An Integrative Neurological Model for Basic Observable Human
... regions of the anterior cingulate gyrus regulate these responses (Phillips, et al., 2003). What is so ...
... regions of the anterior cingulate gyrus regulate these responses (Phillips, et al., 2003). What is so ...
Learning - WordPress.com
... reinforcing a response only part of the time results in slower acquisition greater resistance to extinction ...
... reinforcing a response only part of the time results in slower acquisition greater resistance to extinction ...
Slide 1 - WordPress.com
... show changing of behavior by the use of reinforcement which is given after the desired response. •Positive reinforcement strengthens a behavior by providing a consequence an individual finds rewarding. •Negative reinforcement strengthens behavior because it stops or removes an unpleasant experience. ...
... show changing of behavior by the use of reinforcement which is given after the desired response. •Positive reinforcement strengthens a behavior by providing a consequence an individual finds rewarding. •Negative reinforcement strengthens behavior because it stops or removes an unpleasant experience. ...
Learning Presentation
... involves mental processes and may result from observation or imitation of others ○ Cognitive Map - a mental picture of relationships between events or spatial relationship ○ Latent Learning - changing a behavior that is not immediate, but is demonstrated at a later time. ● Learned Helplessness - a c ...
... involves mental processes and may result from observation or imitation of others ○ Cognitive Map - a mental picture of relationships between events or spatial relationship ○ Latent Learning - changing a behavior that is not immediate, but is demonstrated at a later time. ● Learned Helplessness - a c ...
Chapter-7-Lecture
... its absence. 5. Causes aggression towards the agent. 6. Causes one unwanted behavior to appear in place of another. ...
... its absence. 5. Causes aggression towards the agent. 6. Causes one unwanted behavior to appear in place of another. ...
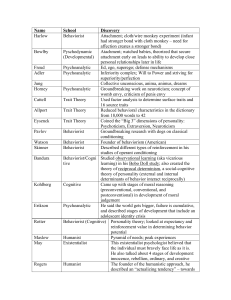
Theorist Names - HallquistCPHS.com
... He built puzzle boxes for hungry cats and discovered the law of effect (in learning new tasks, you repeat only the (random) responses that are reinforced) Developed the first modern intelligence test, still the basis of modern IQ tests Developed two new scales that are more popular today (gives more ...
... He built puzzle boxes for hungry cats and discovered the law of effect (in learning new tasks, you repeat only the (random) responses that are reinforced) Developed the first modern intelligence test, still the basis of modern IQ tests Developed two new scales that are more popular today (gives more ...
unit 6: learning - Mayfield City Schools
... 1. Here is where a neutral stimulus (a bell/tone) is paired with an unconditioned stimulus (dog food) 2. After several trials, the two will elicit the same response (a dog salivating) 3. When the former neutral stimulus (a bell/tone) produces a response (salivation), it is now a ...
... 1. Here is where a neutral stimulus (a bell/tone) is paired with an unconditioned stimulus (dog food) 2. After several trials, the two will elicit the same response (a dog salivating) 3. When the former neutral stimulus (a bell/tone) produces a response (salivation), it is now a ...
Behavioral tox i plant toxins cology of livestock ingesting
... should concurrently examine behavioral and morphological indicators when possible. Table 1 indicates how animal responses to toxins in larkspur and locoweed might vary depending on the type of evaluation. Behavioral toxicology encompasses diverse ways of examining toxicity, and each level of explana ...
... should concurrently examine behavioral and morphological indicators when possible. Table 1 indicates how animal responses to toxins in larkspur and locoweed might vary depending on the type of evaluation. Behavioral toxicology encompasses diverse ways of examining toxicity, and each level of explana ...
Proceedings of 31st International Business Research Conference
... the most part have been ineffective. Bullying in the workplace presents an ethical dilemma for organizations, leaders and employees. Researchers and professionals are seeking to gain a better understanding of why some employers and leaders appear to ignore behaviors of individuals that jeopardize th ...
... the most part have been ineffective. Bullying in the workplace presents an ethical dilemma for organizations, leaders and employees. Researchers and professionals are seeking to gain a better understanding of why some employers and leaders appear to ignore behaviors of individuals that jeopardize th ...
Learning Notes
... The most common example of this is disciplining (e.g. spanking) a child for misbehaving. The reason we do this is because the child begins to associate being punished with the negative behavior. (detentions) ...
... The most common example of this is disciplining (e.g. spanking) a child for misbehaving. The reason we do this is because the child begins to associate being punished with the negative behavior. (detentions) ...
Notes - Interpersonal Research Laboratory
... • "Of several responses made to the same situation those which are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction to the animal will, other things being equal, be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or clo ...
... • "Of several responses made to the same situation those which are accompanied or closely followed by satisfaction to the animal will, other things being equal, be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or clo ...
psy honor ch. 5 study guide learning
... other animals in terms of the physiological responses of the organism to external stimuli in their environment. Skinner maintained that learning occurred as a result of the organism responding to, or operating on, its environment, and coined the term operant conditioning to describe this phenomenon. ...
... other animals in terms of the physiological responses of the organism to external stimuli in their environment. Skinner maintained that learning occurred as a result of the organism responding to, or operating on, its environment, and coined the term operant conditioning to describe this phenomenon. ...
