Unit 5 practice FRQ #3 for final - KEY 3. 2009 AP Bio FRQ # 4 The
... Alternative splicing ............... editing in different ways to get new/different RNA/polypeptides mRNA degradation ................ targets RNA for destruction (miRNA or siRNA) Protein processing ................. polypeptide → _protein modifications (folding, chaperonins, cleavage, etc.) Protein ...
... Alternative splicing ............... editing in different ways to get new/different RNA/polypeptides mRNA degradation ................ targets RNA for destruction (miRNA or siRNA) Protein processing ................. polypeptide → _protein modifications (folding, chaperonins, cleavage, etc.) Protein ...
Gene Section SETBP1 (SET binding protein 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Online updated version : http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Genes/SETBP1ID44031ch18q12.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/48755 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2013 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
... Online updated version : http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Genes/SETBP1ID44031ch18q12.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/48755 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2013 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
10.3 Protein Synthesis
... Going from DNA to Proteins • Let’s review what we’ve done so far: • We take our DNA and convert it into RNA in a process called ________________. • This happens in the _____________. ...
... Going from DNA to Proteins • Let’s review what we’ve done so far: • We take our DNA and convert it into RNA in a process called ________________. • This happens in the _____________. ...
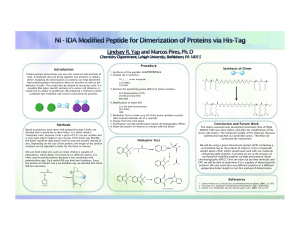
Introduction Methods Procedure Conclusion and Future Work
... (MALDI–TOF) was done before and after the modification of the lysine side chains. The molecular weight of the molecule that was synthesized matched our predicted values. Therefore we continued the experiment We will be using a green fluorescent protein (GFP) containing a six-histidine tag as the pro ...
... (MALDI–TOF) was done before and after the modification of the lysine side chains. The molecular weight of the molecule that was synthesized matched our predicted values. Therefore we continued the experiment We will be using a green fluorescent protein (GFP) containing a six-histidine tag as the pro ...
purpose - cloudfront.net
... Protein Synthesis Practice 1 PURPOSE To review protein synthesis PROCEDURE Place the steps of protein synthesis in the correct order. _____ DNA rejoins & mRNA leaves the nucleus _____ the mRNA codons pair up with the tRNA anticodons; amino acids are added _____ DNA unzips _____ a mRNA copy of the DN ...
... Protein Synthesis Practice 1 PURPOSE To review protein synthesis PROCEDURE Place the steps of protein synthesis in the correct order. _____ DNA rejoins & mRNA leaves the nucleus _____ the mRNA codons pair up with the tRNA anticodons; amino acids are added _____ DNA unzips _____ a mRNA copy of the DN ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ...
... Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ...
FARM ANIMAL NUTRITION
... Saturated – no double bonds – animal origin Unsaturated & polyunsaturated – plant origin Precursors of cholesterol, prostaglandin and structural components of cells • Some vitamins are fat soluble ...
... Saturated – no double bonds – animal origin Unsaturated & polyunsaturated – plant origin Precursors of cholesterol, prostaglandin and structural components of cells • Some vitamins are fat soluble ...
DNA - California State University, Stanislaus
... Mutations that add nucleotides or lose nucleotides from a gene are called frameshift mutations ...
... Mutations that add nucleotides or lose nucleotides from a gene are called frameshift mutations ...
Proteins Behaving badly - The University of Oklahoma
... diseases. These aggregates, called amyloid, are believed to be the root cause of disease pathology. Although it was once believed that the insoluble aggregates were the biologically active species, a growing body of data suggests that intermediates along the aggregation pathway, rather than the fina ...
... diseases. These aggregates, called amyloid, are believed to be the root cause of disease pathology. Although it was once believed that the insoluble aggregates were the biologically active species, a growing body of data suggests that intermediates along the aggregation pathway, rather than the fina ...
taqman protein assays
... This technique allows to develop new applications that can´t be done using traditional protein analysis techniques, for example, protein, mRNA and miRNA can be analyzed on the same sample, which is of high biological potential. The effect of interfering RNAs on pr ...
... This technique allows to develop new applications that can´t be done using traditional protein analysis techniques, for example, protein, mRNA and miRNA can be analyzed on the same sample, which is of high biological potential. The effect of interfering RNAs on pr ...
Binding Kinetics of Protein Lipid Interactions Using OpenSPR
... Binding Kinetics of Protein-Lipid Interactions using OpenSPR™ Procedure SUMMARY ...
