Learning - Bremerton School District
... Therefore, a pigeon and a person do not differ in their learning. However, behaviorists later suggested that learning is constrained by an animal’s biology. ...
... Therefore, a pigeon and a person do not differ in their learning. However, behaviorists later suggested that learning is constrained by an animal’s biology. ...
The Basics Of Addiction Counseling
... dynamic, such as individual, family or group therapy. Within each of these settings, there are many different counseling theories practiced by addiction professionals; however, no one therapy or counseling approach is appropriate for all situations or clients. Depending on the school of thought of t ...
... dynamic, such as individual, family or group therapy. Within each of these settings, there are many different counseling theories practiced by addiction professionals; however, no one therapy or counseling approach is appropriate for all situations or clients. Depending on the school of thought of t ...
Document
... Classical Conditioning • Association: the KEY element in classical conditioning – Pavlov considered classical conditioning to be a form of learning through association, in time, of a neutral stimulus and a stimulus that incites a response. – Any stimulus can be paired with another to make an assoc ...
... Classical Conditioning • Association: the KEY element in classical conditioning – Pavlov considered classical conditioning to be a form of learning through association, in time, of a neutral stimulus and a stimulus that incites a response. – Any stimulus can be paired with another to make an assoc ...
Document
... – In classical conditioning, a person or animal learns to associate a neutral stimulus (the conditioned stimulus, or CS) with a stimulus (the unconditioned stimulus, or US) that naturally produces a behavior (the unconditioned response, or UR). As a result of this association, the previously neutral ...
... – In classical conditioning, a person or animal learns to associate a neutral stimulus (the conditioned stimulus, or CS) with a stimulus (the unconditioned stimulus, or US) that naturally produces a behavior (the unconditioned response, or UR). As a result of this association, the previously neutral ...
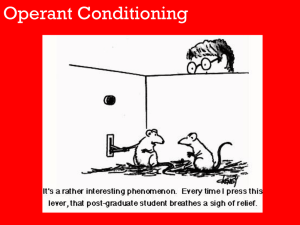
Operant Conditioning - Fleming County Schools
... This is known as: This is known as: ________________ ________________ ...
... This is known as: This is known as: ________________ ________________ ...
Behaviorism as a Theory of Personality: A Critical Look
... Inability to explain the development of human language. Although Skinner's ideas on operant conditioning are able to explain phobias and neurosis, they are sadly lacking in applicability to the more complex human behaviors of language and memory. The theory's inability to explain the language phenom ...
... Inability to explain the development of human language. Although Skinner's ideas on operant conditioning are able to explain phobias and neurosis, they are sadly lacking in applicability to the more complex human behaviors of language and memory. The theory's inability to explain the language phenom ...
UNIT VI Notes File
... psychology should focus on how organisms respond to stimuli in the environment (Behaviorism) – today most psychologists agree that classical conditioning is the basic form of learning by which all organisms adapt to their environment Watson applied Pavlov’s work to humans – Watson believed that alth ...
... psychology should focus on how organisms respond to stimuli in the environment (Behaviorism) – today most psychologists agree that classical conditioning is the basic form of learning by which all organisms adapt to their environment Watson applied Pavlov’s work to humans – Watson believed that alth ...
File
... 2) Hurrying home in the winter (operant) to get out of the cold (stimulus). 3) Giving in to a dog’s begging (operant) so that it stops barking (stimulus). 4) Setting a timer on the oven (operant) to avoid burning the cookies (stimulus). 5) Leaving a movie theatre (operant) to escape the movie (stimu ...
... 2) Hurrying home in the winter (operant) to get out of the cold (stimulus). 3) Giving in to a dog’s begging (operant) so that it stops barking (stimulus). 4) Setting a timer on the oven (operant) to avoid burning the cookies (stimulus). 5) Leaving a movie theatre (operant) to escape the movie (stimu ...
LT2Ch4c
... faster rats run down an alley. Likelihood and intensity of a response depends on size of reward. ...
... faster rats run down an alley. Likelihood and intensity of a response depends on size of reward. ...
Tinbergen`s four questions, biologically useless behavior
... in survival or reproduction, what stimuli elicit it, its ontogeny and evolutionary history) when applied to man solely from biological point of view seem to be often inappropriate. For example, what is the survival function of behaviors that have emerged in modern man such as burial, artwork, and re ...
... in survival or reproduction, what stimuli elicit it, its ontogeny and evolutionary history) when applied to man solely from biological point of view seem to be often inappropriate. For example, what is the survival function of behaviors that have emerged in modern man such as burial, artwork, and re ...
