Chapter 6 Learning - Home | W. W. Norton & Company
... • Behaviorism: a formal learning theory from the early twentieth century – John Watson: focused on environment and associated effects as key determinants of learning – B. F. Skinner: designed animal experiments to discover basic rules of learning ...
... • Behaviorism: a formal learning theory from the early twentieth century – John Watson: focused on environment and associated effects as key determinants of learning – B. F. Skinner: designed animal experiments to discover basic rules of learning ...
Chapter 7: Motivation Concepts
... Self-Determination Theory Proposes that people prefer to feel they have control over their actions. Research on self-determination theory has focused on cognitive evaluation theory. People paid for work feel less like they want to do it and more like they have to it. Proposes that in additio ...
... Self-Determination Theory Proposes that people prefer to feel they have control over their actions. Research on self-determination theory has focused on cognitive evaluation theory. People paid for work feel less like they want to do it and more like they have to it. Proposes that in additio ...
Seminar: Skinner`s Analysis of Verbal Behavior
... ideas.’ To report that a man salivates when he hears the dinner bell may be to overlook the fact that the dinner bell first “makes him think of dinner” and that he then salivates because he thinks of dinner. But there is no evidence that thinking of dinner, as that expression has been defined here, ...
... ideas.’ To report that a man salivates when he hears the dinner bell may be to overlook the fact that the dinner bell first “makes him think of dinner” and that he then salivates because he thinks of dinner. But there is no evidence that thinking of dinner, as that expression has been defined here, ...
The Process of Learning: Skinner`s Scientific Analysis of
... Education” the authors Frank Milhollan and Bill E. Forisha discuss in detail all the aspects of conditioning and operant conditioning. Here is the comprehensive summary of the concepts: Two classes of behavior: ‘Reflex’ or ‘involuntary’ or ‘respondent behavior’ or ‘elicited’ [Spontaneous] Voluntary’ ...
... Education” the authors Frank Milhollan and Bill E. Forisha discuss in detail all the aspects of conditioning and operant conditioning. Here is the comprehensive summary of the concepts: Two classes of behavior: ‘Reflex’ or ‘involuntary’ or ‘respondent behavior’ or ‘elicited’ [Spontaneous] Voluntary’ ...
ABC`s of ABA - Ventura County SELPA
... Restricted behavior is limited in focus, interest, or activity, such as preoccupation with a single television program, toy, or game. Self-injury includes movements that injure or can injure the person, such as eye poking, skin picking, hand biting, and head banging. Autism Across the Life Span 2012 ...
... Restricted behavior is limited in focus, interest, or activity, such as preoccupation with a single television program, toy, or game. Self-injury includes movements that injure or can injure the person, such as eye poking, skin picking, hand biting, and head banging. Autism Across the Life Span 2012 ...
Psychology – Dr. Saman – Lecture 2
... NS and UCS pairings must not be more than about 1/2 second apart for best results Repeated NS/UCS pairings are called “training trials” Presentations of CS without UCS pairings are called “extinction trials” Intensity of UCS effects how many training trials are necessary for conditioning to occur ...
... NS and UCS pairings must not be more than about 1/2 second apart for best results Repeated NS/UCS pairings are called “training trials” Presentations of CS without UCS pairings are called “extinction trials” Intensity of UCS effects how many training trials are necessary for conditioning to occur ...
Educational Psychology: Theory and Practice Chapter 2
... Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development Stage III: Initiative versus Guilt (3 to 6 Years) During this period, children’s maturing motor and language skills permit them to be increasingly vigorous in exploring their social and physical environment. Parents who permit children to run, jump, play ...
... Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development Stage III: Initiative versus Guilt (3 to 6 Years) During this period, children’s maturing motor and language skills permit them to be increasingly vigorous in exploring their social and physical environment. Parents who permit children to run, jump, play ...
`Superstition` in the Pigeon
... It is perhaps not quite correct to say that conditioned behavior has been set up without any previously determined contingency whatsoever. We have appealed to a uniform sequence of responses in the behavior of the pigeon to obtain an over-all net contingency. When we arrange a clock to present food ...
... It is perhaps not quite correct to say that conditioned behavior has been set up without any previously determined contingency whatsoever. We have appealed to a uniform sequence of responses in the behavior of the pigeon to obtain an over-all net contingency. When we arrange a clock to present food ...
The Psychology of Learning and Behavior
... known for his studies of reflex behavior. He was born in Ryazan', and educated at the University of Saint Petersburg and at the Military Medical Academy, St. Petersburg; from 1884 to 1886 he studied in Breslau (now Wroclaw, Poland) and Leipzig, Germany. Before the Russian Revolution he served as dir ...
... known for his studies of reflex behavior. He was born in Ryazan', and educated at the University of Saint Petersburg and at the Military Medical Academy, St. Petersburg; from 1884 to 1886 he studied in Breslau (now Wroclaw, Poland) and Leipzig, Germany. Before the Russian Revolution he served as dir ...
here
... Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation • Intrinsic Motivation: desire to perform the behavior effectively and for its own sake. • Extrinsic Motivation: desire to behave in a certain way to receive external rewards or avoid threatened punishment. ...
... Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation • Intrinsic Motivation: desire to perform the behavior effectively and for its own sake. • Extrinsic Motivation: desire to behave in a certain way to receive external rewards or avoid threatened punishment. ...