... Binding Kinetics of Protein-Lipid Interactions using OpenSPR™ Procedure SUMMARY ...
THIN FILM STRUCTURES
... dimensional (3-D) space. This is done after considering the conformations in the 3-D space due to the degrees of freedom possessed by these structures. We next present a novel directionality-based windowed chirp waveform representation for the protein 3-D structure and use this representation to co ...
... dimensional (3-D) space. This is done after considering the conformations in the 3-D space due to the degrees of freedom possessed by these structures. We next present a novel directionality-based windowed chirp waveform representation for the protein 3-D structure and use this representation to co ...
From DNA to Protein - MrsDaintreysOnlineClassroom
... 10. Label the following diagram with all of the following terms: Transcription, translation, DNA, mRNA, tRNA, ribosomes, amino acids, anticodons ...
... 10. Label the following diagram with all of the following terms: Transcription, translation, DNA, mRNA, tRNA, ribosomes, amino acids, anticodons ...
Building Secondary Structures
... 2. Add the hydrogen bonds between an oxygen and a nitrogen. a. What effect does the addition of the hydrogen bonds have on the stability of these secondary structures? The structure is more stable with hydrogen bonds. b. Why does a hydrogen bond have to be between an oxygen and a nitrogen? A hydroge ...
... 2. Add the hydrogen bonds between an oxygen and a nitrogen. a. What effect does the addition of the hydrogen bonds have on the stability of these secondary structures? The structure is more stable with hydrogen bonds. b. Why does a hydrogen bond have to be between an oxygen and a nitrogen? A hydroge ...
Page 1
... Questions I – IX are multiple choice questions. Only one answer is correct for each question. Write down your answer on a blank answering paper. For example: Question VII, correct answer = A. Write each answer on a new line. Questions X to XII are traditional questions that require longer answers. M ...
... Questions I – IX are multiple choice questions. Only one answer is correct for each question. Write down your answer on a blank answering paper. For example: Question VII, correct answer = A. Write each answer on a new line. Questions X to XII are traditional questions that require longer answers. M ...
Macromolecules Worksheet #2 - Bi-YOLO-gy
... Part E. Which food molecule (monosaccharide, polysaccharide, lipid, protein) would you eat if… 68. …you needed a quick boost of energy? ...
... Part E. Which food molecule (monosaccharide, polysaccharide, lipid, protein) would you eat if… 68. …you needed a quick boost of energy? ...
Alternative G-19
... nonsense, and frameshift. Include (and label) the coding DNA, template DNA, RNA, and Amino acid sequences that changed. You MUST include the full amino acid sequences from [start] to [stop] even if there are no changes. 2) Rank the 5 mutations you made to your own protein in order from the least aff ...
... nonsense, and frameshift. Include (and label) the coding DNA, template DNA, RNA, and Amino acid sequences that changed. You MUST include the full amino acid sequences from [start] to [stop] even if there are no changes. 2) Rank the 5 mutations you made to your own protein in order from the least aff ...
Protein (nutrient)
Proteins are essential nutrients for the human body. They are one of the building blocks of body tissue, and can also serve as a fuel source. As a fuel, proteins contain 4 kcal per gram, just like carbohydrates and unlike lipids, which contain 9 kcal per gram. The most important aspect and defining characteristic of protein from a nutritional standpoint is its amino acid composition.Proteins are polymer chains made of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. During human digestion, proteins are broken down in the stomach to smaller polypeptide chains via hydrochloric acid and protease actions. This is crucial for the synthesis of the essential amino acids that cannot be biosynthesized by the body.There are nine essential amino acids which humans must obtain from their diet in order to prevent protein-energy malnutrition. They are phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, and histidine. There are five dispensable amino acids which humans are able to synthesize in the body. These five are alanine, aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid and serine. There are six conditionally essential amino acids whose synthesis can be limited under special pathophysiological conditions, such as prematurity in the infant or individuals in severe catabolic distress. These six are arginine, cysteine, glycine, glutamine, proline and tyrosine.Humans need the essential amino acids in certain ratios. Some protein sources contain amino acids in a more or less 'complete' sense. This has given rise to various ranking systems for protein sources, as described in the article.Animal sources of protein include meats, dairy products, fish and eggs. Vegan sources of protein include whole grains, pulses, legumes, soy, and nuts. Vegetarians and vegans can get enough essential amino acids by eating a variety of plant proteins. It is commonly believed that athletes should consume a higher-than-normal protein intake to maintain optimal physical performance.