Learning refers to a relatively __PERMANENT__ change in behavior. 3. __REFLEXES___ are simple automatic behaviors which are not included within the definition o ...
Class cond notes
... Behaviorism: Psychological perspective that emphasizes the role of learning and experience in determining behavior. A strict behavioralist believes that babies are tabula rasa and the study of psychology should focus purely on observable behaviors and not unobservable thoughts. Learning –a relativel ...
... Behaviorism: Psychological perspective that emphasizes the role of learning and experience in determining behavior. A strict behavioralist believes that babies are tabula rasa and the study of psychology should focus purely on observable behaviors and not unobservable thoughts. Learning –a relativel ...
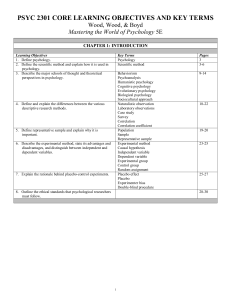
psyc 2301 core learning objectives and key terms
... In a longitudinal study, the same group of participants is followed and measured at different ages, over a period of years. Such studies allow researchers to observe age-related changes in individuals. There are some drawbacks to a longitudinal study, however. It is time consuming and expensive, and ...
... In a longitudinal study, the same group of participants is followed and measured at different ages, over a period of years. Such studies allow researchers to observe age-related changes in individuals. There are some drawbacks to a longitudinal study, however. It is time consuming and expensive, and ...
Motivation
... • People actively and regularly determine their own goals and means of achieving them • Intrinsic motivation engage in behavior for internal pleasure & satisfaction of activity itself ...
... • People actively and regularly determine their own goals and means of achieving them • Intrinsic motivation engage in behavior for internal pleasure & satisfaction of activity itself ...
Chapter 7 Week 1
... (having had a bad day) swoops her up and spanks her. f) An AP psychology student develops a terrible headache after studying for a big exam. He takes two aspirin and theheadache disappears. g) Two siblings, who usually spend most of their time fighting, finally play peaceably. Dad peeks in and sighs ...
... (having had a bad day) swoops her up and spanks her. f) An AP psychology student develops a terrible headache after studying for a big exam. He takes two aspirin and theheadache disappears. g) Two siblings, who usually spend most of their time fighting, finally play peaceably. Dad peeks in and sighs ...
Introductory Psychology 85-102 2013 Exam I Review Notes The
... go together in the world (or what are reliable signals of impending events) and also organisms learning to repeat behaviors that "work" in leading to pleasure (which often results from the satisfaction of basic drives and thus has adaptive value). Not all behavior or learning fits these basic models ...
... go together in the world (or what are reliable signals of impending events) and also organisms learning to repeat behaviors that "work" in leading to pleasure (which often results from the satisfaction of basic drives and thus has adaptive value). Not all behavior or learning fits these basic models ...
Psychological behaviorism

Psychological behaviorism is a form of behaviorism - a major theory within psychology which holds that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcements. The theory recommends that psychological concepts (such as personality, learning and emotion) are to be explained in terms of observable behaviors that respond to stimulus. Behaviorism was first developed by John B. Watson (1912), who coined the term ""behaviorism,"" and then B.F. Skinner who developed what is known as ""radical behaviorism."" Watson and Skinner rejected the idea that psychological data could be obtained through introspection or by an attempt to describe consciousness; all psychological data, in their view, was to be derived from the observation of outward behavior. Recently, Arthur W. Staats has proposed a psychological behaviorism - a ""paradigmatic behaviorist theory"" which argues that personality consists of a set of learned behavioral patterns, acquired through the interaction between an individual's biology, environment, cognition, and emotion. Holth also critically reviews psychological behaviorism as a ""path to the grand reunification of psychology and behavior analysis"".Psychological behaviorism’s theory of personality represents one of psychological behaviorism’s central differences from the preceding behaviorism’s; the other parts of the broader approach as they relate to each other will be summarized in the paradigm sections