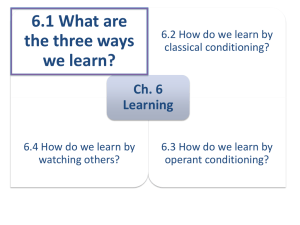
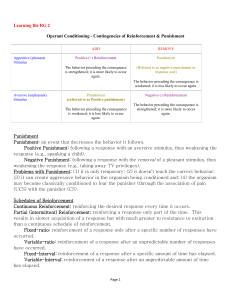
Learning file RG 2
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
... Cognitive Map: a mental representation of the layout of one's environment. Latent Learning: learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate it Overjustification Effect: the effect of promising a reward for doing what one already likes to do. The person may now s ...
Aggression
... inward (lead to feelings of worthlessness and depression, e.g. suicide) or outward (lead to hostility toward others). -Specific aggressive behavior patterns are learned experiences and learning processes during childhood, but biological elements is still underlying basis for aggression. ...
... inward (lead to feelings of worthlessness and depression, e.g. suicide) or outward (lead to hostility toward others). -Specific aggressive behavior patterns are learned experiences and learning processes during childhood, but biological elements is still underlying basis for aggression. ...
Learning: Chapter 5
... 28. Explain how a optimistic and pessimistic explanatory style are different. Do the same for Type A and Type B behavior patterns. 29. What are the effects of stimulant drugs on our ability to handle stress? 30. How do collectivist versus individualistic cultures differ in their handling of stressfu ...
... 28. Explain how a optimistic and pessimistic explanatory style are different. Do the same for Type A and Type B behavior patterns. 29. What are the effects of stimulant drugs on our ability to handle stress? 30. How do collectivist versus individualistic cultures differ in their handling of stressfu ...
Abnormal-Psychology-in-a-Changing-World-7th
... Which of the following is NOT one of the three regions of the mind described by Freud? a. the conscious c. the preconscious b. the superconscious d. the unconscious ...
... Which of the following is NOT one of the three regions of the mind described by Freud? a. the conscious c. the preconscious b. the superconscious d. the unconscious ...
CBCC-KA Examination Study Objectives
... Recognize common physical signs and behaviors that may suggest a canine has a medical condition; discuss when you would suggest veterinary counsel and when and how you might limit a training plan Describe the challenges involved in helping a client understand the need for a proper veterinary dia ...
... Recognize common physical signs and behaviors that may suggest a canine has a medical condition; discuss when you would suggest veterinary counsel and when and how you might limit a training plan Describe the challenges involved in helping a client understand the need for a proper veterinary dia ...
Single-Subject/Small-n Research and Designs
... • argue against History and Maturation threats • do not require recovery of baseline Three Multiple baseline designs: 1. Multiple baseline across individuals (or ...
... • argue against History and Maturation threats • do not require recovery of baseline Three Multiple baseline designs: 1. Multiple baseline across individuals (or ...
Theories and Models
... these cognitive structures could be modified or adapted through the processes of assimilation and adaptation (Huitt & Hummel, 2003). Assimilation involves transforming the environment to fit the existing structure, while accommodation involves changing the existing structure to accept something in ...
... these cognitive structures could be modified or adapted through the processes of assimilation and adaptation (Huitt & Hummel, 2003). Assimilation involves transforming the environment to fit the existing structure, while accommodation involves changing the existing structure to accept something in ...
classical conditioning - Warren County Public Schools
... environment in a way that produces positive consequences and avoids negative ones. Edward Thorndike’s PUZZLE BOX using a cat in a box with several strings and levers, Thorndike devised a “puzzle box” in which the animal had to perform tasks ranging from simple to complex to escape from the box and r ...
... environment in a way that produces positive consequences and avoids negative ones. Edward Thorndike’s PUZZLE BOX using a cat in a box with several strings and levers, Thorndike devised a “puzzle box” in which the animal had to perform tasks ranging from simple to complex to escape from the box and r ...
Questions - Ms. Paras
... Defense Mechanism: Redirecting a forbidden desire into a socially acceptable desire. SUBLIMATION Defense Mechanism: Not accepting the truth or the reality of a situation. ...
... Defense Mechanism: Redirecting a forbidden desire into a socially acceptable desire. SUBLIMATION Defense Mechanism: Not accepting the truth or the reality of a situation. ...
Psychology Course Description
... About AP® The College Board’s Advanced Placement Program® (AP®) enables students to pursue college-level studies while still in high school. Through more than 30 courses, each culminating in a rigorous exam, AP provides willing and academically prepared students with the opportunity to earn colleg ...
... About AP® The College Board’s Advanced Placement Program® (AP®) enables students to pursue college-level studies while still in high school. Through more than 30 courses, each culminating in a rigorous exam, AP provides willing and academically prepared students with the opportunity to earn colleg ...
jolene sy cv - UMBC Psychology
... Sy, J. R. (2011). Evaluations of delayed reinforcement in children with developmental disabilities. Invited presentation at the 2011 meeting of the Missouri Association for Behavior Analysis, Saint Louis, MO. Sy, J. R., & Vollmer, T. R. (2011). The effects of reinforcement delay on the acquisition o ...
... Sy, J. R. (2011). Evaluations of delayed reinforcement in children with developmental disabilities. Invited presentation at the 2011 meeting of the Missouri Association for Behavior Analysis, Saint Louis, MO. Sy, J. R., & Vollmer, T. R. (2011). The effects of reinforcement delay on the acquisition o ...
Learning - Stephen F. Austin State University
... fail to act to escape from a situation because of a history of repeated failures in the past. ...
... fail to act to escape from a situation because of a history of repeated failures in the past. ...