Lecture 5: a. finish learning and differential association b. social
... • Individual-level theories – Rational choice/deterrence (econ) – Moffitt’s 2-group (biology & psychology) ...
... • Individual-level theories – Rational choice/deterrence (econ) – Moffitt’s 2-group (biology & psychology) ...
View/Open - ESIRC - Emporia State University
... Matute (1994) argues that conditions of response-independent reinforcement commonly used in human research do not lead to learned helplessness, but rather to superstitious behavior and illusion of control. Helplessness results from the individual's learned expectations that their responses are indep ...
... Matute (1994) argues that conditions of response-independent reinforcement commonly used in human research do not lead to learned helplessness, but rather to superstitious behavior and illusion of control. Helplessness results from the individual's learned expectations that their responses are indep ...
AP Psychology Learning PPT
... behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely ...
... behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely, and behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely ...
Learning
... and well- being in a variety of ways ! Examples ! Patients can develop classically conditioned sideeffects to drugs given as cancer treatments ! Former drug users often feel a craving when they are again in the drug-using context ...
... and well- being in a variety of ways ! Examples ! Patients can develop classically conditioned sideeffects to drugs given as cancer treatments ! Former drug users often feel a craving when they are again in the drug-using context ...
Chapter 6 Learning - Home | W. W. Norton & Company
... • Learning: a relatively enduring change in behavior due to experience – Central to almost all areas of human existence ...
... • Learning: a relatively enduring change in behavior due to experience – Central to almost all areas of human existence ...
AbPsych Chapter 2 Handouts
... ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ...
... ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ...
Learning - bethwallace
... The acquisition of knowledge or skills through experience, practice, or study, or by being taught. Knowledge acquired in this way. ...
... The acquisition of knowledge or skills through experience, practice, or study, or by being taught. Knowledge acquired in this way. ...
Notes
... – simple associations between stimuli • Today’s researchers – considering how imagined stimuli (e.g., thoughts) can produce a response ...
... – simple associations between stimuli • Today’s researchers – considering how imagined stimuli (e.g., thoughts) can produce a response ...
Learning - ISA
... Extinction: The diminishing (or lessening) of a learned response, when an unconditioned stimulus does not follow a conditioned stimulus. In other words, the CS no longer elicits the CR. ◦ To acquire a CR, we repeatedly pair a neutral stimulus with the UCS. But, if we want to reverse this learning, w ...
... Extinction: The diminishing (or lessening) of a learned response, when an unconditioned stimulus does not follow a conditioned stimulus. In other words, the CS no longer elicits the CR. ◦ To acquire a CR, we repeatedly pair a neutral stimulus with the UCS. But, if we want to reverse this learning, w ...
Influence of Reinforcement Contingencies and Cognitive Styles on
... and nature of conditioning and, by extension therefore, affective responses to consumer environments. In also drawing attention to the role of individual differences in the meditation of emotion and behavior, Rolls (2005) paid particular attention to the claim that extraversion–introversion and neur ...
... and nature of conditioning and, by extension therefore, affective responses to consumer environments. In also drawing attention to the role of individual differences in the meditation of emotion and behavior, Rolls (2005) paid particular attention to the claim that extraversion–introversion and neur ...
Interaction of Classical and Operaant Conditioning
... longer distance makes it more difficult for the bird to ...
... longer distance makes it more difficult for the bird to ...
learning test
... Learning Test AP Psychology Mr. Gambale 1. With which of the following quotes would you most associate B .F. Skinner? a. “To my mind, empathy in itself is a healing agent.” b. “Just as hunger impels a person to eat, so does dissonance impel a person to change his opinions or behavior.” c. “Operant c ...
... Learning Test AP Psychology Mr. Gambale 1. With which of the following quotes would you most associate B .F. Skinner? a. “To my mind, empathy in itself is a healing agent.” b. “Just as hunger impels a person to eat, so does dissonance impel a person to change his opinions or behavior.” c. “Operant c ...
Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning Chapter 7
... Punishment is often applied unequally. ...
... Punishment is often applied unequally. ...
Classical Conditioning
... salivating when the dispenser sound kept occurring without the meat powder following. ...
... salivating when the dispenser sound kept occurring without the meat powder following. ...
Lecture 1: Mirroring and Social Cognition
... performed by “biological” agents Rizzolatti and Sinigaglia, Nature Reviews Neurosci, 2010 ...
... performed by “biological” agents Rizzolatti and Sinigaglia, Nature Reviews Neurosci, 2010 ...