3 slides
... Z Punishers elicit a variety of emotional reactions that we would rather not have associated with a situation (e.g., fear of parents, anger toward parents) Z Punishment can trigger aggressive behavior, which is not a desired outcome Z Punishment can lead to avoidance learning (e.g., avoid parent or ...
... Z Punishers elicit a variety of emotional reactions that we would rather not have associated with a situation (e.g., fear of parents, anger toward parents) Z Punishment can trigger aggressive behavior, which is not a desired outcome Z Punishment can lead to avoidance learning (e.g., avoid parent or ...
Instrumental Conditioning: Theoretical Issues
... Z Punishers elicit a variety of emotional reactions that we would rather not have associated with a situation (e.g., fear of parents, anger toward parents) Z Punishment can trigger aggressive behavior, which is not a desired outcome Z Punishment can lead to avoidance learning (e.g., avoid parent or ...
... Z Punishers elicit a variety of emotional reactions that we would rather not have associated with a situation (e.g., fear of parents, anger toward parents) Z Punishment can trigger aggressive behavior, which is not a desired outcome Z Punishment can lead to avoidance learning (e.g., avoid parent or ...
here
... behavior effectively and for its own sake. • Extrinsic Motivation: desire to behave in a certain way to receive external rewards or avoid threatened punishment. ...
... behavior effectively and for its own sake. • Extrinsic Motivation: desire to behave in a certain way to receive external rewards or avoid threatened punishment. ...
Learning - smw15.org
... You have to have the ability to reproduce the behavior in the first place. For example: Some people can watch Olympic ice skaters all day long, yet not be able to reproduce their jumps, because they can’t ice skate at all! On the other hand, if they could skate, their performance would in fact i ...
... You have to have the ability to reproduce the behavior in the first place. For example: Some people can watch Olympic ice skaters all day long, yet not be able to reproduce their jumps, because they can’t ice skate at all! On the other hand, if they could skate, their performance would in fact i ...
Major components involved in observational learning
... You have to have the ability to reproduce the behavior in the first place. For example: Some people can watch Olympic ice skaters all day long, yet not be able to reproduce their jumps, because they can’t ice skate at all! On the other hand, if they could skate, their performance would in fact i ...
... You have to have the ability to reproduce the behavior in the first place. For example: Some people can watch Olympic ice skaters all day long, yet not be able to reproduce their jumps, because they can’t ice skate at all! On the other hand, if they could skate, their performance would in fact i ...
Innate/Learned Behavior Powerpoint
... A rat was placed inside the Skinner box If the rat pressed down a lever inside the box then the box would release a food pellet Soon, the rat pressed the lever far more often than he would just by chance. But with each instance of lever pressing, the operant is reinforced by reward with food ...
... A rat was placed inside the Skinner box If the rat pressed down a lever inside the box then the box would release a food pellet Soon, the rat pressed the lever far more often than he would just by chance. But with each instance of lever pressing, the operant is reinforced by reward with food ...
Organizational Behavior 11e - Stephen P. Robbins
... human behavior is learned observationally through modeling: from observing others one forms an idea of how new behaviors are performed, and on later occasions this coded information serves as a guide for action.” - Albert Bandura, Social Learning Theory, 1977 ...
... human behavior is learned observationally through modeling: from observing others one forms an idea of how new behaviors are performed, and on later occasions this coded information serves as a guide for action.” - Albert Bandura, Social Learning Theory, 1977 ...
Name: Date: Block: Note: For each of the ten examples below
... A professor has a policy of exempting students from the final exam if they maintain perfect attendance during the quarter. His students’ attendance increases dramatically. If Classical: NSUSIf Operant: CSURReinforcementCRPunishment8. You check the coin return slot on a pay telephone and find a quart ...
... A professor has a policy of exempting students from the final exam if they maintain perfect attendance during the quarter. His students’ attendance increases dramatically. If Classical: NSUSIf Operant: CSURReinforcementCRPunishment8. You check the coin return slot on a pay telephone and find a quart ...
LECTURE 26 INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR
... – Few differences between men and women that affect job performance (like physical ability) – Should operate on assumption that there is no significant difference in performance based on gender (consider profession as well) – Women have higher absenteeism rate ...
... – Few differences between men and women that affect job performance (like physical ability) – Should operate on assumption that there is no significant difference in performance based on gender (consider profession as well) – Women have higher absenteeism rate ...
A.P. Psychology 6 (C) - Operant Conditioning
... Which one do you think is least effective? Which one do you think is most effective? Which one do you think is most addictive? ...
... Which one do you think is least effective? Which one do you think is most effective? Which one do you think is most addictive? ...
Psychology PPT Week Four - K-Dub
... What is going on in your body and thoughts?” 3.Reflect Feelings “It seems like you are disappointed; am I right?” ...
... What is going on in your body and thoughts?” 3.Reflect Feelings “It seems like you are disappointed; am I right?” ...
Theory of planned behavior

In psychology, the theory of planned behavior (abbreviated TPB) is a theory that links beliefs and behavior. The concept was proposed by Icek Ajzen to improve on the predictive power of the theory of reasoned action by including perceived behavioural control. It is one of the most predictive persuasion theories. It has been applied to studies of the relations among beliefs, attitudes, behavioral intentions and behaviors in various fields such as advertising, public relations, advertising campaigns and healthcare.The theory states that attitude toward behavior, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control, together shape an individual's behavioral intentions and behaviors.